* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Structured Questions
Introduction to evolution wikipedia , lookup
History of biology wikipedia , lookup
Ornamental bulbous plant wikipedia , lookup
Paleontology wikipedia , lookup
Plant use of endophytic fungi in defense wikipedia , lookup
Binomial nomenclature wikipedia , lookup
Koinophilia wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Soil microbiology wikipedia , lookup
Bacterial taxonomy wikipedia , lookup
Sexual reproduction wikipedia , lookup
Developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Living things in culture wikipedia , lookup
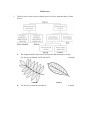
Biodiversity 1. The key below can be used to identify species of trees from the shape of their leaves. a The diagrams below show one leaf from two different species of tree. Use the key to identify leaf X and leaf Y. (2 marks) Leaf X b Use the key to describe an oak leaf. Leaf Y (1 mark) 2. The key describes different types of geese. Use the information in the key to answer the questions. a Give one way in which a Snow goose and a Barnacle goose are the same. (1 mark) b List all the information that the key gives about a Canada goose. (2 marks) 3. The table below shows some features of five British butterflies. Butterfly species Wing shading Wing tip Wing spots Large White Pale Black Yes Orange Tip Pale Orange No Peacock Dark Blue Yes Red Admiral Dark White Yes Wood White Pale Black No Complete the key using the information given in the table. 1 2 3 4 (3 marks) Pale wing shading ……………………………………… Go to 2 Dark wing shading …………………………………….. a ___________ b _______________ …………………………………… c ___________ Orange wing tip ………………………………………... Orange Tip Spots on wings …………………………………………. Large White No spots on wings ……………………………………… d ___________ Blue Wing tip ………………………………………….. Peacock e _______________ ……………………………………. f ____________ 4. The key gives information about some water plants growing in a pond. Plant is fully submerged in water ……………………… Plant has leaves on or above surface…………………… Grows in deep water …………………………………… Grows in shallow water ………………………………... Plant has roots in soil …………………………………... Plant is free floating on water surface ………………….. Long and thin leaves …………………………………… Round leaves …………………………………………… Go to 2 Go to 3 Elodea Starwort Go to 4 Water hyacinth Water hawthorn Go to 5 5 Resistant to frost ……………………………………...... Cannot survive frost ……………………………………. Water lily Lotus a Use the key to identify the plant from the photograph and its description. (1 mark) 1 2 3 4 Photograph b c Description The plant has its roots in the soil at the bottom of the pond and does not tolerate frost very well. Which plant grows submerged in deep water? (1 mark) Give three features that the Water lily and the Lotus have in common. (2 marks) 5. Use the key below to identify each of the animals by placing its letter W, X, Y or Z in the correct box. (4 marks) 1 2 3 W X Y Z Wings present Insect or Wings absent Go to 2 Shell present Snail or Shell absent Go to 3 Eight legs Spider or More than eight legs Centipede 6. The origin of Homo sapiens sapiens is a topic which has fascinated generations of scientists. How did we evolve? Are we still evolving? Why are there no other Homo species alive today? a The study of the evolutionary ancestors of H. sapiens sapiens involves the science of taxonomy. Explain the meaning of the term taxonomy. (3 marks) b The table below shows the main taxonomic groups. P Q R S T U V Taxonomic Species Order Family Kingdom Class Phylum Genus group Place the letters representing the taxonomic groups in the correct order. The first one has been done for you. (3 marks) S c Different species cannot breed together to produce fertile young. Explain why they cannot produce fertile young. (1 mark) 7. a b List the four kingdoms that consist of eukaryotes. (4 marks) State three features of the organisms in the kingdom Eubacteria. (3 marks) 8. The table below shows the classification of three animals. Cat Tiger Lion Class Mammalia Mammalia Mammalia Order Carnivora Carnivora Carnivora Family Felidae Felidae Felidae Genus Felis Panthera Panthera Species domesticus tigris leo a Which animals, cats or tigers, are more closely related to lions? Explain briefly. (2 marks) b Carolus Linnaeus developed a system of naming organisms called binomial nomenclauture. In this system, all organisms are given a two-word scientific name. i State the scientific name of lions in Linnaeus’s naming system. (1 mark) ii What is the advantage of using this naming system in scientific studies? (1 mark) 9. a b State two reasons why bats are not birds. State two reasons why whales are mammals but not fish. (2 marks) (2 marks) 10. The table below shows