Answers
... 18. Gene ________ refers to the combined processes of transcription and translation. A. expression B. replication C. modification D. regulation 19. Most eukaryotic genes contain coding sequences called ________ that are interspersed with ...
... 18. Gene ________ refers to the combined processes of transcription and translation. A. expression B. replication C. modification D. regulation 19. Most eukaryotic genes contain coding sequences called ________ that are interspersed with ...
made of three parts sugar, phosphate, and base Scientist that
... along each of the DNA strands and adds nucleotides according to the base-pairing rules ...
... along each of the DNA strands and adds nucleotides according to the base-pairing rules ...
DNA Replication Worksheet
... 16. Sentence Arrange – Put the steps of DNA replication in the correct order by writing a number in the space before each statement. (1-4) ______ Two new, identical molecules of DNA are formed. ______ Helicase begins to break the hydrogen bonds between nitrogen bases to unzip the DNA. ______ Cell ca ...
... 16. Sentence Arrange – Put the steps of DNA replication in the correct order by writing a number in the space before each statement. (1-4) ______ Two new, identical molecules of DNA are formed. ______ Helicase begins to break the hydrogen bonds between nitrogen bases to unzip the DNA. ______ Cell ca ...
Protein Synthesis - mvhs
... REVIEW: DNA TERMS DNA Base Nucleotide Sugar A, T, C, G Double Helix DNA polymerase III Helicase Topoisomerase ...
... REVIEW: DNA TERMS DNA Base Nucleotide Sugar A, T, C, G Double Helix DNA polymerase III Helicase Topoisomerase ...
DNA Replication
... Each time a new cell is made, the cell must receive an exact copy of the parent cell DNA. The new cells then receive the instructions and information needed to function. The process of copying DNA is called replication. Replication occurs in a unique way – instead of copying a complete new strand of ...
... Each time a new cell is made, the cell must receive an exact copy of the parent cell DNA. The new cells then receive the instructions and information needed to function. The process of copying DNA is called replication. Replication occurs in a unique way – instead of copying a complete new strand of ...
Study guide for Ch 13-16,18 Test AP Biology 2014
... Know what nitrogen bases are opposite each other and be able to calculate the percentage of the other nitrogen bases if you know one Ex. If thymine = 20%, you should be able to calculate how much adenine there is and then calculate cytosine and guanine. (Chargaff’s Rule) What type of mutation occurs ...
... Know what nitrogen bases are opposite each other and be able to calculate the percentage of the other nitrogen bases if you know one Ex. If thymine = 20%, you should be able to calculate how much adenine there is and then calculate cytosine and guanine. (Chargaff’s Rule) What type of mutation occurs ...
DNA, Protein Synthesis, and Gene Expression Review Historical
... 4. Which bases are purine, and which are pyrimidine? What is the basic structure of each (single ring or double ring)? 5. Why is DNA called a double helix? 6. What is in the DNA backbone, and why are they considered antiparallel? 7. What are the base pairing rules for DNA? 8. What is the name of the ...
... 4. Which bases are purine, and which are pyrimidine? What is the basic structure of each (single ring or double ring)? 5. Why is DNA called a double helix? 6. What is in the DNA backbone, and why are they considered antiparallel? 7. What are the base pairing rules for DNA? 8. What is the name of the ...
The Discovery of DNA
... Change in genotype and phenotype because of assimilation of external DNA by a cell Used disease-causing (pathogenic) and nondisease-causing (nonpathogenic) bacteria and mice But what caused the change in phenotype?? He wasn’t sure… ...
... Change in genotype and phenotype because of assimilation of external DNA by a cell Used disease-causing (pathogenic) and nondisease-causing (nonpathogenic) bacteria and mice But what caused the change in phenotype?? He wasn’t sure… ...
DNA/RNA/Protein Synthesis Study Guide
... double helix adenine thymine guanine cytosine purine pyrimidine gene DNA polymerase Okazaki fragments leading strand lagging strand replication fork transcription ribose uracil RNA polymerase codon anticodon ribosome translation (protein synthesis) mRNA tRNA rRNA ...
