
Document
... (d) explain that genetic engineering involves the extraction of genes from one organism, or the manufacture of genes, in order to place them in another organism (often of a different species) such that the receiving organism expresses the gene product; (e) describe how sections of DNA containing a d ...
... (d) explain that genetic engineering involves the extraction of genes from one organism, or the manufacture of genes, in order to place them in another organism (often of a different species) such that the receiving organism expresses the gene product; (e) describe how sections of DNA containing a d ...
Recombinant DNA technology engineering) involves combining genes from genes.
... Enzymes are used to “cut and paste” DNA •Restriction enzymes were first discovered in bacteria in the late 1960s. •In nature, bacteria use restriction enzymes to cut up intruder DNA from phages and from other organisms into nonfunctional pieces. The bacteria first chemically modify their own DNA so ...
... Enzymes are used to “cut and paste” DNA •Restriction enzymes were first discovered in bacteria in the late 1960s. •In nature, bacteria use restriction enzymes to cut up intruder DNA from phages and from other organisms into nonfunctional pieces. The bacteria first chemically modify their own DNA so ...
Biology Study Guide
... kingdoms and identify the following for each: prokaryote/eukaryote, sexual/asexual reproduction, autotrophic/heterotrophic. What is a domain? Bacteria and Viruses: (Chap 20) Who is Fleming and why was his discovery significant? Why is a virus not considered a living organism? Draw a picture of a vir ...
... kingdoms and identify the following for each: prokaryote/eukaryote, sexual/asexual reproduction, autotrophic/heterotrophic. What is a domain? Bacteria and Viruses: (Chap 20) Who is Fleming and why was his discovery significant? Why is a virus not considered a living organism? Draw a picture of a vir ...
Detection and Measurement of Genetic Variation
... sequences. It refers to a difference between samples of homologous DNA molecules that come from differing locations of restriction enzyme sites. It took advantage of the existence of bacterial enzymes known as restriction endonucleases or restriction enzymes. These enzymes are produced by various ba ...
... sequences. It refers to a difference between samples of homologous DNA molecules that come from differing locations of restriction enzyme sites. It took advantage of the existence of bacterial enzymes known as restriction endonucleases or restriction enzymes. These enzymes are produced by various ba ...
Xenograpsus testudinatus
... Environmental conditions in hydrothermal vents are considered to be unsuitable for most marine organisms due to discharge of hot and acidic water with high sulfur content. The crab Xenograpsus testudinatus is endemic to the shallow-water hydrothermal vents of Kue- ishan Island, Taiwan. This study ai ...
... Environmental conditions in hydrothermal vents are considered to be unsuitable for most marine organisms due to discharge of hot and acidic water with high sulfur content. The crab Xenograpsus testudinatus is endemic to the shallow-water hydrothermal vents of Kue- ishan Island, Taiwan. This study ai ...
Degnan_10032014
... in gut microbes. In the last decade, study of microbial pathogens has revealed the important functions RNA regulators are responsible for, particularly the ability of RNAs to turn ‘on’ and ‘off’ genes essential for causing disease in hosts. We hypothesize that these types of RNA regulators (RNA ribo ...
... in gut microbes. In the last decade, study of microbial pathogens has revealed the important functions RNA regulators are responsible for, particularly the ability of RNAs to turn ‘on’ and ‘off’ genes essential for causing disease in hosts. We hypothesize that these types of RNA regulators (RNA ribo ...
9-1
... Restriction enzymes cut DNA. Restriction enzymes act as “molecular scissors.” 1)come from various types of bacteria 2)allow scientists to more easily study and manipulate genes 3)cut DNA at a specific nucleotide sequence called a restriction site Restriction maps show the lengths of DNA fragments. G ...
... Restriction enzymes cut DNA. Restriction enzymes act as “molecular scissors.” 1)come from various types of bacteria 2)allow scientists to more easily study and manipulate genes 3)cut DNA at a specific nucleotide sequence called a restriction site Restriction maps show the lengths of DNA fragments. G ...
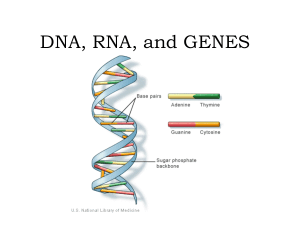
DNA, RNA, and GENES
... code for the order in which the amino acids bond. • Ribosomal RNA makes up ribosomes, where proteins are built. • Transfer RNA brings amino acids to the ribosomes to build the proteins. ...
... code for the order in which the amino acids bond. • Ribosomal RNA makes up ribosomes, where proteins are built. • Transfer RNA brings amino acids to the ribosomes to build the proteins. ...
Recombinant DNA
... They are the means by which antibiotic resistance is often transferred from one bacteria to another (remember the mice in Griffith’s experiments?) They do not usually contain genes essential to the bacteria under normal conditions ...