the classification of tigers, but in an incorrect order. Level of classification Classification of tigers P Genus Panthera Q Kingdom Animalia R Species tigris S Class Mammalia T Phylum Chordata U Family Felidae V Order Carnivora a Using the letters in the table, arrange the levels of classification in the correct order. Start with the level with largest number of organisms. (2 marks) b c Give the scientific name of tigers. (1 mark) Give an example of organisms that are in the same phylum as tigers. (1 mark) d Although tigers can mate with lions to produce offspring, they are considered to be two different species. Explain why. (2 marks) 11. The diagram below shows the structure of a bacterium. X a b Name structure X and state its function. (2 marks) State one similarity and one difference in the structure of a bacterium and an archaebacterium. (4 marks) 12. Biologists once grouped archaebacteria and bacteria into the same kingdom due to their structural similarities. With the advancement of technology, biologists found that archaebacteria are more closely related to eukaryotes than to bacteria in the evolutionary history. Therefore archaebacteria and bacteria have been classified into two different groups in the modern six-kingdom system. a State two structural similarities of archaebacteria and bacteria which distinguish them from other organisms. b (2 marks) How did biologists know that archaebacteria are more closely related to eukaryotes than to bacteria in the evolutionary history? c (2 marks) Which aspect of the nature of science does this example illustrate? (1 mark) 13. The table below shows some features of four organisms belonging to different kingdoms. Cells contain cell wall Cells contain true nucleus Contains chlorophyll a b W Yes Yes Yes X Yes Yes No Y Yes No No Z Yes No No What are the possible kingdoms that W, X, Y and Z belong to? (4 marks) State two features that allow us to distinguish between Y and Z. (2 marks) 14. The photograph below shows some organisms on a slice of bread. X a b c Give the name of these organisms. (1 mark) Name structure X. (1 mark) Although these organisms have cell walls, they are not classified into the kingdom Plantae. i ii State the kingdom they belong to. (1 mark) Describe how the mode of nutrition of the organisms in this kingdom is different from that of plants. (2 marks) iii Apart from the mode of nutrition, give two other features of the organisms in this kingdom to explain why they are not classified into the kingdom Plantae. (2 marks) 15. The photographs below show three organisms, X, Y and Z. X a b c d Y Z How do Y and Z obtain their food? (2 marks) Apart from the mode of nutrition, give one other feature that X is i like Y and Z. (1 mark) ii unlike Y and Z. (1 mark) State the role of X in the energy flow of an ecosystem. (1 mark) How is the reproduction of Y different from Z? (2 marks) 16. The photographs below show six animals, P, Q, R, S, T and U. P a b c d Q R S T U Give one feature that distinguishes Q and S from P, R, T and U. (1 mark) Based on the feature in a, name the group to which Q and S belong. (1 mark) Give two features that classify Q and S into different groups. (2 marks) The dichotomous key below can be used to identify P, R, T and U. 1 a Have jointed legs…………………….. Go to 2 b Do not have jointed legs……………... Go to 3 2 3 i ii a b a b Have wings…………………………… Insect Do not have wings…………………… Arachnid Have spiny skin………………………. Echinoderm Do not have spiny skin……………….. Cnidarian Which animal is a cnidarian? (1 mark) With reference to the dichotomous key provided, give two characteristics of an echinoderm. (2 marks) 17. Suppose a spacecraft returns from a mission to a planet with several specimens of a particular kind of organisms. Scientists try to classify them with the classification system that we use for the organisms on earth. One of the specimens has structures similar to a backbone. It has no limbs and looks like a snake and an eel. How can we determine whether it is a fish, an amphibian or a reptile? (3 marks) 18. a Use the dichotomous key below to classify organisms P, Q, R, S, T, U and V into different groups. (3 marks) 1 Cells with cell walls………………………………... Cells without cell walls…………………………….. Go to 2 Go to 3 2 With chlorophyll…………………………………… Without chlorophyll………………………………... Most are single-celled organisms………………….. Multicellular organisms……………………………. With roots………………………………………….. Without roots……………………………………….. With seeds………………………………………….. Go to 4 P Q R Go to 5 S Go to 6 Without seeds………………………………………. With fruits………………………………………….. Without fruits………………………………………. T U V 3 4 5 6 b How may the season affect the usefulness of the above key for classifying a particular plant? (2 marks) 19. The diagrams below show six animals, P, Q, R, S, T and U. a P Q R S T U Identify the animals using the dichotomous key below. 