Study Guide Unit 4 - Mrs. Wolodkowicz`s Biological Realm
... write the definitions for DNA & RNA, transcription & translation, autosome, & sex linkage. the components of DNA the nitrogen bases & their complementary base pairs in DNA & RNA functions of tRNA & mRNA the laws of segregation & independent assortment the terms: dominant, recessive, geno ...
... write the definitions for DNA & RNA, transcription & translation, autosome, & sex linkage. the components of DNA the nitrogen bases & their complementary base pairs in DNA & RNA functions of tRNA & mRNA the laws of segregation & independent assortment the terms: dominant, recessive, geno ...
LDL receptors
... Fetal DNA was isolated from two amniotic-fluid samples using the QIAamp Viral RNA Mini Kit. Individual PCRs contained primer sets specific for the RH sequences (83–158 bp) indicated, as well as hGH (434 bp) as internal control. D2–D10 refer to the specific exons targeted within the RHD gene. c(cyt48 ...
... Fetal DNA was isolated from two amniotic-fluid samples using the QIAamp Viral RNA Mini Kit. Individual PCRs contained primer sets specific for the RH sequences (83–158 bp) indicated, as well as hGH (434 bp) as internal control. D2–D10 refer to the specific exons targeted within the RHD gene. c(cyt48 ...
AP BIOLOGY CHAPTER 16 OUTLINE
... A. The search for the genetic material led to DNA: science as a process Proteins were thought to be the genetic material because: ...
... A. The search for the genetic material led to DNA: science as a process Proteins were thought to be the genetic material because: ...
The Effects of Predictive Genetic Testing on the - Antioch Co-op
... of the double stranded DNA template into two single stranded molecules Annealing - The oligonucleotide primers anneal to or find their complementary sequences on the two single-stranded template strands of DNA. These act as primers for taq polymerase. All of this is done at 60℃ Extension - Taq polym ...
... of the double stranded DNA template into two single stranded molecules Annealing - The oligonucleotide primers anneal to or find their complementary sequences on the two single-stranded template strands of DNA. These act as primers for taq polymerase. All of this is done at 60℃ Extension - Taq polym ...
2559 P Ramsfield
... harknessii) is a serious threat to exotic Pinus radiata forests in New Zealand. As the pathogen is not present in New Zealand and because of the long period of time between infection and spore production, a DNA based marker has been developed that is able to detect the presence of pathogen DNA withi ...
... harknessii) is a serious threat to exotic Pinus radiata forests in New Zealand. As the pathogen is not present in New Zealand and because of the long period of time between infection and spore production, a DNA based marker has been developed that is able to detect the presence of pathogen DNA withi ...
Sample Prep for Denaturing PAGE of DNA
... Sample Prep for Denaturing PAGE of DNA DNA samples for denaturing gel electrophoresis must be denatured prior to loading, to avoid time dependent denaturation artifacts on the gel. This is usually carried out by diluting the sample into 95% formamide and heating to 95°C, see the Dideoxy Sequencing ( ...
... Sample Prep for Denaturing PAGE of DNA DNA samples for denaturing gel electrophoresis must be denatured prior to loading, to avoid time dependent denaturation artifacts on the gel. This is usually carried out by diluting the sample into 95% formamide and heating to 95°C, see the Dideoxy Sequencing ( ...
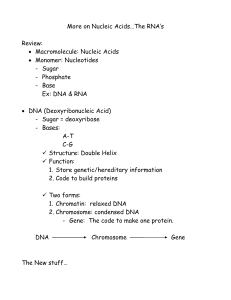
Notes: More on Nucleic Acids
... Structure: Double Helix Function: 1. Store genetic/hereditary information 2. Code to build proteins Two forms: 1. Chromatin: relaxed DNA 2. Chromosome: condensed DNA - Gene: The code to make one protein. DNA ...
... Structure: Double Helix Function: 1. Store genetic/hereditary information 2. Code to build proteins Two forms: 1. Chromatin: relaxed DNA 2. Chromosome: condensed DNA - Gene: The code to make one protein. DNA ...
DNA notes File
... Mutations in the _____________ may not be as serious Mutations in _____________ mean that the mutation is permanent. Mutations bring ___________ to a species. Mutations can be ________________ and _____________ ...
... Mutations in the _____________ may not be as serious Mutations in _____________ mean that the mutation is permanent. Mutations bring ___________ to a species. Mutations can be ________________ and _____________ ...
DNA Sequencing
... identification process and increases the number of genes tested by more than tenfold. It reduces the overall amount of time required to bring new products to market by selecting the best possible traits for yield and disease resistance and enables in-depth characterization of those products. As a re ...
... identification process and increases the number of genes tested by more than tenfold. It reduces the overall amount of time required to bring new products to market by selecting the best possible traits for yield and disease resistance and enables in-depth characterization of those products. As a re ...
