Directed Reading Packet
... 2. Explain how the nervous system helped Hakeem, from the chapter introduction, from falling. ...
... 2. Explain how the nervous system helped Hakeem, from the chapter introduction, from falling. ...
Powerpoint examples of tissues
... of differing heights, some not reaching the free surface; nuclei seen at different levels; may contain mucus-secreting cells and bear cilia. Cilia ...
... of differing heights, some not reaching the free surface; nuclei seen at different levels; may contain mucus-secreting cells and bear cilia. Cilia ...
red blood cells
... 1) Kidneys respond to a lower than normal oxygen concentration in the blood by releasing the hormone erythropoietin. 2) Erythropoietin travels to the red bone marrow and stimulates an increase in the production of red blood cells (RBCs). 3) The red bone marrow manufactures RBCs from stem cells that ...
... 1) Kidneys respond to a lower than normal oxygen concentration in the blood by releasing the hormone erythropoietin. 2) Erythropoietin travels to the red bone marrow and stimulates an increase in the production of red blood cells (RBCs). 3) The red bone marrow manufactures RBCs from stem cells that ...
BIOL_105_PRACTICE__FINAL_Exam_Q
... Fill in the following table by placing the letter that matches the statement with the organism. A for Generally True, commonly known to occur or have occurred, or present as a characteristic; B for Both True and False, can occur in some situations and / or species; C for False, does not generally oc ...
... Fill in the following table by placing the letter that matches the statement with the organism. A for Generally True, commonly known to occur or have occurred, or present as a characteristic; B for Both True and False, can occur in some situations and / or species; C for False, does not generally oc ...
Biology 2015 – Evolution and Diversity
... During this week and next week’s lab you’ll be studying organisms that once would have been included in the kingdom Protista. These are eukaryotic organisms, mostly single-celled, that are not plants, animals or fungi. For convenience, these organisms are still widely referred to as protists. Those ...
... During this week and next week’s lab you’ll be studying organisms that once would have been included in the kingdom Protista. These are eukaryotic organisms, mostly single-celled, that are not plants, animals or fungi. For convenience, these organisms are still widely referred to as protists. Those ...
Notes on Invertebrates
... Orthoptera (cricket, roach, grasshopper) Flight is the key to the success of insects, enabling them to escape predators, find food and mates, and disperse more easily than non-flying forms. This is made possible with complex nervous systems and exoskeleton for muscle attachment. Many insects undergo ...
... Orthoptera (cricket, roach, grasshopper) Flight is the key to the success of insects, enabling them to escape predators, find food and mates, and disperse more easily than non-flying forms. This is made possible with complex nervous systems and exoskeleton for muscle attachment. Many insects undergo ...
NAME
... (a) Explain why the process of natural selection is commonly known as ‘survival of the fittest’. ...
... (a) Explain why the process of natural selection is commonly known as ‘survival of the fittest’. ...
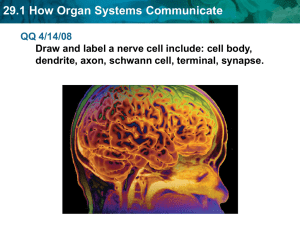
29.1 How Organ Systems Communicate - Morales Biology
... Draw and label a nerve cell include: cell body, dendrite, axon, schwann cell, terminal, synapse. ...
... Draw and label a nerve cell include: cell body, dendrite, axon, schwann cell, terminal, synapse. ...
MEMBRANES
... 5. Blood reservoir – when other body organs need blood supply, the nervous system constricts dermal blood flow 6. Production of Vitamin D – UV light converts circulating cholesterol into Vitamin D precursor which is needed for calcium metabolism ...
... 5. Blood reservoir – when other body organs need blood supply, the nervous system constricts dermal blood flow 6. Production of Vitamin D – UV light converts circulating cholesterol into Vitamin D precursor which is needed for calcium metabolism ...
Chapter 32
... completely disassociated, its cells can reassemble into a new sponge. • Sponges depend on water movement through their bodies to obtain food and are often oriented at right angles to current flow so that they may intercept water as it flows past. • Sponges reproduce both sexually and asexually. In m ...
... completely disassociated, its cells can reassemble into a new sponge. • Sponges depend on water movement through their bodies to obtain food and are often oriented at right angles to current flow so that they may intercept water as it flows past. • Sponges reproduce both sexually and asexually. In m ...
Second Announcement About the Conference Registration Fee
... abstracts will be accepted after October 31, 2014. How to Submit: Take a print out of the duly filled registration form (available at conference website) and send to the Conference Secretariat along with DD/multicity Cheque and otherrequisite details before the dead line. A letter from the superviso ...
... abstracts will be accepted after October 31, 2014. How to Submit: Take a print out of the duly filled registration form (available at conference website) and send to the Conference Secretariat along with DD/multicity Cheque and otherrequisite details before the dead line. A letter from the superviso ...
Mrs. Kristen Biology/ACC Bio Photosynthesis Worksheet What is the
... 6. How does the amount of energy in light change as the wavelength increases? ...
... 6. How does the amount of energy in light change as the wavelength increases? ...
Semester II Review – Science 6 Name: ____
... 1. ___________________________________ to filter and remove waste products from your blood and control water and salt balance in the bloodstream 2. ___________________________________ to produce children 3. ___________________________________ to make hormones 4. ___________________________________ t ...
... 1. ___________________________________ to filter and remove waste products from your blood and control water and salt balance in the bloodstream 2. ___________________________________ to produce children 3. ___________________________________ to make hormones 4. ___________________________________ t ...
