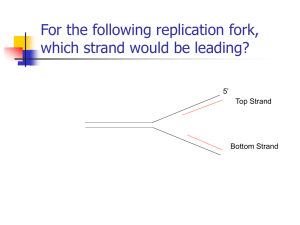
SBI4U: Molecular Genetics Unit Review
... 3. What is the difference between the 5’ end of nucleic acids and the 3’ end? Draw a diagram to show this. 4. When new DNA or RNA is synthesized, in which direction does it grow? 5. What are two different kinds of bonds that hold nucleic acids together? 6. Write the complementary DNA strand: 5’- A A ...
... 3. What is the difference between the 5’ end of nucleic acids and the 3’ end? Draw a diagram to show this. 4. When new DNA or RNA is synthesized, in which direction does it grow? 5. What are two different kinds of bonds that hold nucleic acids together? 6. Write the complementary DNA strand: 5’- A A ...
DNA-ReplicationName-Per
... You will draw out the steps of the S phase of Interphase, DNA replication. In each box, draw the event described. You will use 3 different colors: one for the original strands of DNA, one for the leading strand, and one for the lagging strand. You must label all the bold words in each drawing and in ...
... You will draw out the steps of the S phase of Interphase, DNA replication. In each box, draw the event described. You will use 3 different colors: one for the original strands of DNA, one for the leading strand, and one for the lagging strand. You must label all the bold words in each drawing and in ...
Bio 313 worksheet 7 - Iowa State University
... C. At the beginning of every Okazaki fragment D. At multiple places within an Okazaki fragment 1060 Hixson-Lied Student Success Center 515-294-6624 [email protected] http://www.si.iastate.edu ...
... C. At the beginning of every Okazaki fragment D. At multiple places within an Okazaki fragment 1060 Hixson-Lied Student Success Center 515-294-6624 [email protected] http://www.si.iastate.edu ...
DNA Replication Amoeba Sisters Video
... DNA Replication Amoeba Sisters Video As you watch the animation on DNA Replication, answer the following questions. ...
... DNA Replication Amoeba Sisters Video As you watch the animation on DNA Replication, answer the following questions. ...
DNA Structure and Replication
... Once DNA has been replicated, there is one problem. The usual replication machinery provides no way to complete the 5 ends after the RNA primer is removed, so repeated rounds of replication produce shorter and shorter DNA molecules. To compensate for this repeated shortening process, repetitive seq ...
... Once DNA has been replicated, there is one problem. The usual replication machinery provides no way to complete the 5 ends after the RNA primer is removed, so repeated rounds of replication produce shorter and shorter DNA molecules. To compensate for this repeated shortening process, repetitive seq ...
Chapter 16 DNA
... G, A, T, C nucleotides complementary to template strand 500 nuc/sec Continuous elongation until end of chromosome ...
... G, A, T, C nucleotides complementary to template strand 500 nuc/sec Continuous elongation until end of chromosome ...
DNA Replication
... Each time a new cell is made, the cell must receive an exact copy of the parent cell DNA. The new cells then receive the instructions and information needed to function. The process of copying DNA is called replication. Replication occurs in a unique way – instead of copying a complete new strand of ...
... Each time a new cell is made, the cell must receive an exact copy of the parent cell DNA. The new cells then receive the instructions and information needed to function. The process of copying DNA is called replication. Replication occurs in a unique way – instead of copying a complete new strand of ...
Chromosomal Structure HWK
... (b) A telomere is a long sequence of repetitive, noncoding DNA that is found at the end of chromosomes, while a centromere is a constricted region of a chromosome that holds two replicated chromosome strands together (c) A LINE is a DNA sequence of 5000 to 7000 nucleotides that are repetitive and al ...
... (b) A telomere is a long sequence of repetitive, noncoding DNA that is found at the end of chromosomes, while a centromere is a constricted region of a chromosome that holds two replicated chromosome strands together (c) A LINE is a DNA sequence of 5000 to 7000 nucleotides that are repetitive and al ...
Is an inducible operon normally off or on?
... they do not contain a nucleus In eukaryotes, transcription is completed in the nucleus before translation can take place in the cytoplasm ...
... they do not contain a nucleus In eukaryotes, transcription is completed in the nucleus before translation can take place in the cytoplasm ...
DNA - Menihek Home Page
... The two sides are said to be complementary. Not only are the base pairs opposite, but the two strands are also antiparallel – that is, the phosphate groups run in opposite directions. One side runs 5’ to 3’ and the other runs 3’ to 5’. These numbers refer to which of the five carbon atoms in deoxyri ...
... The two sides are said to be complementary. Not only are the base pairs opposite, but the two strands are also antiparallel – that is, the phosphate groups run in opposite directions. One side runs 5’ to 3’ and the other runs 3’ to 5’. These numbers refer to which of the five carbon atoms in deoxyri ...
DNA Composition and Structure
... thymine and guanine to cytosine remained constant at approximately 1:1 between each two; and 2) The base composition was not the same in all organisms. ...
