Chapter 1--Introduction to Physiology and
... 42. The concentration of salt in the extracellular fluid influences how water enters and leaves cells. True False ...
... 42. The concentration of salt in the extracellular fluid influences how water enters and leaves cells. True False ...
DNA and its Building Blocks
... © Garland Science, Molecular Biology of The Cell, 4th Edition AI@ASU, BY510, Oct. 25, 2005 ...
... © Garland Science, Molecular Biology of The Cell, 4th Edition AI@ASU, BY510, Oct. 25, 2005 ...
Human Body Systems and Disease
... Antibiotics – if you get sick with some types of bacteria antibiotics will kill them Ex. Penicillin for strep throat Antibiotics do not kill viruses. Bacteria can become used to antibiotics so stronger antibiotics have to be used to kill them. ...
... Antibiotics – if you get sick with some types of bacteria antibiotics will kill them Ex. Penicillin for strep throat Antibiotics do not kill viruses. Bacteria can become used to antibiotics so stronger antibiotics have to be used to kill them. ...
BIOLOGY 12
... and added to test tubes containing three substrates as shown below. The test tubes are allowed to stand for one hour. Blue litmus paper, which turns red in the presence of an acid, is used as an indicator. ...
... and added to test tubes containing three substrates as shown below. The test tubes are allowed to stand for one hour. Blue litmus paper, which turns red in the presence of an acid, is used as an indicator. ...
S 7.1 All living organisms are com- posed of cells, from just one to
... about living things. However, they didn't explain where cells came from. Until their time, most people thought that living things could come from nonliving matter. In 1855, Virchow proposed that new cells are formed only from cells that already exist. '~1 cells come from cells;' wrote Virchow. ...
... about living things. However, they didn't explain where cells came from. Until their time, most people thought that living things could come from nonliving matter. In 1855, Virchow proposed that new cells are formed only from cells that already exist. '~1 cells come from cells;' wrote Virchow. ...
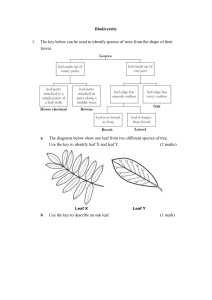
Structured Questions
... Plant has leaves on or above surface…………………… Grows in deep water …………………………………… Grows in shallow water ………………………………... Plant has roots in soil …………………………………... Plant is free floating on water surface ………………….. Long and thin leaves …………………………………… ...
... Plant has leaves on or above surface…………………… Grows in deep water …………………………………… Grows in shallow water ………………………………... Plant has roots in soil …………………………………... Plant is free floating on water surface ………………….. Long and thin leaves …………………………………… ...
Structure and Function in Living Things
... Fungi structures Figure 15.9 shows the structure of a typical fungus. All fungi are made up of thread-like filaments called hyphae. The cells that make up the hyphae sometimes contain two, three, or even more nuclei. In the fungi you are familiar with, the hyphae grow into whatever the fungus is fee ...
... Fungi structures Figure 15.9 shows the structure of a typical fungus. All fungi are made up of thread-like filaments called hyphae. The cells that make up the hyphae sometimes contain two, three, or even more nuclei. In the fungi you are familiar with, the hyphae grow into whatever the fungus is fee ...
LECTURE OUTLINE
... The tissues of the human body can be categorized into four major types: epithelial tissue, connective tissue, muscular tissue, and nervous tissue. Cancers are classified according to the type of tissue from which they arise. Epithelial Tissue Epithelial tissue consists of tightly packed cells that f ...
... The tissues of the human body can be categorized into four major types: epithelial tissue, connective tissue, muscular tissue, and nervous tissue. Cancers are classified according to the type of tissue from which they arise. Epithelial Tissue Epithelial tissue consists of tightly packed cells that f ...
Dissection guide - MUGAN`S BIOLOGY PAGE
... Examine first the larger female cross section. Note the thick non-cellular cuticle on the outside of the body wall. Below the cuticle is the thinner syncytial epidermis, which contains nuclei but few cell walls. The longitudinal muscles making up most of the body wall appear as fluffy, irregular mas ...