Five Functions of Your Skeletal System - Carson
... 1. Gelatin-like substance where the work of the cell is done 2. Thread-like hereditary material made of DNA and proteins 3. Packages materials to take outside the cell 4. Cells make their proteins on these two-part structures. 5. Directs all the activities of the cell 6. Releases energy for the cell ...
... 1. Gelatin-like substance where the work of the cell is done 2. Thread-like hereditary material made of DNA and proteins 3. Packages materials to take outside the cell 4. Cells make their proteins on these two-part structures. 5. Directs all the activities of the cell 6. Releases energy for the cell ...
? Hormones are transported
... Leucocytes are far less numerous than red blood corpuscles. Leucocytes are larger than red blood corpuscles and have a definite nucleus. They are irregular in shape, slightly translucent and nearly colourless.They are able to change their shape because of the fact that they move by means of pseudopo ...
... Leucocytes are far less numerous than red blood corpuscles. Leucocytes are larger than red blood corpuscles and have a definite nucleus. They are irregular in shape, slightly translucent and nearly colourless.They are able to change their shape because of the fact that they move by means of pseudopo ...
cell – structure and function
... (i) The plasma membrane encloses the cell contents. (ii) It provides cell shape (in animal cells) e.g. the characteristic shape of red blood cells, nerve cells, and bone cells. (iii) It allows transport of certain substances into and out of the cell but not all substances so much it is termed ‘selec ...
... (i) The plasma membrane encloses the cell contents. (ii) It provides cell shape (in animal cells) e.g. the characteristic shape of red blood cells, nerve cells, and bone cells. (iii) It allows transport of certain substances into and out of the cell but not all substances so much it is termed ‘selec ...
Animal Structure and Function
... Regulation – Animals must control necessary body processes (such as metabolism) using the nervous system and endocrine system (which produces hormones). Hormones are chemical messengers that can control target cells or tissue. 1. Annelids have an anterior “brain” with ganglia extending to each body ...
... Regulation – Animals must control necessary body processes (such as metabolism) using the nervous system and endocrine system (which produces hormones). Hormones are chemical messengers that can control target cells or tissue. 1. Annelids have an anterior “brain” with ganglia extending to each body ...
4 Points: Hard - Cloudfront.net
... • Which organelle • Rough ER transports proteins (must say “rough”) and ribosome around the cell? ...
... • Which organelle • Rough ER transports proteins (must say “rough”) and ribosome around the cell? ...
Human Body Project
... Fold a piece of computer paper in half. Each body system should take up two halves 7 systems will have 2 sections each, 1 system will have 1 section, and the cover will be the remaining section The key feature is to give an overall sense of the organization and function of each of the 8 systems. You ...
... Fold a piece of computer paper in half. Each body system should take up two halves 7 systems will have 2 sections each, 1 system will have 1 section, and the cover will be the remaining section The key feature is to give an overall sense of the organization and function of each of the 8 systems. You ...
Introduction to Cancer Biology
... DNA mutations result in defects in the regulatory circuits of a cell, which disrupt normal cell proliferation behaviour. However the complexity of this disease is not as simple at the cellular and molecular level. Individual cell behaviour is not autonomous, and it usually relies on external signals ...
... DNA mutations result in defects in the regulatory circuits of a cell, which disrupt normal cell proliferation behaviour. However the complexity of this disease is not as simple at the cellular and molecular level. Individual cell behaviour is not autonomous, and it usually relies on external signals ...
4- Phylum CNIDARIA Contains about 9000 living species(at 1977
... into a thread whose tip may be open or closed. The thread normally lies coiled within the sac and at the point of inversion there is usually a lid or operculum. A stimulus to the cnidocil, where present, and/or to the surface of the cnidoblast, causes the nematocyst thread to be everted. According t ...
... into a thread whose tip may be open or closed. The thread normally lies coiled within the sac and at the point of inversion there is usually a lid or operculum. A stimulus to the cnidocil, where present, and/or to the surface of the cnidoblast, causes the nematocyst thread to be everted. According t ...
The Integumentary System
... To function in protection, the epidermis must rely on its ability to create & repair itself following an injury. New cells must be made at the same rate that dead cells flake off. Cells push off from the stratum basale into each upper layer until they die. Regeneration time for a cell is about ...
... To function in protection, the epidermis must rely on its ability to create & repair itself following an injury. New cells must be made at the same rate that dead cells flake off. Cells push off from the stratum basale into each upper layer until they die. Regeneration time for a cell is about ...
Functions of the Circulatory System Your circulatory system is a
... Your circulatory system is a “highway” network in your body, linking all of its parts. It consists of the heart, blood vessels, and blood. The circulatory system has three main functions. First, it carries needed substances to cells. Second, it carries waste products away from cells. Third, it trans ...
... Your circulatory system is a “highway” network in your body, linking all of its parts. It consists of the heart, blood vessels, and blood. The circulatory system has three main functions. First, it carries needed substances to cells. Second, it carries waste products away from cells. Third, it trans ...
Developmental biology

Developmental biology is the study of the process by which animals and plants grow and develop, and is synonymous with ontogeny. In animals most development occurs in embryonic life, but it is also found in regeneration, asexual reproduction and metamorphosis, and in the growth and differentiation of stem cells in the adult organism. In plants, development occurs in embryos, during vegetative reproduction, and in the normal outgrowth of roots, shoots and flowers.Practical outcomes from the study of animal developmental biology have included in vitro fertilization, now widely used in fertility treatment, the understanding of risks from substances that can damage the fetus (teratogens), and the creation of various animal models for human disease which are useful in research. Developmental Biology has also help to generate modern stem cell biology which promises a number of important practical benefits for human health.Many of the processes of development are now well understood, and some major textbooks of the subject are