... double helix adenine thymine guanine cytosine purine pyrimidine gene DNA polymerase Okazaki fragments leading strand lagging strand replication fork transcription ribose uracil RNA polymerase codon anticodon ribosome translation (protein synthesis) mRNA tRNA rRNA ...
DNA
... A always pairs with T and C always pairs with G. This is because of the number of bonds formed between the bases. Two hydrogen bonds form between A and T and three between C and G. Write the compliment for GGCTATTGGCA. ...
... A always pairs with T and C always pairs with G. This is because of the number of bonds formed between the bases. Two hydrogen bonds form between A and T and three between C and G. Write the compliment for GGCTATTGGCA. ...
Test Review: Chapters 9, 10, 11 DNA as Genetic Material
... What experiment proved DNA replication was semi-conservative in eukaryotes? What enzymes are used in the replication process and what are their functions? helicase gyrase/topoisomerase primase polymerase ligase Differentiate between the leading and lagging strand according to the direction of repli ...
... What experiment proved DNA replication was semi-conservative in eukaryotes? What enzymes are used in the replication process and what are their functions? helicase gyrase/topoisomerase primase polymerase ligase Differentiate between the leading and lagging strand according to the direction of repli ...
Okazaki Fragments
... Replication requires the following steps 1-Unwinding Begins at Origins of Replication Two strands open forming Replication ...
... Replication requires the following steps 1-Unwinding Begins at Origins of Replication Two strands open forming Replication ...
Sample Final Exam Questions
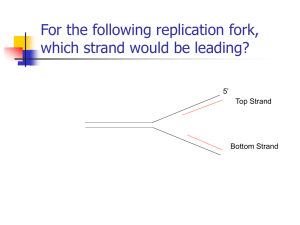
... i) On which template strand (A or B) would there be continuous replication by DNA polymerase? What is this newly synthesized daughter strand called during DNA replication? ii) On which template strand (A or B) would there be discontinous replication by DNA polymerase? What is this newly synthesized ...
... i) On which template strand (A or B) would there be continuous replication by DNA polymerase? What is this newly synthesized daughter strand called during DNA replication? ii) On which template strand (A or B) would there be discontinous replication by DNA polymerase? What is this newly synthesized ...
Unit 4 Review: Molecular Genetics
... 9) Eukaryotic cells modify mRNA after transcription. Describe how the pre-mRNA is modified with respect to: a) the 5’ ends and 3’ ends ...
... 9) Eukaryotic cells modify mRNA after transcription. Describe how the pre-mRNA is modified with respect to: a) the 5’ ends and 3’ ends ...
Document
... Sci 7 Ch 10.2 Section Review and Concepts Questions 1. What is selective breeding? ________________________________________________________________ ...
... Sci 7 Ch 10.2 Section Review and Concepts Questions 1. What is selective breeding? ________________________________________________________________ ...
Sect 12.2
... Summarize the role of the enzymes involved in the replication of DNA. Explain how leading and lagging strand are synthesized differently. ...
... Summarize the role of the enzymes involved in the replication of DNA. Explain how leading and lagging strand are synthesized differently. ...
Ch9notes
... They worked with _______________________. It is a virus that infects bacteria and produces more viruses when the bacterial cell ruptures. They used _______ phages to infect ___________ bacterial cell. They used radioactive _________ to label the protein coat and __________to label the DNA core .The ...
... They worked with _______________________. It is a virus that infects bacteria and produces more viruses when the bacterial cell ruptures. They used _______ phages to infect ___________ bacterial cell. They used radioactive _________ to label the protein coat and __________to label the DNA core .The ...
Chapter 9: DNA - Elmwood Park Memorial High School
... 5. The term double ______________ is used to describe the shape of DNA. 6. A virus that infects bacteria. 7. Enzyme that separates DNA by breaking the hydrogen bonds that link the nitrogen bases. 8. Name for a DNA subunit. 9. The process by which DNA is copied. 10. A replication _________ ...
... 5. The term double ______________ is used to describe the shape of DNA. 6. A virus that infects bacteria. 7. Enzyme that separates DNA by breaking the hydrogen bonds that link the nitrogen bases. 8. Name for a DNA subunit. 9. The process by which DNA is copied. 10. A replication _________ ...