DNA - PBworks
... DNA Structure DNA consists of two molecules that are arranged into a ladder-like structure called a Double Helix. A molecule of DNA is made up of millions of ...
... DNA Structure DNA consists of two molecules that are arranged into a ladder-like structure called a Double Helix. A molecule of DNA is made up of millions of ...
Presentación de PowerPoint
... A. DNA and histones B. DNA and chromatin C. Chromatin and nucleotides D. Mature RNA and histones • Which base is connected to its complementary base in a base pair by three hydrogen bonds? A. Uracil B. Thymine C. Guanine D. Adenine • What is the distinction between highly repetitive DNA sequences an ...
... A. DNA and histones B. DNA and chromatin C. Chromatin and nucleotides D. Mature RNA and histones • Which base is connected to its complementary base in a base pair by three hydrogen bonds? A. Uracil B. Thymine C. Guanine D. Adenine • What is the distinction between highly repetitive DNA sequences an ...
Replication Animation Lab
... 1. What enzyme unwinds the DNA? 2. What is the enzyme that builds the new strand of DNA (specific)? 3. What is the name of the strand that is built continuously? 4. Why is there a leading and lagging strand of DNA? 5. What enzyme synthesizes the first few nucleotides of a new strand? 6. How many nuc ...
... 1. What enzyme unwinds the DNA? 2. What is the enzyme that builds the new strand of DNA (specific)? 3. What is the name of the strand that is built continuously? 4. Why is there a leading and lagging strand of DNA? 5. What enzyme synthesizes the first few nucleotides of a new strand? 6. How many nuc ...
Lecture
... E. coli; this permits cloning of larger DNA fragments (up to 45kb) than can be introduced into bacterial hosts in plasmid vectors. ...
... E. coli; this permits cloning of larger DNA fragments (up to 45kb) than can be introduced into bacterial hosts in plasmid vectors. ...
Jeffreys - OldForensics 2012-2013
... first developed DNA fingerprinting techniques those of which are commonly used today for police and detective work, paternity tests, and immigration issues ...
... first developed DNA fingerprinting techniques those of which are commonly used today for police and detective work, paternity tests, and immigration issues ...
Multiple choice questions
... is more accurate than the clone contig method is normally used with large genomes takes more time than other genome sequencing approaches Restriction endonucleases are located in the nucleus of cells degrade DNA completely bind to DNA are enzymes are proteins were discovered in the 1980s ...
... is more accurate than the clone contig method is normally used with large genomes takes more time than other genome sequencing approaches Restriction endonucleases are located in the nucleus of cells degrade DNA completely bind to DNA are enzymes are proteins were discovered in the 1980s ...
objective: 1) to describe how the structure of dna allows it to copy itself
... ladder, the helix must first unwind and unzip using an enzyme called DNA helicase ...
... ladder, the helix must first unwind and unzip using an enzyme called DNA helicase ...
Recombination
... A. It has extra genes not found in other yeasts. B. It does not require nitrogen for growth. ...
... A. It has extra genes not found in other yeasts. B. It does not require nitrogen for growth. ...
Aim: What are some techniques used in DNA engineering?
... from two differnt alleles will produce different band patterns, allowing us to distinguish them apart. ...
... from two differnt alleles will produce different band patterns, allowing us to distinguish them apart. ...
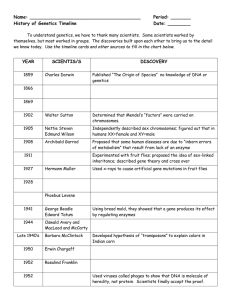
Name
... themselves, but most worked in groups. The discoveries built upon each other to bring us to the detail we know today. Use the timeline cards and other sources to fill in the chart below. ...
... themselves, but most worked in groups. The discoveries built upon each other to bring us to the detail we know today. Use the timeline cards and other sources to fill in the chart below. ...
Bisulfite sequencing

Bisulphite sequencing (also known as bisulfite sequencing) is the use of bisulphite treatment of DNA to determine its pattern of methylation. DNA methylation was the first discovered epigenetic mark, and remains the most studied. In animals it predominantly involves the addition of a methyl group to the carbon-5 position of cytosine residues of the dinucleotide CpG, and is implicated in repression of transcriptional activity.Treatment of DNA with bisulphite converts cytosine residues to uracil, but leaves 5-methylcytosine residues unaffected. Thus, bisulphite treatment introduces specific changes in the DNA sequence that depend on the methylation status of individual cytosine residues, yielding single- nucleotide resolution information about the methylation status of a segment of DNA. Various analyses can be performed on the altered sequence to retrieve this information. The objective of this analysis is therefore reduced to differentiating between single nucleotide polymorphisms (cytosines and thymidine) resulting from bisulphite conversion (Figure 1).