... Examine first the larger female cross section. Note the thick non-cellular cuticle on the outside of the body wall. Below the cuticle is the thinner syncytial epidermis, which contains nuclei but few cell walls. The longitudinal muscles making up most of the body wall appear as fluffy, irregular mas ...
Cornell Notes: Body Systems - CGW-Life-Science
... Cornell Notes: Organization of the Body How the body is organized: AKA Levels of Organization 1. Cells 2. Tissues 3. Organs 4. Organ systems 5. (organism) Tissue: cells working together with a common purpose Four main types: 1. connective tissue 2. muscle tissue 3. epithelial tissue 4. nervous tissu ...
... Cornell Notes: Organization of the Body How the body is organized: AKA Levels of Organization 1. Cells 2. Tissues 3. Organs 4. Organ systems 5. (organism) Tissue: cells working together with a common purpose Four main types: 1. connective tissue 2. muscle tissue 3. epithelial tissue 4. nervous tissu ...
2.15 Answers
... 1. Fungi are heterotrophs (consumers) and lack the structures and ability to produce food. 2. The following criteria are used to classify fungi: often have many nuclei per cell; have few or no storage molecules; have no roots; often have chitin in their cell walls; are heterotrophs; do not reproduce ...
... 1. Fungi are heterotrophs (consumers) and lack the structures and ability to produce food. 2. The following criteria are used to classify fungi: often have many nuclei per cell; have few or no storage molecules; have no roots; often have chitin in their cell walls; are heterotrophs; do not reproduce ...
INTRODUCTION OF RESPIRATORY SYSTEM
... 4. The no. of mucous-secreting cells ↓s 5. The no. of cilia ↓s 6. The total cross-sectional area ↑s (2.5 cm2 in the trachea thru 180 cm2 in terminal bronchioles to 11,800 cm2 in the alveoli; about are in contact with capillaries7000cm2 ) ...
... 4. The no. of mucous-secreting cells ↓s 5. The no. of cilia ↓s 6. The total cross-sectional area ↑s (2.5 cm2 in the trachea thru 180 cm2 in terminal bronchioles to 11,800 cm2 in the alveoli; about are in contact with capillaries7000cm2 ) ...
RNA polymerase I
... Ribosomal subunit assembly • Done in nucleolus • 2 protein types associate with rRNA as it's processed – Proteins that remain in ribosomal subunits – proteins that have transient interaction with rRNA • needed for processing ...
... Ribosomal subunit assembly • Done in nucleolus • 2 protein types associate with rRNA as it's processed – Proteins that remain in ribosomal subunits – proteins that have transient interaction with rRNA • needed for processing ...
Slide 1 - Skyline R2 School
... It is produced when body cells break down food and give off energy ...
... It is produced when body cells break down food and give off energy ...
Body Systems
... Skeletal System (pages 443-449) • What are the 3 types of movable bone joints and how do each one of them move? (pg 447) ...
... Skeletal System (pages 443-449) • What are the 3 types of movable bone joints and how do each one of them move? (pg 447) ...
2.4 Movement of Chemicals in Plants and Animals
... When gases move into and out of an organism they need to move across the surface of the body. In some organisms this could be a general movement across the entire body surface, but in most, a special surface area has been developed for this to occur. This is called the respiratory surface. ...
... When gases move into and out of an organism they need to move across the surface of the body. In some organisms this could be a general movement across the entire body surface, but in most, a special surface area has been developed for this to occur. This is called the respiratory surface. ...
Movement of Chemicals in Plants and Animals
... When gases move into and out of an organism they need to move across the surface of the body. In some organisms this could be a general movement across the entire body surface, but in most, a special surface area has been developed for this to occur. This is called the respiratory surface. ...
... When gases move into and out of an organism they need to move across the surface of the body. In some organisms this could be a general movement across the entire body surface, but in most, a special surface area has been developed for this to occur. This is called the respiratory surface. ...
Early Evolution of Life | Principles of Biology from Nature Education
... has DNA enclosed in a nucleus, an endoplasmic reticulum that participates in protein synthesis, a cytoskeleton that allows it to change shape to engulf other cells and transport materials, and mitochondria that use oxygen and glucose to produce energy-containing molecules for the cell. The process o ...
