DNA Worksheet
... 3. DNA is sometimes described as a twisted ladder. What is this shape called? ___________________ ...
... 3. DNA is sometimes described as a twisted ladder. What is this shape called? ___________________ ...
PowerPoint ******
... binding sites to proteins, especially in the domain of metal-based drugs. • It should ultimately provide data that facilitate drug design and discovery. ...
... binding sites to proteins, especially in the domain of metal-based drugs. • It should ultimately provide data that facilitate drug design and discovery. ...
Use the diagram to match the letter (A-C) to the correct term(1
... 6. ______ Individual nitrogen base. 7. ______ Sugar-phosphate backbone. 8. In DNA, which of the following determines the traits of an organism? a. Amount of adenine b. Number of sugars c. Sequence of nitrogen bases d. Strength of hydrogen bonds 9. You have separated the nucleotides in a piece of DNA ...
... 6. ______ Individual nitrogen base. 7. ______ Sugar-phosphate backbone. 8. In DNA, which of the following determines the traits of an organism? a. Amount of adenine b. Number of sugars c. Sequence of nitrogen bases d. Strength of hydrogen bonds 9. You have separated the nucleotides in a piece of DNA ...
Bozeman DNA Replication Name http://www.youtube.com/watch?v
... When in the cell cycle does DNA replication occur? What do prokaryotes use as a method to copy their cells? What are the three theories of DNA replication? How did the Meselson-Stahl experiment prove the semi-conservative theory? In the semiconservative theory, where does the DNA split? What are the ...
... When in the cell cycle does DNA replication occur? What do prokaryotes use as a method to copy their cells? What are the three theories of DNA replication? How did the Meselson-Stahl experiment prove the semi-conservative theory? In the semiconservative theory, where does the DNA split? What are the ...
Answers
... cellular hypersensitivity to ultraviolet (UV) radiation, a high incidence of skin cancer and premature aging. Based on these clinical characteristics, what is the underlying cause for this disease? A. defects in DNA repair B. defects in DNA replication C. lack of telomerase activity D. shortened tel ...
... cellular hypersensitivity to ultraviolet (UV) radiation, a high incidence of skin cancer and premature aging. Based on these clinical characteristics, what is the underlying cause for this disease? A. defects in DNA repair B. defects in DNA replication C. lack of telomerase activity D. shortened tel ...
Ch. 16 Stem Notes
... a. Leading strand b. Lagging strand c. Okazaki fragments d. DNA ligase e. Primer 15. Label the diagram below: ...
... a. Leading strand b. Lagging strand c. Okazaki fragments d. DNA ligase e. Primer 15. Label the diagram below: ...
Quiz Review: Chapter 11: Eukaryotic Genome Organization Chapter
... Telomeres are the “caps” at the end of chromosomes, composed of highly repetitive sequences of DNA. Each time a cell replicates its DNA prior to cell division, nucleotide(s) are result, leaving the new cell with less DNA than the parent cell. As a cell continues to divide, especially labile cells, t ...
... Telomeres are the “caps” at the end of chromosomes, composed of highly repetitive sequences of DNA. Each time a cell replicates its DNA prior to cell division, nucleotide(s) are result, leaving the new cell with less DNA than the parent cell. As a cell continues to divide, especially labile cells, t ...
Ib Biology DNA Replication Questions 1. What is the function of
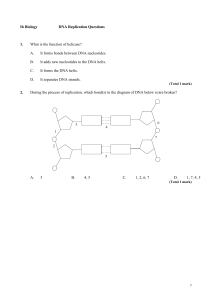
... During the process of replication, which bond(s) in the diagram of DNA below is/are broken? ...
... During the process of replication, which bond(s) in the diagram of DNA below is/are broken? ...
13 4 (a) Genetic modification of organisms uses a
... Some of the enzymes and vectors that are important in genetic modification are given an identifying letter in Table 4.1. Table 4.1 enzymes ...
... Some of the enzymes and vectors that are important in genetic modification are given an identifying letter in Table 4.1. Table 4.1 enzymes ...
Supplementary Information (doc 63K)
... DNA repair mutants that we report here is reminiscent of that observed in germ cells of telomere replication defective C. elegans mutants(1). One such mutant, trt-1, which has lost functional telomerase reverse transcriptase, shows a decline in transgenerational replicative capacity but not in post- ...
... DNA repair mutants that we report here is reminiscent of that observed in germ cells of telomere replication defective C. elegans mutants(1). One such mutant, trt-1, which has lost functional telomerase reverse transcriptase, shows a decline in transgenerational replicative capacity but not in post- ...
Chapter 16 DNA: The Genetic Material The Nature of Genetic
... Different Termination • Telomeres = special structures found on ends of eukaryotic chromosomes (TTAGGG) – Functions: protect ends of chromosomes from nucleases – Keeps one chromosome from linking to another ...
... Different Termination • Telomeres = special structures found on ends of eukaryotic chromosomes (TTAGGG) – Functions: protect ends of chromosomes from nucleases – Keeps one chromosome from linking to another ...
Document
... DNA molecule packed together with proteins • The bacterial chromosome is a double-stranded, circular DNA molecule associated with a small amount of protein • Eukaryotic chromosomes have linear DNA molecules associated with a large amount of ...
... DNA molecule packed together with proteins • The bacterial chromosome is a double-stranded, circular DNA molecule associated with a small amount of protein • Eukaryotic chromosomes have linear DNA molecules associated with a large amount of ...
Name:
... 8. What are the three primary differences between DNA and RNA? 9. List the three different types of RNA and their functions. 10. Click on “next” at the bottom of the page. What happens during the process known as transcription? 11. What is a codon and what does each one stand for on an mRNA strand? ...