1 With 4 pairs of legs or fewer legs……………... Go to 2 2 3 4 5 With more than 4 pairs of legs………………… With wings ……………………………………. Without wings ...………………………………. With 1 pair of wings ……………………..…… With 2 pairs of wings …………………..……... With legs ……...………………………………. Without legs ………………………..…………. With 1 pair of legs per segment ……………... With more than 1 pair of legs per segment ….... (6 marks) Go to 5 Go to 3 Go to 4 Glossina Brachytera Eremobates Lumbricus Scutigerella Spirobolus b Explain what a dichotomous key is. (2 marks) c d Why the six animals can be classified into the same group? (1 mark) Which two of them can be separated from the other four and put into the same group? Explain briefly. (3 marks) 20. The table below shows the classification of a sample of animals belonging to the class Mammalia. a b Name the classification levels i to iv shown in the table. i ii (4 marks) Human Zebra Horse Class Mammalia Mammalia Mammalia i Primates Perissodactyla Perissodactyla ii Hominidae Equidae Equidae iii Homo Equus Equus iv sapiens zebra caballus Each organism is given a scientific name according to the naming system binomial nomenclature. Explain the meaning of ‘binomial nomenclature’. (3 marks) Give the scientific name of zebra. (1 mark) 21. Fossils of an unknown animal have been discovered. It is believed that the animal is an intermediate form between reptiles and birds in the process of the evolution. a State two common features found in birds and reptiles. (2 marks) b State one feature found in birds but not in reptiles. (1 mark) c Name three other groups of vertebrates and give one example for d each group. (6 marks) What is the common characteristic of vertebrates? (1 mark) 22. The diagrams below show six organisms, P, Q, R, S, T and U. nucleus nucleus chloroplast P Q green leaves green leaves true roots rhizoids R S T U Give reason(s) for each of the following. a b c i P and Q are grouped into the same domain. (1 mark) ii P and Q are put into different kingdoms. (1 mark) i R and S are grouped into the same kingdom. (2 marks) ii R and S are put into different phyla. (2 marks) i T and U are grouped into the same kingdom. (4 marks) ii T and U are put into different groups. (2 marks) 23. In a field study, a student identified three species of trees and recorded them as follows: a The student named these trees using binomial nomenclature. Explain the meaning of the term ‘binomial nomenclature’ with the names of the three species given by the student. b State two mistakes made by the student in writing the names of the three species of trees. c (2 marks) Is species Y more similar to species X or species Z in characteristics? Explain briefly. d (3 marks) (3 marks) The three species of trees produce fruits in spring. Name the kingdom and the group they belong to. (2 marks) 24. The diagrams below show two different plants. X a Y Which one, X or Y, is a monocotyledonous plant and which is a dicotyledonous plant? Explain briefly. b Apart from the answer given in a, state one other difference between monocotyledonous and dicotyledonous plants. c (4 marks) (2 marks) X and Y belong to the same group of plants. Give four common features of the plants in this group. (4 marks) 25. The diagram below shows the classification of vertebrates into five different groups. Group P: Hairy skin Group Q: Slimy skin without scales Vertebrates Group R: Slimy scales Group S: Feathers Group T: Dry scales a Name the groups P, Q, R, S and T. (5 marks) b Give one feature that is unique to the organisms in groups P and S. (1 mark) c Why is a moist naked skin important to the organisms in group Q? (2 marks) d Are bats and whales belong to the same group? If yes, name the group and state one unique feature of this group that is not listed in the above diagram. If no, name the groups and state one unique feature of each group. (3 marks) 26. The photographs below show the leaves of four different plants. Pine a i ii iii Grass Maple Frangipani Which of the plants has to be put into a different group from the others? (1 mark) Name the group it belongs to and give one reason. State one other plant in this group. (2 marks) (1 mark) b Using the external features of the leaves of the plants, construct a dichotomous key for identification of the above plants. (3 marks) c What is the difference between the reproduction of pines and grass? (1 mark) 27. The diagrams below show six animals. Snail Crab Fish Bee Pig Frog a These animals belong to two different major groups. Give the names of these groups. (2 marks) b Classify the above animals into the two major groups answered in a. (3 marks) c On average, pigs consume more food per unit weight than frogs do. Why? (3 marks) d Both bats and bees can fly. Why do they belong to different major groups? (2 marks) 28. Discuss on the facts that a cat and a pigeon are classified into two subdivisions of the same major group of animals. (10 marks) 29. Fungi belonged to a class under the kingdom Plantae in the old two-kingdom system, but it is now classified as an individual kingdom in the modern six-kingdom system. Discuss whether fungi should be included in the kingdom Plantae. (10 marks) Answers 1. a Leaf X: Rowan 1m Leaf Y: Laurel 1m b Its leaf is made up of one part and it leaf edge has a wavy outline. 