... has DNA enclosed in a nucleus, an endoplasmic reticulum that participates in protein synthesis, a cytoskeleton that allows it to change shape to engulf other cells and transport materials, and mitochondria that use oxygen and glucose to produce energy-containing molecules for the cell. The process o ...
Animal Organ Systems (Student Version)
... __________ which perform tasks. Tissues that are alike work together to form ____________ which complete jobs. Organs work together in __________________ to carry out processes. Organ systems work together to support the life of an ________________. ...
... __________ which perform tasks. Tissues that are alike work together to form ____________ which complete jobs. Organs work together in __________________ to carry out processes. Organ systems work together to support the life of an ________________. ...
Understanding Our Environment
... Axil - Angle between a petiole and the stem. Axillary Bud located in axil. - Terminal Bud often found at twig tip. Stipules - Paired appendages at the base of a leaf. Often remain throughout leaf life span. Deciduous trees and shrubs have dormant axillary buds with leaf scars left after leaves ...
... Axil - Angle between a petiole and the stem. Axillary Bud located in axil. - Terminal Bud often found at twig tip. Stipules - Paired appendages at the base of a leaf. Often remain throughout leaf life span. Deciduous trees and shrubs have dormant axillary buds with leaf scars left after leaves ...
BIOL 2401 Unit and Final Exam Study Guides
... 1. The cytoplasm of the skeletal muscle cell is called ... 2. The cell membrane of the skeletal muscle cell is called… 3. What are the four properties of the muscle? 4. Explain the diverse functions of the muscle tissue. 5. A skeletal muscle cell can also be called… 6. A group of muscle cells i ...
... 1. The cytoplasm of the skeletal muscle cell is called ... 2. The cell membrane of the skeletal muscle cell is called… 3. What are the four properties of the muscle? 4. Explain the diverse functions of the muscle tissue. 5. A skeletal muscle cell can also be called… 6. A group of muscle cells i ...
Using the Rapid Chill Surgical Technique to Examine a Live
... Students will break up into lab groups of three to four using the rapid chill technique described in the accompanying article to prepare a goldfish for close examination under a video microscope. Each group will be given a live goldfish, chopped ice, spring water, a thermometer, and a spoon. They wi ...
... Students will break up into lab groups of three to four using the rapid chill technique described in the accompanying article to prepare a goldfish for close examination under a video microscope. Each group will be given a live goldfish, chopped ice, spring water, a thermometer, and a spoon. They wi ...
CHAPTER 8 “BACTERIA” (P. 210)
... (against life) - used to kill or slow the growth of bacteria. Ex. penicillin amoxocillin What is antibiotic resistance? ...
... (against life) - used to kill or slow the growth of bacteria. Ex. penicillin amoxocillin What is antibiotic resistance? ...
K CHAPTER 2: BODY TISSUES AND MEMBRANES At the end of
... 1.1. Embryonic tissue Approximately 13 or 14 days after fertilization, the cells that give rise to the new individual, called embryonic stem cells form a slightly elongated disk consisting of two layers called the ectoderm and the endoderm. Cells of ectoderm then migrate between the two layers to fo ...
... 1.1. Embryonic tissue Approximately 13 or 14 days after fertilization, the cells that give rise to the new individual, called embryonic stem cells form a slightly elongated disk consisting of two layers called the ectoderm and the endoderm. Cells of ectoderm then migrate between the two layers to fo ...
Developmental biology

Developmental biology is the study of the process by which animals and plants grow and develop, and is synonymous with ontogeny. In animals most development occurs in embryonic life, but it is also found in regeneration, asexual reproduction and metamorphosis, and in the growth and differentiation of stem cells in the adult organism. In plants, development occurs in embryos, during vegetative reproduction, and in the normal outgrowth of roots, shoots and flowers.Practical outcomes from the study of animal developmental biology have included in vitro fertilization, now widely used in fertility treatment, the understanding of risks from substances that can damage the fetus (teratogens), and the creation of various animal models for human disease which are useful in research. Developmental Biology has also help to generate modern stem cell biology which promises a number of important practical benefits for human health.Many of the processes of development are now well understood, and some major textbooks of the subject are