Unit 4 Part2 wksht3
... 2. What do we call the new DNA that has the gene added to it? _________________________________ ...
... 2. What do we call the new DNA that has the gene added to it? _________________________________ ...
Gene Technology
... manipulating genes for practical purposes. Can be as simple as selective breeding and as complex as gene splicing. • A. Recombinant DNA- DNA that contains pieces of DNA form another organism • B. Gene splicing- type of genetic engineering process done by inserting genes from one organism into anothe ...
... manipulating genes for practical purposes. Can be as simple as selective breeding and as complex as gene splicing. • A. Recombinant DNA- DNA that contains pieces of DNA form another organism • B. Gene splicing- type of genetic engineering process done by inserting genes from one organism into anothe ...
Unit 1 Rev 2 - Mr. Lesiuk
... Notes #2 as well. L.O. A – 0 Intro To The Importance Of DNA: ___ 1. List two specific examples of your cells making proteins. ___ 2. Name the three main nutrient groups/chemicals used by cells. ___ 3. What are the basic building blocks that make up a protein molecule? ___ 4. Many of the proteins/enz ...
... Notes #2 as well. L.O. A – 0 Intro To The Importance Of DNA: ___ 1. List two specific examples of your cells making proteins. ___ 2. Name the three main nutrient groups/chemicals used by cells. ___ 3. What are the basic building blocks that make up a protein molecule? ___ 4. Many of the proteins/enz ...
DNA Structure powerpoint
... A. Frederick Griffith – Discovers that a factor in diseased bacteria can transform harmless bacteria into deadly bacteria ...
... A. Frederick Griffith – Discovers that a factor in diseased bacteria can transform harmless bacteria into deadly bacteria ...
Frontiers of Genetics
... • Combine genes from different sources, even different species, into a single DNA molecule • Bacteria have small circular pieces of DNA called plasmids separate from their larger single chromosome • Plasmids can replicate and pass between bacterial cells allowing gene sharing – associated with antib ...
... • Combine genes from different sources, even different species, into a single DNA molecule • Bacteria have small circular pieces of DNA called plasmids separate from their larger single chromosome • Plasmids can replicate and pass between bacterial cells allowing gene sharing – associated with antib ...
PLANT GENETIC ENGINEERING (Genetic Transformation)
... It is the most widely used transformation technique in plants. Agrobacterium tumefaciens, a soil bacteria, contains a Ti plasmid (tumor-inducing) which normally infects dicotyledonous plant cells, making the bacteria an excellent vector for the transfer of foreign DNA. By removing the tumor inducing ...
... It is the most widely used transformation technique in plants. Agrobacterium tumefaciens, a soil bacteria, contains a Ti plasmid (tumor-inducing) which normally infects dicotyledonous plant cells, making the bacteria an excellent vector for the transfer of foreign DNA. By removing the tumor inducing ...
DNAi Timeline: A Scavenger Hunt
... 3. When did Drs. Watson and Crick and Wilkins receive the Nobel Prize in Physiolgoy or Medicine for solving the structure of DNA? _______________________________________ 4. J. Craig Venter’s Company, Celera Genomics, worked on this very important project. ________________________________________ 5. ...
... 3. When did Drs. Watson and Crick and Wilkins receive the Nobel Prize in Physiolgoy or Medicine for solving the structure of DNA? _______________________________________ 4. J. Craig Venter’s Company, Celera Genomics, worked on this very important project. ________________________________________ 5. ...
the nucleic acids - This is MySchool
... Present in all cells and virtually restricted to the nucleus The amount of DNA in somatic cells (body cells) of any given species is constant (like the number of chromosomes) The DNA content of gametes (sex cells) is half that of somatic cells. In cases of polyploidy (multiple sets of chromosomes) t ...
... Present in all cells and virtually restricted to the nucleus The amount of DNA in somatic cells (body cells) of any given species is constant (like the number of chromosomes) The DNA content of gametes (sex cells) is half that of somatic cells. In cases of polyploidy (multiple sets of chromosomes) t ...
Genetic engineering - Association of the British Pharmaceutical
... of bacteria, animals and plants – and potentially change medicine for ever. ...
... of bacteria, animals and plants – and potentially change medicine for ever. ...