... thymine and guanine to cytosine remained constant at approximately 1:1 between each two; and 2) The base composition was not the same in all organisms. ...
Introduction to Genetics WINTER 2017 EXAM I 1. In one strand of
... H U G E are four dominant genes controlling tomato size that are each located on different chromosomes. A cross is carried out between Plant 1 with genotype- Hh Uu Gg ee and Plant 2 of genotype- hh Uu Gg Ee. 27. What percentage of the progeny are expected to be phenotypically identical to Plant 1? A ...
... H U G E are four dominant genes controlling tomato size that are each located on different chromosomes. A cross is carried out between Plant 1 with genotype- Hh Uu Gg ee and Plant 2 of genotype- hh Uu Gg Ee. 27. What percentage of the progeny are expected to be phenotypically identical to Plant 1? A ...
Chapter 12
... 2. _______ this information in the cells. 3. _________ this information in the cells. Study the book – cell analogy on page 342 of your textbook.A book can __________information, you can _______information from this book and the book after being copied can be ____________ or ___________ to others. ...
... 2. _______ this information in the cells. 3. _________ this information in the cells. Study the book – cell analogy on page 342 of your textbook.A book can __________information, you can _______information from this book and the book after being copied can be ____________ or ___________ to others. ...
12.2 DNA Replication ppt
... Action: Adds new nucleotides to the exposed bases using the base-pair rule; also proofreads every connection at this time (avg. 1 error per 2 billion nucleotides) Result: 2 new double DNA strands are created (but still attached) ...
... Action: Adds new nucleotides to the exposed bases using the base-pair rule; also proofreads every connection at this time (avg. 1 error per 2 billion nucleotides) Result: 2 new double DNA strands are created (but still attached) ...
Exam Review 2B -- Rodermel
... 2. Diagram Rolling Circle replication below. Include the 3 different products that can result. (Be sure to include leading and lagging strand, origin of replication, directionality of the ...
... 2. Diagram Rolling Circle replication below. Include the 3 different products that can result. (Be sure to include leading and lagging strand, origin of replication, directionality of the ...
1.d Standard curve construction and validation of the C t
... Although we did not determine copy number for Mc1r in Menidia, it is known to be a single copy gene in many teleost species [33]. We cloned (QIAGEN Plasmid Kit) and sequenced the plasmids at the DNA Sequencing Facility (Health Science Center) at Stony Brook University. Candidate primer sets were des ...
... Although we did not determine copy number for Mc1r in Menidia, it is known to be a single copy gene in many teleost species [33]. We cloned (QIAGEN Plasmid Kit) and sequenced the plasmids at the DNA Sequencing Facility (Health Science Center) at Stony Brook University. Candidate primer sets were des ...
Name Ch 12 Study Guide
... sequence on one parent strand is A-T-T-C-G-C; the base sequence that will complement that parent strand is __________________________________________ 11) Who was Rosalind Franklin? 12) What was her contribution to the discovery of DNA? 13) Why is the work of Rosalind Franklin overlooked in the disco ...
... sequence on one parent strand is A-T-T-C-G-C; the base sequence that will complement that parent strand is __________________________________________ 11) Who was Rosalind Franklin? 12) What was her contribution to the discovery of DNA? 13) Why is the work of Rosalind Franklin overlooked in the disco ...
DNA Worksheet 1. What does DNA stand for? 2. What does DNA do
... 7. Who first found the shape of DNA? ...
... 7. Who first found the shape of DNA? ...
Day 9: DNA Powerpoint
... Essentially the same process as copying the leading strand of DNA only ...
... Essentially the same process as copying the leading strand of DNA only ...
DNA & Protein Synthesis Jeopardy - Warren Hills Regional School
... This adjective is used to describe the DNA strands in the double helix, because one strand runs in the 5’ to 3’ direction, while the other runs from the 3’ to 5’ direction. ...
... This adjective is used to describe the DNA strands in the double helix, because one strand runs in the 5’ to 3’ direction, while the other runs from the 3’ to 5’ direction. ...
Telomere

A telomere is a region of repetitive nucleotide sequences at each end of a chromatid, which protects the end of the chromosome from deterioration or from fusion with neighboring chromosomes. Its name is derived from the Greek nouns telos (τέλος) 'end' and merοs (μέρος, root: μερ-) 'part.' For vertebrates, the sequence of nucleotides in telomeres is TTAGGG. This sequence of TTAGGG is repeated approximately 2,500 times in humans. During chromosome replication, the enzymes that duplicate DNA cannot continue their duplication all the way to the end of a chromosome, so in each duplication the end of the chromosome is shortened (this is because the synthesis of Okazaki fragments requires RNA primers attaching ahead on the lagging strand). The telomeres are disposable buffers at the ends of chromosomes which are truncated during cell division; their presence protects the genes before them on the chromosome from being truncated instead.Over time, due to each cell division, the telomere ends become shorter. They are replenished by an enzyme, telomerase reverse transcriptase.