1 - BEHS Science
... 14.double helix: a “spiral staircase” of two strands of nucleotides twisting around a central axis 15.complementary: the sequence of bases on one strand determines the sequence of bases on the other strand 16.replication: the process of synthesizing a new strand of DNA 17.helicase: enzymes that cata ...
... 14.double helix: a “spiral staircase” of two strands of nucleotides twisting around a central axis 15.complementary: the sequence of bases on one strand determines the sequence of bases on the other strand 16.replication: the process of synthesizing a new strand of DNA 17.helicase: enzymes that cata ...
DNA RNA Test Review Guide
... Name the process during which copies of DNA are made. Name the process during which a complementary RNA strand is made from DNA. Name the process during which amino acids are assembled into polypeptides according to DNA instructions. Give another name for a large polypeptide Name the monomer and mon ...
... Name the process during which copies of DNA are made. Name the process during which a complementary RNA strand is made from DNA. Name the process during which amino acids are assembled into polypeptides according to DNA instructions. Give another name for a large polypeptide Name the monomer and mon ...
Lecture #7 Date - Helena High School
... Replication fork: ‘Y’-shaped region where new strands of DNA are elongating Helicase:catalyzes the untwisting of the DNA at the replication fork DNA polymerase:catalyzes the elongation of new DNA ...
... Replication fork: ‘Y’-shaped region where new strands of DNA are elongating Helicase:catalyzes the untwisting of the DNA at the replication fork DNA polymerase:catalyzes the elongation of new DNA ...
Is an inducible operon normally off or on?
... Put the following enzymes in order for DNA replication ...
... Put the following enzymes in order for DNA replication ...
phosphorus - Sacred Heart Academy
... complementary bases • Replication occurs in the 5‘ to 3‘ direction (lead strand and lag strand); bases can only be added to the 3’ end of the growing DNA molecule • Other enzymes correct errors, remove primers, seal “nicks” in the backbone ...
... complementary bases • Replication occurs in the 5‘ to 3‘ direction (lead strand and lag strand); bases can only be added to the 3’ end of the growing DNA molecule • Other enzymes correct errors, remove primers, seal “nicks” in the backbone ...
Eukaryotic DNA replication

Eukaryotic DNA replication is a conserved mechanism that restricts DNA replication to only once per cell cycle. Eukaryotic DNA replication of chromosomal DNA is central for the duplication of a cell and is necessary for the maintenance of the eukaryotic genome.DNA replication is the action of DNA polymerases synthesizing a DNA strand complementary to the original template strand. To synthesize DNA, the double-stranded DNA is unwound by DNA helicases ahead of polymerases, forming a replication fork containing two single-stranded templates. Replication processes permit the copying of a single DNA double helix into two DNA helices, which are divided into the daughter cells at mitosis. The major enzymatic functions carried out at the replication fork are well conserved from prokaryotes to eukaryotes, but the replication machinery in eukaryotic DNA replication is a much larger complex, coordinating many proteins at the site of replication, forming the replisome.The replisome is responsible for copying the entirety of genomic DNA in each proliferative cell. This process allows for the high-fidelity passage of hereditary/genetic information from parental cell to daughter cell and is thus essential to all organisms. Much of the cell cycle is built around ensuring that DNA replication occurs without errors.In G1 phase of the cell cycle, many of the DNA replication regulatory processes are initiated. In eukaryotes, the vast majority of DNA synthesis occurs during S phase of the cell cycle, and the entire genome must be unwound and duplicated to form two daughter copies. During G2, any damaged DNA or replication errors are corrected. Finally, one copy of the genomes is segregated to each daughter cell at mitosis or M phase. These daughter copies each contain one strand from the parental duplex DNA and one nascent antiparallel strand.This mechanism is conserved from prokaryotes to eukaryotes and is known as semiconservative DNA replication. The process of semiconservative replication for the site of DNA replication is a fork-like DNA structure, the replication fork, where the DNA helix is open, or unwound, exposing unpaired DNA nucleotides for recognition and base pairing for the incorporationof free nucleotides into double-stranded DNA.