... They are the means by which antibiotic resistance is often transferred from one bacteria to another (remember the mice in Griffith’s experiments?) They do not usually contain genes essential to the bacteria under normal conditions ...
Wadsworth Center
... Color-coded beads are added to identify the tagged primers. Attached to each differently colored bead is an anti-TAG sequence specific to one of the extended TAG primers. Each anti-TAG only binds to the complementary TAG sequence on the primer. ...
... Color-coded beads are added to identify the tagged primers. Attached to each differently colored bead is an anti-TAG sequence specific to one of the extended TAG primers. Each anti-TAG only binds to the complementary TAG sequence on the primer. ...
The ocean as regional enabler A Pacific Northwest success
... • Identify metabolic processes that differentiate microbial communities across aquatic habitats; • Characterize microbial metabolic responses to chemical and physical gradients. ...
... • Identify metabolic processes that differentiate microbial communities across aquatic habitats; • Characterize microbial metabolic responses to chemical and physical gradients. ...
2 Exam paper_2006[1] - University of Leicester
... for the answers by selecting this link and stating clearly which exam year you require the answers for Exam Answers ...
... for the answers by selecting this link and stating clearly which exam year you require the answers for Exam Answers ...
Name____________________________ DNA Investigation
... Use website #2 to answer the following questions after watching the animation: 4—What is the first step of protein synthesis called? 5—What is the second step of protein synthesis called? What happens during this step? 6—What three nitrogen bases make up the “start codon”? ___ ___ ___ 7—What type ...
... Use website #2 to answer the following questions after watching the animation: 4—What is the first step of protein synthesis called? 5—What is the second step of protein synthesis called? What happens during this step? 6—What three nitrogen bases make up the “start codon”? ___ ___ ___ 7—What type ...
CP Biology 9.2 Copying DNA PCR uses polymerase to copy DNA
... PCR is a three step process PCR uses four materials: the DNA to be copied, DNA polymerases, lots of each of the four nucleotides – A, G, C, and T – and two primers. A Primer is a short piece of DNA that acts as the starting place for a new strand. A primer is needed because DNA polymerase cannot sta ...
... PCR is a three step process PCR uses four materials: the DNA to be copied, DNA polymerases, lots of each of the four nucleotides – A, G, C, and T – and two primers. A Primer is a short piece of DNA that acts as the starting place for a new strand. A primer is needed because DNA polymerase cannot sta ...
Rapid communication A multiplex reverse transcriptase
... Arabidopsis thaliana leaf (1±2 mg). Repeated determinations of the same samples and determinations of samples from dierent individuals of the same genotype and age ...
... Arabidopsis thaliana leaf (1±2 mg). Repeated determinations of the same samples and determinations of samples from dierent individuals of the same genotype and age ...
DNA Cot- I, human A7639 Comment
... and reannealing under conditions that enrich repetitive elements. Therefore Cot-I fraction of human genomic DNA predominatly consists of rapidly annealing repetitive elements. COT I Human DNA can be used for suppressing crosshybridization to human repetitive DNA in filter and microarray hybridizatio ...
... and reannealing under conditions that enrich repetitive elements. Therefore Cot-I fraction of human genomic DNA predominatly consists of rapidly annealing repetitive elements. COT I Human DNA can be used for suppressing crosshybridization to human repetitive DNA in filter and microarray hybridizatio ...
BIOL 2416 Genetics
... • Germ line cell are used to make egg or sperm cells • An Aa germ line means = half of the egg or sperm cells will be A, and the other half will be a – Allow the chimeric baby mice to grow up and breed with a regular AA mouse • Each grandbaby mouse will get an A gamete from the regular parent • If t ...
... • Germ line cell are used to make egg or sperm cells • An Aa germ line means = half of the egg or sperm cells will be A, and the other half will be a – Allow the chimeric baby mice to grow up and breed with a regular AA mouse • Each grandbaby mouse will get an A gamete from the regular parent • If t ...
1_3_nucl_acid_2.ppt
... Components of DNA Topology : Twist • The clockwise turns of R-H double helix generate a positive Twist (T). • The counterclockwise turns of L-H helix (Z form) generate a negative T. • T = Twisting Number B form DNA: + (# bp/10 bp per twist) A form NA: + (# bp/11 bp per twist) Z DNA: - (# bp/12 bp p ...
... Components of DNA Topology : Twist • The clockwise turns of R-H double helix generate a positive Twist (T). • The counterclockwise turns of L-H helix (Z form) generate a negative T. • T = Twisting Number B form DNA: + (# bp/10 bp per twist) A form NA: + (# bp/11 bp per twist) Z DNA: - (# bp/12 bp p ...















![2 Exam paper_2006[1] - University of Leicester](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/011309448_1-9178b6ca71e7ceae56a322cb94b06ba1-300x300.png)






