Ms. Setzer-The Brain!
... More intelligent animals have increased “uncommitted” or association areas of the cortex. ...
... More intelligent animals have increased “uncommitted” or association areas of the cortex. ...
Transmission of information between neurons
... If injured when young, some functions can relocate Generally the longer an organism’s life span, the larger the cortical area in order to accommodate learning Ability to learn makes an organism flexible in its environment Organisms with long life spans and large capacities for learning are s ...
... If injured when young, some functions can relocate Generally the longer an organism’s life span, the larger the cortical area in order to accommodate learning Ability to learn makes an organism flexible in its environment Organisms with long life spans and large capacities for learning are s ...
Chapter 3 Class Notes / Biological Foundations
... Neurons do not actually touch each other to send their messages along a neural pathway. The synapse or synaptic cleft is the tiny gap found between the axon (terminal buttons) of one neuron and the dendrites of another. When a neural message is received at the dendrites, it is processed through the ...
... Neurons do not actually touch each other to send their messages along a neural pathway. The synapse or synaptic cleft is the tiny gap found between the axon (terminal buttons) of one neuron and the dendrites of another. When a neural message is received at the dendrites, it is processed through the ...
10 - Karmayog .org
... This is the state of unconsciousness that we go into once in 24 hours and it is brought about when all inputs through our five senses are cut out or brought to a minimum. It is an important state for it helps in repair and renew body functions for the tasks of the next day. You will spend about a th ...
... This is the state of unconsciousness that we go into once in 24 hours and it is brought about when all inputs through our five senses are cut out or brought to a minimum. It is an important state for it helps in repair and renew body functions for the tasks of the next day. You will spend about a th ...
WHAT PARTS DO YOU KNOW THAT ARE IN THE NERVOUS SYSTEM?
... THE NERVOUS SYSTEM? • Brain • Spinal Cord • Peripheral Nerves ...
... THE NERVOUS SYSTEM? • Brain • Spinal Cord • Peripheral Nerves ...
signals in a storm - Columbia University
... and a dendrite (blue) on the receiver. (The blueYet neuroscientists are hobbled by the fact green structure is a nonneuronal cell that aids that synapses are extremely complex, vanishneurons in their normal function.) ingly small and extraordinarily fast. Thanks to One important observation made pos ...
... and a dendrite (blue) on the receiver. (The blueYet neuroscientists are hobbled by the fact green structure is a nonneuronal cell that aids that synapses are extremely complex, vanishneurons in their normal function.) ingly small and extraordinarily fast. Thanks to One important observation made pos ...
Biological Psychology A branch of psychology concerned with links
... and cerebral hemispheres; associated with emotions like fear and aggresion and drives such as those for food and ...
... and cerebral hemispheres; associated with emotions like fear and aggresion and drives such as those for food and ...
The Brain - Central Connecticut State University
... Receives information from all the senses except smell and routes it to the higher brain regions that deal with seeing, hearing, tasting, and touching. ...
... Receives information from all the senses except smell and routes it to the higher brain regions that deal with seeing, hearing, tasting, and touching. ...
CHAPTER 21 THE NERVOUS SYSTEM and SENSES
... The Tactile Corpuscles of Meissner are grouped on the skin of the fingertips, lips, and orifices of the body and the nipples. Only stimulated when touched, meissner corpuscles tells the brain the shape and feel of an object in the hand. They adjust constantly to the environment, which is why the br ...
... The Tactile Corpuscles of Meissner are grouped on the skin of the fingertips, lips, and orifices of the body and the nipples. Only stimulated when touched, meissner corpuscles tells the brain the shape and feel of an object in the hand. They adjust constantly to the environment, which is why the br ...
SBI 4U Homeostasis 3
... spinal column is a fluid called the cerebrospinal fluid. It moves hormones, white blood cells, and nutrients across the blood-brain barrier. Cerebrospinal fluid also acts as a cushion to the brain as it circulates between two layers of the meninges, the arachnoid and pia mater. ...
... spinal column is a fluid called the cerebrospinal fluid. It moves hormones, white blood cells, and nutrients across the blood-brain barrier. Cerebrospinal fluid also acts as a cushion to the brain as it circulates between two layers of the meninges, the arachnoid and pia mater. ...
The Nervous System
... 1. information gathered by the PNS and sent to the CNS and then back to the PNS is transmitted through your body by electrical charges that travel up to 248 MPH. The messengers and receivers of these transmissions are neurons. 2. Three types of neurons a. sensory neurons – carry signals from sense r ...
