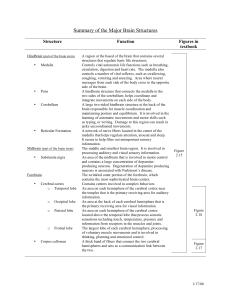
Summary of the Major Brain Structures
... hemispheres and acts as a communication link between the two. ...
... hemispheres and acts as a communication link between the two. ...
Consciousness and Awareness
... A Gordon: “If I move my arms back and forth in front of my eyes, I see them, even though I have been blind for more than thirty years.” J Lusseyran: “My screen was always as big as I needed it to be. Because it was nowhere in space and everywhere at the same time…” ...
... A Gordon: “If I move my arms back and forth in front of my eyes, I see them, even though I have been blind for more than thirty years.” J Lusseyran: “My screen was always as big as I needed it to be. Because it was nowhere in space and everywhere at the same time…” ...
the nervous system
... • Controls and Coordinates functions throughout the body • Responds to internal and external stimuli ...
... • Controls and Coordinates functions throughout the body • Responds to internal and external stimuli ...
Explaining How a Thought is Formed
... Each spinal nerve has a receptor located in the skin and nerves, muscles, tendons and ligaments, organs and other tissues are connected to that spinal nerve. They develop together in embryo and grow from the spinal cord to the tissues. IN other words, signals from all these areas pass through neuron ...
... Each spinal nerve has a receptor located in the skin and nerves, muscles, tendons and ligaments, organs and other tissues are connected to that spinal nerve. They develop together in embryo and grow from the spinal cord to the tissues. IN other words, signals from all these areas pass through neuron ...
PsychSim5: Neural Messages 1 PsychSim 5: NEURAL MESSAGES
... This activity explains the way that neurons communicate with each other. Neuron Parts Match the part of the neuron identified with its description: o ...
... This activity explains the way that neurons communicate with each other. Neuron Parts Match the part of the neuron identified with its description: o ...
Scientists are Growing Tiny Cerebral Cortexes in Petri
... balls of cortical tissue—the key working tissue in the human brain—in a dish. And much, like our brains, these simplified, petri dish brains are abuzz with neuronal activity. As off-the-wall insane as this sounds, it isn’t just some mad science experiment. These tiny, 3D structures function much lik ...
... balls of cortical tissue—the key working tissue in the human brain—in a dish. And much, like our brains, these simplified, petri dish brains are abuzz with neuronal activity. As off-the-wall insane as this sounds, it isn’t just some mad science experiment. These tiny, 3D structures function much lik ...
The correct answers are marked with asterisks Psychology 101
... them to describe in detail 5 events from their childhood, one of which did not actually happen. Loftus found that the siblings : a. were easily able to detect the "false" event as something that never happened. b. at first, did not recognize the "false" event, but did so when told that one event in ...
... them to describe in detail 5 events from their childhood, one of which did not actually happen. Loftus found that the siblings : a. were easily able to detect the "false" event as something that never happened. b. at first, did not recognize the "false" event, but did so when told that one event in ...
Chapter 40
... b) Long-term memory involves encoding information and then consolidating, a process that depends on the hippocampus and involves the expression of genes c) Memory circuits are formed throughout the brain d) No particular area can be labeled as the site of memory, rather memories may be stored in var ...
... b) Long-term memory involves encoding information and then consolidating, a process that depends on the hippocampus and involves the expression of genes c) Memory circuits are formed throughout the brain d) No particular area can be labeled as the site of memory, rather memories may be stored in var ...
The Nervous System - Needham.K12.ma.us
... – Speeds up breathing and heart rate – Stops digestion and urination – Dilates Pupils • Parasympathetic—Normal Body Maintenance – Moderates breathing and heart rate – Allows for digestion and urination – Constricts Pupils ...
... – Speeds up breathing and heart rate – Stops digestion and urination – Dilates Pupils • Parasympathetic—Normal Body Maintenance – Moderates breathing and heart rate – Allows for digestion and urination – Constricts Pupils ...
The Scientific Method - Northwest ISD Moodle
... Neurotransmissions and the nervous systems: (neurotransmission is often nicknamed the “all-or-nothing response” to explain the electrical firing of neurons and the chemical release of neurotransmitters) o Axons, dendrites, synaptic gap and myelin sheath o Specific neurotransmitters: Acetylcholine, e ...
... Neurotransmissions and the nervous systems: (neurotransmission is often nicknamed the “all-or-nothing response” to explain the electrical firing of neurons and the chemical release of neurotransmitters) o Axons, dendrites, synaptic gap and myelin sheath o Specific neurotransmitters: Acetylcholine, e ...
Review Sheet 1 scientific method and neurobiology
... Neurotransmissions and the nervous systems: (neurotransmission is often nicknamed the “all-or-nothing response” to explain the electrical firing of neurons and the chemical release of neurotransmitters) o Axons, dendrites, synaptic gap and myelin sheath o Specific neurotransmitters: Acetylcholine, e ...