1m a Both have a white face. 1m b It has black feet, a black face and a white throat. 2m a Go to 4 0.5m b Black wing tip 0.5m c Go to 3 0.5m d Wood White 0.5m e White wing tip 0.5m f Red Admiral 0.5m a Water hawthorn 1m b Elodea 1m c They have round leaves. They have roots in soil. They have leaves on or above 2. 3. 4. surface. 2m 5. Insect: X 1m Snail :Y 1m Spider: Z 1m Centipede: W 1m a 1m 6. Taxonomy is the classification of organisms, which indicates how closely the species are related and how they are similar b genetically. 1m It also includes the naming of organisms. 1m U, T, Q, R, V, P 3m 19 c Chromosome number differs in two species. The chromosomes cannot pair up during gamete formation. 1m a Protista, Fungi, Plantae, Animalia 1m x 4 b Their cell walls contain no cellulose / are made of peptidoglycan. 1m 7. They have no true nucleus. Their genetic material is in the form of a circular ring of DNA. 1m They have no membrane-bound organelles / mitochondria / chloroplasts. 1m a Tigers. Tigers and lions are in the same genus. 2m b i Panthera leo 1m ii The scientific names are universal. This enables scientists to communicate 8. accurately. 1m 9. a Any two from: 1m x 2 Bats have no feathers / have hair rather than feathers. Bats have no dry scales on their legs. Bats do not lay eggs. b Any two from: 1m x 2 Whales breathe with lungs instead of gills. Whales give birth to small mammals instead of laying eggs. Their young develop inside the mother's body. Female whales have well-developed mammary glands to feed their young. 10. a Q, T, S, V, U, P, R 2m b Panthera tigris 1m c Humans / cats / dogs 1m (or other reasonable answers) d Their offspring are infertile / sterile. 1m Organisms of the same species can interbreed to produce fertile offspring. 1m 11. a X: flagellum 1m It is used for locomotion. 1m 20 b Similarity: Both of them are prokaryotes / have no true nucleus / have a circular ring of DNA. 2m Difference: The cell wall of a bacterium contains peptidoglycan, while that of an archaebacterium contains no peptidoglycan. / The lipids in the cell membrane of an archaebacterium are different from those of a bacterium. 2m Both of them are single-celled organisms. 1m 12. a Both of them are prokaryotes / have no true nucleus / have a circular ring of DNA. 1m Biologists studied the DNA sequence / genetic material of archaebacteria 1m and found that it is more similar to eukaryotes’ than to bacteria’s. 1m c Scientific knowledge is subject to change when new evidence appears. 1m a W: Plantae 1m X: Fungi 1m Y, Z: Eubacteria / Archaebacteria 1m x 2 The chemical composition of the cell walls. 1m The chemical composition of the cell membranes. 1m a Bread moulds 1m b X: hypha 1m c i Fungi 1m ii They carry out parasitic or saprophytic nutrition 1m while plants carry out autotrophic nutrition. 1m They have no chlorophyll while plants have chlorophyll. 1m b 13. b 14. iii Their cell wall contains no cellulose but that of plants contains cellulose. 1m 15. a Y and Z carry out photosynthesis to make their own food. 2m b i Its cells have cell walls / it cannot move around. 1m ii It does not contain chlorophyll. / It does not have any roots, stems or leaves. 1m 21 c Decomposer 1m d Y produces spores for reproduction 1m while Z produces flowers and seeds for reproduction. 1m a Q and S have a backbone while P, R, T and U do not. 1m b Vertebrates 1m c Any two from: 1m x 2 16. Q breathes with lungs while S breathes with gills. Q gives birth to young while S lays eggs. The female of Q has mammary glands while S does not. Q is a homoiotherm while S is a poikilotherm. d i T 1m ii It has spiny skin but have no jointed legs. 2m 17. If the specimen has gills and its body is covered with slimy scales, it can be classified as a fish. 1m If the specimen has lungs and its body is covered with moist naked skin, it can be classified as an amphibian. 1m If the specimen has lungs and its skin is covered with dry hard scales, it can be classified as a reptile. 1m 18. a P: Fungi Q: Protista R: Animalia S: non-vascular plants T: ferns U: flowering plants V: conifers b The season may affect flower and seed production. 