15.2 Recombinant DNA
... Like bacterial plasmids, the DNA molecules used for transformation of plant and animal cells contain genetic markers that help scientists identify which cells have been transformed. ...
... Like bacterial plasmids, the DNA molecules used for transformation of plant and animal cells contain genetic markers that help scientists identify which cells have been transformed. ...
Characterization of head-hunter proteins for exchange of genetic information between cells.
... Acquiring new genetic information is a critical way for a cell to adapt to the changing environment. This is particularly prevalent in bacteria as they exchange DNA molecules like plasmids at high frequencies; and this is important for bacteria to acquire resistance to antibiotics. The machinery for ...
... Acquiring new genetic information is a critical way for a cell to adapt to the changing environment. This is particularly prevalent in bacteria as they exchange DNA molecules like plasmids at high frequencies; and this is important for bacteria to acquire resistance to antibiotics. The machinery for ...
Science and Society: Unit 2 Review Packet Directions: Use your
... 3. Fully describe the following processes: a. Replication -- _________________________________________________ b. Transcription -- _______________________________________________ c. Translation -- _________________________________________________ ...
... 3. Fully describe the following processes: a. Replication -- _________________________________________________ b. Transcription -- _______________________________________________ c. Translation -- _________________________________________________ ...
Biotechnology & Genetic Engineering
... • Genetically-modified Organisms : an organism that contains some genes from another species – Useful Applications: • 1. Making medicines • 2.Genetically-modified foods • 3.Other Applications ...
... • Genetically-modified Organisms : an organism that contains some genes from another species – Useful Applications: • 1. Making medicines • 2.Genetically-modified foods • 3.Other Applications ...
Chapter 11 Concept Check Questions
... 3. Desribe the experimental design that allowed Hershey and Chase to distinguish between the two options for genetic material. ...
... 3. Desribe the experimental design that allowed Hershey and Chase to distinguish between the two options for genetic material. ...
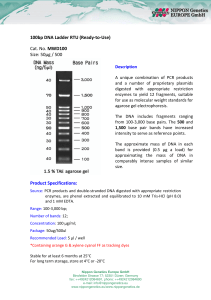
100bp DNA Ladder RTU (Ready-to-Use) Cat. No. MWD100 Size
... enzymes to yield 12 fragments, suitable for use as molecular weight standards for agarose gel electrophoresis. The DNA includes fragments ranging from 100-3,000 base pairs. The 500 and 1,500 base pair bands have increased intensity to serve as reference points. The approximate mass of DNA in each ba ...
... enzymes to yield 12 fragments, suitable for use as molecular weight standards for agarose gel electrophoresis. The DNA includes fragments ranging from 100-3,000 base pairs. The 500 and 1,500 base pair bands have increased intensity to serve as reference points. The approximate mass of DNA in each ba ...
Introduction
... life. DNA can be linked up to form a long chain of molecule called chromosome. DNA can be found in the nucleus of the cell. DNA controls all the cellular activities. The order of bases is important in determining the characteristic of an organism. The DNA molecule is arranged as a double helix, whic ...
... life. DNA can be linked up to form a long chain of molecule called chromosome. DNA can be found in the nucleus of the cell. DNA controls all the cellular activities. The order of bases is important in determining the characteristic of an organism. The DNA molecule is arranged as a double helix, whic ...
Transformation (genetics)
In molecular biology, transformation is the genetic alteration of a cell resulting from the direct uptake and incorporation of exogenous genetic material (exogenous DNA) from its surroundings and taken up through the cell membrane(s). Transformation occurs naturally in some species of bacteria, but it can also be effected by artificial means in other cells. For transformation to happen, bacteria must be in a state of competence, which might occur as a time-limited response to environmental conditions such as starvation and cell density.Transformation is one of three processes by which exogenous genetic material may be introduced into a bacterial cell, the other two being conjugation (transfer of genetic material between two bacterial cells in direct contact) and transduction (injection of foreign DNA by a bacteriophage virus into the host bacterium).""Transformation"" may also be used to describe the insertion of new genetic material into nonbacterial cells, including animal and plant cells; however, because ""transformation"" has a special meaning in relation to animal cells, indicating progression to a cancerous state, the term should be avoided for animal cells when describing introduction of exogenous genetic material. Introduction of foreign DNA into eukaryotic cells is often called ""transfection"".