... Neurotransmissions and the nervous systems: (neurotransmission is often nicknamed the “all-or-nothing response” to explain the electrical firing of neurons and the chemical release of neurotransmitters) o Axons, dendrites, synaptic gap and myelin sheath o Specific neurotransmitters: Acetylcholine, e ...
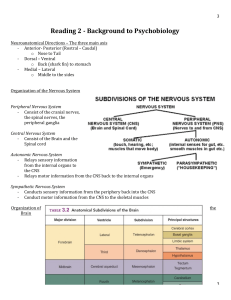
Reading 2 - Background to Psychobiology
... - Sulcus (plural) – The space between the folds of the cerebral cortex - Fissure – A space that is not created by a fold of the brain - The white matter mostly consist of axons o You can think of the brain as many servers that are interconnected (subcortical and cerebral cortex/different area ...
... - Sulcus (plural) – The space between the folds of the cerebral cortex - Fissure – A space that is not created by a fold of the brain - The white matter mostly consist of axons o You can think of the brain as many servers that are interconnected (subcortical and cerebral cortex/different area ...
The Truth about Weed - Copley
... Pons – a structure located on the brain stem that conduct signals from the cerebrum down to the cerebellum and medulla, and tracts that carry the sensory signals up into the thalamus Synapse - a structure that permits a neuron (or nerve cell) to pass an electrical or chemical signal to another cell ...
... Pons – a structure located on the brain stem that conduct signals from the cerebrum down to the cerebellum and medulla, and tracts that carry the sensory signals up into the thalamus Synapse - a structure that permits a neuron (or nerve cell) to pass an electrical or chemical signal to another cell ...
Inside the Human Brain - Hale
... The cerebellum, responsible for organizing thoughts and cognition, changes the most during adolescence. The cerebellum is not fully developed until a person is 21 years old. This lack of development can account for adolescents not always hearing or understanding what their parents or teachers are tr ...
... The cerebellum, responsible for organizing thoughts and cognition, changes the most during adolescence. The cerebellum is not fully developed until a person is 21 years old. This lack of development can account for adolescents not always hearing or understanding what their parents or teachers are tr ...
TEST TWO PSYC 2314 Lifespan, Growth and Development
... sugar water and frown when offered quinine. This demonstrates that newborns can discriminate between various tastes. 18. Cross-modal perception is the ability to recognize with one sense an object that was learned through another sense. 19. Attention skills of adolescents are advanced relative to th ...
... sugar water and frown when offered quinine. This demonstrates that newborns can discriminate between various tastes. 18. Cross-modal perception is the ability to recognize with one sense an object that was learned through another sense. 19. Attention skills of adolescents are advanced relative to th ...
Psychology 1 - Modules 24
... ____ 39. Although our capacity for storing information is large, we are still limited in the number of permanent memories we can form. ____ 40. Children, teenagers and adults are capable of constructing false memories from stories they are told. ____ 41. Only a few people have any type of photograph ...
... ____ 39. Although our capacity for storing information is large, we are still limited in the number of permanent memories we can form. ____ 40. Children, teenagers and adults are capable of constructing false memories from stories they are told. ____ 41. Only a few people have any type of photograph ...
Neurons
... • Has two main parts: the central nervous system and the peripheral nervous system. • BOTH are composed of neurons, or nerve cells, that transmit messages to different parts of the body. • Neurons have three main parts: cell body (produces energy), dendrites (DELIVERS info to the cell body), and axo ...
... • Has two main parts: the central nervous system and the peripheral nervous system. • BOTH are composed of neurons, or nerve cells, that transmit messages to different parts of the body. • Neurons have three main parts: cell body (produces energy), dendrites (DELIVERS info to the cell body), and axo ...
AP_Chapter_2[1] - HopewellPsychology
... with optimal cognitive functioning & feeling of well-being among women. ...
... with optimal cognitive functioning & feeling of well-being among women. ...
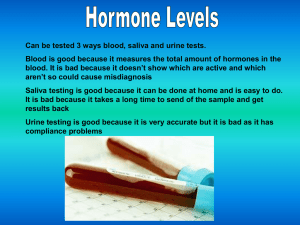
Hormone Levels and EEG (Ashanti)
... EEG is useful because the time resolution is very high. As other methods for researching brain activity have time resolution between seconds and minutes, the EEG has a resolution down to sub-millisecond. It is also good because other methods for exploring functions in the brain rely on blood flow or ...
... EEG is useful because the time resolution is very high. As other methods for researching brain activity have time resolution between seconds and minutes, the EEG has a resolution down to sub-millisecond. It is also good because other methods for exploring functions in the brain rely on blood flow or ...


















![AP_Chapter_2[1] - HopewellPsychology](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008569681_1-9cf3b4caa50d34e12653d8840c008c05-300x300.png)