... 1. information gathered by the PNS and sent to the CNS and then back to the PNS is transmitted through your body by electrical charges that travel up to 248 MPH. The messengers and receivers of these transmissions are neurons. 2. Three types of neurons a. sensory neurons – carry signals from sense r ...
Aris Noriel
... appear to handle information. The difference between neural networks and behavior of individual neurons is semantic networks the specific nodes represent specific concepts or pieces of knowledge. In connectionist networks a piece of knowledge is shown by a particular pattern of activation across an ...
... appear to handle information. The difference between neural networks and behavior of individual neurons is semantic networks the specific nodes represent specific concepts or pieces of knowledge. In connectionist networks a piece of knowledge is shown by a particular pattern of activation across an ...
Memory Lecture
... NT are chemicals which bind to receptors on the dendrite or cell body NT binding causes ion channels to open Ions rush in or out changing the membrane potential (graded potentials) NT is broken down or recycled Q: why break down or recycle the NT? ...
... NT are chemicals which bind to receptors on the dendrite or cell body NT binding causes ion channels to open Ions rush in or out changing the membrane potential (graded potentials) NT is broken down or recycled Q: why break down or recycle the NT? ...
The Neural Control of Behavior
... MOTOR NEURONS: carry messages from the brain or spinal chord, through a nerve, to a muscle or gland ...
... MOTOR NEURONS: carry messages from the brain or spinal chord, through a nerve, to a muscle or gland ...
Inside the brain
... The parietal lobe processes information from the body and senses, and integrates it to help orient the body and carry out movement in space. The occipital lobe is the part of the brain that manages vision, containing dozens of areas that are specialised for processing inputs from the eyes. The tempo ...
... The parietal lobe processes information from the body and senses, and integrates it to help orient the body and carry out movement in space. The occipital lobe is the part of the brain that manages vision, containing dozens of areas that are specialised for processing inputs from the eyes. The tempo ...
Essentials of Anatony and Physiology, 5e (Martini
... Neuroglia that secret cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) are called… Clusters of neuron cell bodies form… Bundles of axons form… The membrane potential of a neuron is dependent on which contributing factors? What is the resting potential of a neuron? Tetrodotoxin prevents sodium channels from opening. What e ...
... Neuroglia that secret cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) are called… Clusters of neuron cell bodies form… Bundles of axons form… The membrane potential of a neuron is dependent on which contributing factors? What is the resting potential of a neuron? Tetrodotoxin prevents sodium channels from opening. What e ...
Brain 2012 - student version
... Figure 3B.13 Left hemisphere tissue devoted to each body part in the motor cortex and the sensory cortex As you can see from this classic though inexact representation, the amount of cortex devoted to a body part is not proportional to that part’s size. Rather, the brain devotes more tissue to sens ...
... Figure 3B.13 Left hemisphere tissue devoted to each body part in the motor cortex and the sensory cortex As you can see from this classic though inexact representation, the amount of cortex devoted to a body part is not proportional to that part’s size. Rather, the brain devotes more tissue to sens ...
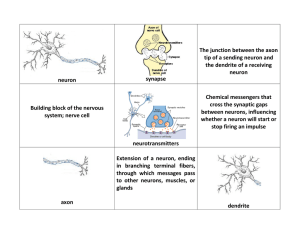
neuron synapse The junction between the axon tip of a sending
... linked to emotion; thought to determine whether we should emotionally react to sensory stimuli, especially with rage or fear; processes emotional memories ...
... linked to emotion; thought to determine whether we should emotionally react to sensory stimuli, especially with rage or fear; processes emotional memories ...
Is There a Connection Between the Brain and Learning?
... • Major functions of the higher levels of the nervous system are learning and memory – Learning is a neural mechanism by which the individual changes his or her behavior as the result of experience – Memory refers to the storage mechanism for what is learned ...
... • Major functions of the higher levels of the nervous system are learning and memory – Learning is a neural mechanism by which the individual changes his or her behavior as the result of experience – Memory refers to the storage mechanism for what is learned ...
AP Psychology
... 27. What other cortex areas does the brain receive information from? 28. The association areas in the frontal lobe allow us to _____________________ 29. How might a lesion affect brain function? 30. What is an EEG and for what purpose is it used? 31. Describe each of the following neuroimaging techn ...
... 27. What other cortex areas does the brain receive information from? 28. The association areas in the frontal lobe allow us to _____________________ 29. How might a lesion affect brain function? 30. What is an EEG and for what purpose is it used? 31. Describe each of the following neuroimaging techn ...