DNA Test Study Guide
... ___________ and one from the ___________. Body cells we also call ________________Because our body cells’ chromosomes are found in pairs, we call them ___________. When arranged on a karyotype, you can see that there are two types of chromosomes, ____________ and ________________. In order for a hum ...
... ___________ and one from the ___________. Body cells we also call ________________Because our body cells’ chromosomes are found in pairs, we call them ___________. When arranged on a karyotype, you can see that there are two types of chromosomes, ____________ and ________________. In order for a hum ...
AP Biology
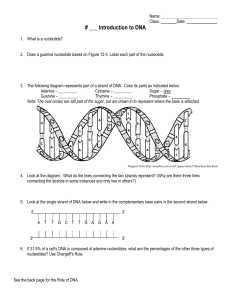
... 7. Label the structures below: include Nucleotide, phosphate, nitrogen base, deoxyribose, double helix, sugar-phosphate backbone, complimentary bases, purine, and pyrimidine, adenine, thymine, cytosine and guanine. ...
... 7. Label the structures below: include Nucleotide, phosphate, nitrogen base, deoxyribose, double helix, sugar-phosphate backbone, complimentary bases, purine, and pyrimidine, adenine, thymine, cytosine and guanine. ...
Cytosine – ______ Sugar
... Note: The oval circles are still part of the sugar, but are drawn in to represent where the base is attached. ...
... Note: The oval circles are still part of the sugar, but are drawn in to represent where the base is attached. ...
Lecture 19 Evolution of Senescence
... Telomeres are regions of highly repetitive DNA at the ends of chromosomes. They prevent the ends of chromosomes from joining together during replication. DNA polymerases are unable to fully replicate Telomeres. ...
... Telomeres are regions of highly repetitive DNA at the ends of chromosomes. They prevent the ends of chromosomes from joining together during replication. DNA polymerases are unable to fully replicate Telomeres. ...
DNA/RNA Worksheet TACGGCACCGTTAGGATT
... Is DNA double-stranded or single-stranded? ________________________________________ ...
... Is DNA double-stranded or single-stranded? ________________________________________ ...
Ch 16 homework
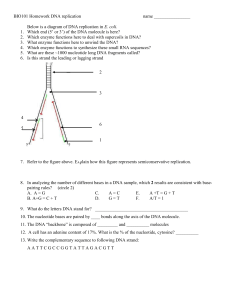
... Which enzyme functions here to deal with supercoils in DNA? What enzyme functions here to unwind the DNA? Which enzyme functions to synthesize these small RNA sequences? What are these ~1000 nucleotide long DNA fragments called? Is this strand the leading or lagging strand ...
... Which enzyme functions here to deal with supercoils in DNA? What enzyme functions here to unwind the DNA? Which enzyme functions to synthesize these small RNA sequences? What are these ~1000 nucleotide long DNA fragments called? Is this strand the leading or lagging strand ...
Unit D : DNA -Functions of DNA - Mr. Lesiuk
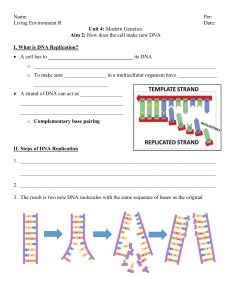
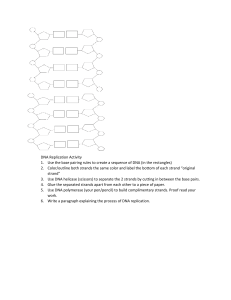
... molecules are present, identical to each other and to the original molecule. 5. Both DNA will now wind back up into their helical shape. - DNA replication is called semiconservative because each new double helix is composed of an old (parental) strand and a new (daughter) strand. ...
... molecules are present, identical to each other and to the original molecule. 5. Both DNA will now wind back up into their helical shape. - DNA replication is called semiconservative because each new double helix is composed of an old (parental) strand and a new (daughter) strand. ...
Problem Set 3A
... location where each of the above enzymes would be functioning at the time of the drawing. 4. What does telomerase use as template for synthesizing more DNA on the ends of chromosomes? What does it use as primer? 5. Why do Ds elements need the presence of an Ac element in order to transpose? 6. What ...
... location where each of the above enzymes would be functioning at the time of the drawing. 4. What does telomerase use as template for synthesizing more DNA on the ends of chromosomes? What does it use as primer? 5. Why do Ds elements need the presence of an Ac element in order to transpose? 6. What ...