... 8. What are the three primary differences between DNA and RNA? 9. List the three different types of RNA and their functions. 10. Click on “next” at the bottom of the page. What happens during the process known as transcription? 11. What is a codon and what does each one stand for on an mRNA strand? ...
EXAM 2
... 35. Any change in the chemical composition of DNA is a _mutation______________. 36. An alteration in the DNA composition that is not passed on to the subsequent genereation is referred to as _somatic______________, while those that can be passed on are referred to as _gametic___________. 37. An alte ...
... 35. Any change in the chemical composition of DNA is a _mutation______________. 36. An alteration in the DNA composition that is not passed on to the subsequent genereation is referred to as _somatic______________, while those that can be passed on are referred to as _gametic___________. 37. An alte ...
Test Review: Chapters 9, 10, 11 DNA as Genetic Material
... What appeared after 1st incubation/replication? What would have appeared in centrifuge tube if conservative? Dispersive? ...
... What appeared after 1st incubation/replication? What would have appeared in centrifuge tube if conservative? Dispersive? ...
Tudor – Down`s syndrome
... syndrome pregnancy, there was a significant inverse correlation between basal FSH and inhibin B concentrations. In the control group, this correlation was not conclusive. These data indicated that the higher basal FSH concentrations observed in women with a history of a Down's syndrome pregnancy ar ...
... syndrome pregnancy, there was a significant inverse correlation between basal FSH and inhibin B concentrations. In the control group, this correlation was not conclusive. These data indicated that the higher basal FSH concentrations observed in women with a history of a Down's syndrome pregnancy ar ...
Chapter 16 Review
... What determines the order of the nucleotide in mRNA? What determines the order of amino acids added to the polypeptide? Any additional nucleotides are added to where/what end? What kind of molecule or substance is the primer that is used to initiate the synthesis of a new DNA strand? What synthesize ...
... What determines the order of the nucleotide in mRNA? What determines the order of amino acids added to the polypeptide? Any additional nucleotides are added to where/what end? What kind of molecule or substance is the primer that is used to initiate the synthesis of a new DNA strand? What synthesize ...
Histones
... deterioration or from fusion with neighboring chromosomes. Its name is derived from the Greek nouns telos (τέλος) 'end' and merοs (μέρος, root: μερ-) 'part.' Telomere regions deter the degradation of genes near the ends of chromosomes by allowing chromosome ends to shorten, which necessarily occurs ...
... deterioration or from fusion with neighboring chromosomes. Its name is derived from the Greek nouns telos (τέλος) 'end' and merοs (μέρος, root: μερ-) 'part.' Telomere regions deter the degradation of genes near the ends of chromosomes by allowing chromosome ends to shorten, which necessarily occurs ...
Karina Espinoza - Werner Syndrome
... Preimplantation Genetic Diagnosis- available for families with ...
... Preimplantation Genetic Diagnosis- available for families with ...
Bio 313 Exam 1 Review - Iowa State University
... How many times does DNA wrap around a histone? How many base pairs does this take? How many base pairs in a nucleosome? ...
... How many times does DNA wrap around a histone? How many base pairs does this take? How many base pairs in a nucleosome? ...
Cell senescence questions
... Cellular senescence refers to the cell response to any of many stimuli. (cell division/shortening telomeres is just one of these stimuli. Others include DNA damage, oxidative stress, etc) See p. 47-p.48 However, senescent cells still produce mRNA and proteins, so they are not really DEAD per se. It ...
... Cellular senescence refers to the cell response to any of many stimuli. (cell division/shortening telomeres is just one of these stimuli. Others include DNA damage, oxidative stress, etc) See p. 47-p.48 However, senescent cells still produce mRNA and proteins, so they are not really DEAD per se. It ...
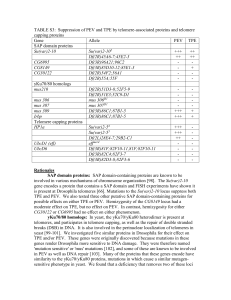
TABLE S3: Suppression of PEV and TPE by telomere
... possible effects on either TPE or PEV. Hemizygosity of the CG8149 locus had a moderate effect on TPE, but no effect on PEV. In contrast, hemizygosity for either CG30122 or CG6995 had no effect on either phenomenon. yKu70/80 homologs: In yeast, the yKu70/yKu80 heterodimer is present at telomeres, and ...
... possible effects on either TPE or PEV. Hemizygosity of the CG8149 locus had a moderate effect on TPE, but no effect on PEV. In contrast, hemizygosity for either CG30122 or CG6995 had no effect on either phenomenon. yKu70/80 homologs: In yeast, the yKu70/yKu80 heterodimer is present at telomeres, and ...
Telomere

A telomere is a region of repetitive nucleotide sequences at each end of a chromatid, which protects the end of the chromosome from deterioration or from fusion with neighboring chromosomes. Its name is derived from the Greek nouns telos (τέλος) 'end' and merοs (μέρος, root: μερ-) 'part.' For vertebrates, the sequence of nucleotides in telomeres is TTAGGG. This sequence of TTAGGG is repeated approximately 2,500 times in humans. During chromosome replication, the enzymes that duplicate DNA cannot continue their duplication all the way to the end of a chromosome, so in each duplication the end of the chromosome is shortened (this is because the synthesis of Okazaki fragments requires RNA primers attaching ahead on the lagging strand). The telomeres are disposable buffers at the ends of chromosomes which are truncated during cell division; their presence protects the genes before them on the chromosome from being truncated instead.Over time, due to each cell division, the telomere ends become shorter. They are replenished by an enzyme, telomerase reverse transcriptase.