3m 1m Flowers and seeds would be produced by the plants only in the right season. 1m 22 19. a b P: Spirobolus 1m Q: Scutigerella 1m R: Glossina 1m S: Eremobates 1m T: Brachytera 1m U: Lumbricus 1m It is a tool for identifying organisms. 1m Organisms can be identified step by step by choosing one of the two alternative features correctly. 1m c They do not have a backbone. 1m d R and T 1m Reasons (any two) : 1m x 2 They have wings. They have three pairs of legs. Their bodies are divided into three parts: head, thorax and abdomen. 20. a b i Order 1m ii Family 1m iii Genus 1m iv Species 1m i The scientific name of an organism consists of two words. 1m The first word is the genus name. 1m The second word is the species name. 1m Equus zebra 1m ii 21. a Any two from: 1m x 2 Both breathe with lungs. Both carry out internal fertilization. Both lay eggs with hard shells. b Birds have feathers. / Birds are homoiotherms. 1m c Fish, amphibians, mammals 1m x 3 (one mark for each correct example) 1m x 3 They all have a backbone. 1m d 23 22. a b i They have a true nucleus. 1m ii Q has chloroplasts but P does not. 1m i Both of them have stems and leaves. 1m Both contain chlorophyll / chloroplasts. 1m R has true roots while S does not. 1m R has vascular tissues while S does not. 1m Their cells do not have a cell wall. 1m They have no chloroplasts / chlorophyll. 1m They can move freely from one place to another. 1m Their irritability is highly developed. 1m T breathes with gills while U breathes with lungs. 1m T moves with fins and tail while U moves with legs. 1m ii c i ii 23. a Binomial nomenclature is a way of naming organisms using universal scientific names. 1m The scientific name of each species consists of two words in Latin. 1m The first word is the genus name and the second word is the species name. 1m b c d The two words of each species should be underlined separately. 1m The second word should begin with a small letter. 1m Y and X belong to two different genera. 1m Y and Z are of the same genus. 1m Therefore Y is more similar to Z than to X. 1m Kingdom: Plantae 1m Group: flowering plants 1m X is a monocotyledonous plant. 1m Its leaves have parallel veins. 1m Y is a dicotyledonous plant. 1m Its leaves have net-like veins. 1m 24. a b A monocotyledonous plant has only one seed leaf / cotyledon in its seeds. 1m A dicotyledonous plant has two seed leaves / cotyledons in its seeds. 1m 24 c They have flowers. 1m They produce seeds. 1m They have roots, stems and leaves. 1m They have vascular tissues. 1m P: Mammals 1m Q: Amphibians 1m R: Fish 1m S: Birds 1m T: Reptiles 1m b They are homoiotherms. 1m c The moist naked skin allows gas exchange through the skin 1m and allows water to be absorbed or lost through the skin. 1m Yes 1m They are mammals. 1m The females have mammary glands. 1m i Pine 1m ii Conifers. The leaves of pine are needle-shaped. 1m x 2 iii Firs / cypresses 1m 1 Leaves are needle-shaped Pine Leaves are not needle-shaped Go to 2 Leaves with parallel veins Grass Leaves with net-like veins Go to 3 Leaves with lobes Maple Leaves without lobes Frangipani 25. a d 26. a b 2 3 c 3m Grass produces flowers for reproduction but pines do not. / The seeds of grass are protected inside fruits while the seeds of pines are naked / found in cones. 1m 27. a Vertebrates, invertebrates b Vertebrates: fish, pig and frog 0.5m x 3 Invertebrates: snail, crab and bee 0.5m x 3 c 1m x 2 Pigs are homoiotherms. 1m They need a higher respiration rate to release more energy 1m for keeping their bodies warm. 1m 25 d Bats have a backbone. 1m Bees do not have a backbone. 1m 28. Same major group: Both are vertebrates. 1m They have a backbone. 1m Different subdivisions: Cat is a mammal while pigeon is a bird. 1m The body of cat is covered with hair while the body of pigeon is covered with feathers. 1m Cat has no beak while pigeon has a beak. 1m Cat has well-developed teeth while pigeon have no teeth. 1m Cat gives birth to kittens while pigeon lays eggs for reproduction. 1m Effective communication 3m 29. Fungi should be included in the kingdom Plantae: Both of them consist of cells with a cell wall. 1m Both of them cannot move to other places freely. 1m Fungi produce spores for reproduction, which is similar to some plants like ferns. 1m Fungi should not be included in the kingdom Plantae: Fungi carry out parasitic or saprophytic nutrition while plants carry out autotrophic nutrition. 1m Fungi do not have roots, stems or leaves while most plants do. 1m Fungi do not have chlorophyll while plants do. 1m The cell wall of fungi is not made up of cellulose while the cell wall of plants is made up of cellulose. 1m Effective communication 3m 26