3-10
... Subject: The structure and replication of DNA. Reading in ‘An introduction to genetic analysis’ (Griffiths et al., 7th edition) Chapter 8: The structure and replication of DNA. ________________________________________________________________________ Key concepts and keywords: DNA: the genetic materi ...
... Subject: The structure and replication of DNA. Reading in ‘An introduction to genetic analysis’ (Griffiths et al., 7th edition) Chapter 8: The structure and replication of DNA. ________________________________________________________________________ Key concepts and keywords: DNA: the genetic materi ...
Telomeres, telomerase and plant development
... The importance of the telomere is underscored by recent studies demonstrating that the maintenance of telomeres on human chromosomes strongly correlates with the capacity for cellular proliferation and carcinogenesis3. This review focuses on plant telomeres, their synthesis by the enzyme telomerase ...
... The importance of the telomere is underscored by recent studies demonstrating that the maintenance of telomeres on human chromosomes strongly correlates with the capacity for cellular proliferation and carcinogenesis3. This review focuses on plant telomeres, their synthesis by the enzyme telomerase ...
DNA Structure
... -What did she study? -What did the photos suggest? Watson and Crick (Last Paragraph) -What did Watson observe? -What did he immediately know? -What did Watson and Crick complete? What year? Chargaff (2nd Paragraph) -What did he find? -Give an example -What is Chargaff’s rule? ...
... -What did she study? -What did the photos suggest? Watson and Crick (Last Paragraph) -What did Watson observe? -What did he immediately know? -What did Watson and Crick complete? What year? Chargaff (2nd Paragraph) -What did he find? -Give an example -What is Chargaff’s rule? ...
Nature Rev.Mol.Cell Biol
... Telomerase is recruited by telomeric proteins and counteracts telomere shortening during DNA replication ...
... Telomerase is recruited by telomeric proteins and counteracts telomere shortening during DNA replication ...
PDF - Lake Forest College
... genetic information to future generations. During DNA replication in cells, enzymes called polymerases are responsible for synthesizing new DNA strands by adding nucleotides that are complementary to the parent strand in a 5’ to 3’ direction. After cell division, daughter cells inherit double strand ...
... genetic information to future generations. During DNA replication in cells, enzymes called polymerases are responsible for synthesizing new DNA strands by adding nucleotides that are complementary to the parent strand in a 5’ to 3’ direction. After cell division, daughter cells inherit double strand ...
LOYOLA COLLEGE (AUTONOMOUS), CHENNAI – 600 034
... 18. What is pattern formation? 19. Expand MODY. Which is the most commonly seen MODY phenotype in India? 20. What is the function of Cytochrome P450 gene (CYP450)? ...
... 18. What is pattern formation? 19. Expand MODY. Which is the most commonly seen MODY phenotype in India? 20. What is the function of Cytochrome P450 gene (CYP450)? ...
Questions on DNA Replication and Enzymes used in DNA replication
... 1. Helicase – to unwind the DNA double helix 2. Single strand binding protein – stabilize the unwound parental DNA 3. Primase – inserts a RNA primer to help DNA nucleotides join onto the parent strand [only one needed on the continuous strand while many are seen on the ‘lagging strand’ (5’ – 3’)] 4. ...
... 1. Helicase – to unwind the DNA double helix 2. Single strand binding protein – stabilize the unwound parental DNA 3. Primase – inserts a RNA primer to help DNA nucleotides join onto the parent strand [only one needed on the continuous strand while many are seen on the ‘lagging strand’ (5’ – 3’)] 4. ...
Media Release, 22 September 2003
... She said a controlled balance of telomerase was needed to help individuals replenish cells during their lifetime. “Cell replenishment is essential for a healthy immune system, and for the skin, hair and intestinal lining,” she said. “But in the genetic lottery of life, some people have what is known ...
... She said a controlled balance of telomerase was needed to help individuals replenish cells during their lifetime. “Cell replenishment is essential for a healthy immune system, and for the skin, hair and intestinal lining,” she said. “But in the genetic lottery of life, some people have what is known ...
Ch. 16 Molecular Basis of Genetics
... helic - = a spiral (helicase: an enzyme that untwists the double helix of DNA at the replication forks) liga - = bound or tied (DNA ligase: a linking enzyme for DNA replication) -phage = to eat (bacteriophages: viruses that infect bacteria) semi - = half (semiconservative model: type of DNA replicat ...
... helic - = a spiral (helicase: an enzyme that untwists the double helix of DNA at the replication forks) liga - = bound or tied (DNA ligase: a linking enzyme for DNA replication) -phage = to eat (bacteriophages: viruses that infect bacteria) semi - = half (semiconservative model: type of DNA replicat ...
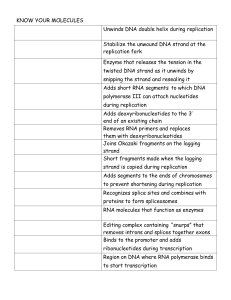
Know your molecules organizer
... replication fork Enzyme that releases the tension in the twisted DNA strand as it unwinds by snipping the strand and resealing it Adds short RNA segments to which DNA polymerase III can attach nucleotides during replication Adds deoxyribonucleotides to the 3’ end of an existing chain Removes RNA pri ...
... replication fork Enzyme that releases the tension in the twisted DNA strand as it unwinds by snipping the strand and resealing it Adds short RNA segments to which DNA polymerase III can attach nucleotides during replication Adds deoxyribonucleotides to the 3’ end of an existing chain Removes RNA pri ...
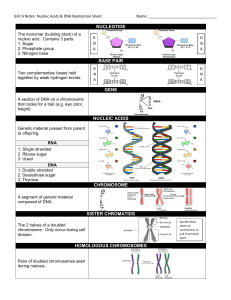
NUCLEOTIDE BASE PAIR GENE NUCLEIC ACIDS CHROMOSOME
... A segment of genetic material composed of DNA. ...
... A segment of genetic material composed of DNA. ...
NIH Press Release - The Progeria Research Foundation
... alternative splicing in multiple other genes," said lead author Kan Cao, Ph.D., an assistant professor of cell biology and molecular genetics at the University of Maryland, College Park. Telomerase is an enzyme that can extend the structure of telomeres so that cells continue to maintain the ability ...
... alternative splicing in multiple other genes," said lead author Kan Cao, Ph.D., an assistant professor of cell biology and molecular genetics at the University of Maryland, College Park. Telomerase is an enzyme that can extend the structure of telomeres so that cells continue to maintain the ability ...
word
... Haloarcula, Thermus thermophilus, E. coli, C. elegans, Saccharomyces, 9. Some general comparisons of eukaryotes to prokaryotes – what is similar, what must be different? Consider RNA processing, DNA replication, repair, ribosomes, tRNA, mRNA; Mg++ was often a cofactor for cleavages DNA replication ( ...
... Haloarcula, Thermus thermophilus, E. coli, C. elegans, Saccharomyces, 9. Some general comparisons of eukaryotes to prokaryotes – what is similar, what must be different? Consider RNA processing, DNA replication, repair, ribosomes, tRNA, mRNA; Mg++ was often a cofactor for cleavages DNA replication ( ...
Exam 1 Study Guide – General Concepts
... Helicase (and counteracting gyrase) Single stranded binding proteins DNA Primase Ligase Okazaki fragments Exonuclease activity (5’-3’ activity vs 3’-5’ proofreading) Eukaryotic DNA Replication Multiple origins of replication Telomeres Telomerase Transcription Prokaryotic (uses one RNA polymerase) St ...
... Helicase (and counteracting gyrase) Single stranded binding proteins DNA Primase Ligase Okazaki fragments Exonuclease activity (5’-3’ activity vs 3’-5’ proofreading) Eukaryotic DNA Replication Multiple origins of replication Telomeres Telomerase Transcription Prokaryotic (uses one RNA polymerase) St ...
Telomere

A telomere is a region of repetitive nucleotide sequences at each end of a chromatid, which protects the end of the chromosome from deterioration or from fusion with neighboring chromosomes. Its name is derived from the Greek nouns telos (τέλος) 'end' and merοs (μέρος, root: μερ-) 'part.' For vertebrates, the sequence of nucleotides in telomeres is TTAGGG. This sequence of TTAGGG is repeated approximately 2,500 times in humans. During chromosome replication, the enzymes that duplicate DNA cannot continue their duplication all the way to the end of a chromosome, so in each duplication the end of the chromosome is shortened (this is because the synthesis of Okazaki fragments requires RNA primers attaching ahead on the lagging strand). The telomeres are disposable buffers at the ends of chromosomes which are truncated during cell division; their presence protects the genes before them on the chromosome from being truncated instead.Over time, due to each cell division, the telomere ends become shorter. They are replenished by an enzyme, telomerase reverse transcriptase.