Hit List vocabulary cards
... Vascular plant tissue composed of tubular cells that transport water and minerals from the roots to the rest of the plant ...
... Vascular plant tissue composed of tubular cells that transport water and minerals from the roots to the rest of the plant ...
Biology EOC Voc Review
... Learned behavior in which an animal, at a specific critical time of its life, forms a social attachment to another object; usually occurs early in life and allows an animal to recognize its mother and others in its species An inherited, genetically based behavior in animals Complex innate behavior p ...
... Learned behavior in which an animal, at a specific critical time of its life, forms a social attachment to another object; usually occurs early in life and allows an animal to recognize its mother and others in its species An inherited, genetically based behavior in animals Complex innate behavior p ...
Tissues and Organs - sciencelanguagegallery
... Tissues made up of the same cells Eg. Cardiac heart muscle red blood cells Organs made up of different tissues Eg. Heart is composed of Cardiac muscle, nerve cells, fat cells, connective tissue and red blood cells ...
... Tissues made up of the same cells Eg. Cardiac heart muscle red blood cells Organs made up of different tissues Eg. Heart is composed of Cardiac muscle, nerve cells, fat cells, connective tissue and red blood cells ...
8.2. Reproduction is a characteristic of living systems and it is
... 1. Living organisms must reproduce to continue the existence of their species. Through reproduction new individuals which resemble their parents are formed. All the organisms alive today arose from preexisting organisms. 2. All the cells in a multicellular organisms result from a single fertilized e ...
... 1. Living organisms must reproduce to continue the existence of their species. Through reproduction new individuals which resemble their parents are formed. All the organisms alive today arose from preexisting organisms. 2. All the cells in a multicellular organisms result from a single fertilized e ...
I. Organization of Living Things TISSUE CELL
... Finally, organs may work together to form an organ system. In the earthworm as well as in the most complex animal, man, the circulatory system carries food and oxygen to all parts of the body. Organs such as the heart and blood vessels work together to carry the blood and form the circulatory system ...
... Finally, organs may work together to form an organ system. In the earthworm as well as in the most complex animal, man, the circulatory system carries food and oxygen to all parts of the body. Organs such as the heart and blood vessels work together to carry the blood and form the circulatory system ...
Cells - TeacherWeb
... Cells All living things are made up of cells. They are the basic units of structure and function in all living things. ...
... Cells All living things are made up of cells. They are the basic units of structure and function in all living things. ...
100 living environment regents facts
... 25. Cleavage is the type of mitotic cell division without a change in cell size involved in embryonic development 26. During development of humans in the uterus (intrauterine development), the chorion, amnion, and placenta are necessary to maintain homeostasis. 27. If parents with desirable characte ...
... 25. Cleavage is the type of mitotic cell division without a change in cell size involved in embryonic development 26. During development of humans in the uterus (intrauterine development), the chorion, amnion, and placenta are necessary to maintain homeostasis. 27. If parents with desirable characte ...
115 things you should know for the living environment
... sperm cell with a haploid egg cell to form a diploid cell called a zygote. 25. Cleavage is the type of mitotic cell division without a change in cell size involved in embryonic development. 26. During intrauterine development in humans, the chorion, amnion, and placenta are necessary to maintain hom ...
... sperm cell with a haploid egg cell to form a diploid cell called a zygote. 25. Cleavage is the type of mitotic cell division without a change in cell size involved in embryonic development. 26. During intrauterine development in humans, the chorion, amnion, and placenta are necessary to maintain hom ...
Chapter 24
... excretory system liver, pancreas glands, hair, and dermis layer of thyroid, nails skin parathyroid urinary bladder ...
... excretory system liver, pancreas glands, hair, and dermis layer of thyroid, nails skin parathyroid urinary bladder ...
CELL
... constant component of plant cells. Next, the nuclei were also observed and recognized as such in some animal cells. •Finally, a living substance called PROTOPLASM was ...
... constant component of plant cells. Next, the nuclei were also observed and recognized as such in some animal cells. •Finally, a living substance called PROTOPLASM was ...
Animal Cells/ Cellular Function
... environment necessary to maintain life. They make predictions based on these understandings. L2.p1 Cells All organisms are composed of cells, from just one cell to many cells. Water accounts for more than two-thirds of the weight of a cell, which gives cells many of their properties. In multicellula ...
... environment necessary to maintain life. They make predictions based on these understandings. L2.p1 Cells All organisms are composed of cells, from just one cell to many cells. Water accounts for more than two-thirds of the weight of a cell, which gives cells many of their properties. In multicellula ...
Cell growth and division
... 18. What happens in the G1 phase? 19. What happens in the S phase? 20. What happens in the G2 phase? 21. Describe the two phases of cell division in eukaryotes: ...
... 18. What happens in the G1 phase? 19. What happens in the S phase? 20. What happens in the G2 phase? 21. Describe the two phases of cell division in eukaryotes: ...
Chapter Outline
... viii. Homeotic genes are highly conserved and are found in the genomes of many organisms. d. Apoptosis i. Apotosis (programmed cell death) is important in morphogenesis. ii. When a cell-death signal is received, an inhibiting protein becomes inactive, allowing a cell-death cascade to proceed. 42.3 H ...
... viii. Homeotic genes are highly conserved and are found in the genomes of many organisms. d. Apoptosis i. Apotosis (programmed cell death) is important in morphogenesis. ii. When a cell-death signal is received, an inhibiting protein becomes inactive, allowing a cell-death cascade to proceed. 42.3 H ...
Chapter 1: What is Biology
... Their experiments disproved abiogenesis Miller and Urey: recreated conditions of early earth in a lab to see if they could produce the believed 1st organic molecules ...
... Their experiments disproved abiogenesis Miller and Urey: recreated conditions of early earth in a lab to see if they could produce the believed 1st organic molecules ...
Asexual and Sexual Reproduction
... results in two daughter cells from a single parent cell. • The daughter cells are identical to each other and to the parent cell. • It is asexual reproduction. ...
... results in two daughter cells from a single parent cell. • The daughter cells are identical to each other and to the parent cell. • It is asexual reproduction. ...
functions of the circulatory system
... FUNCTIONS OF THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM The circulatory system has seven major functions: ...
... FUNCTIONS OF THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM The circulatory system has seven major functions: ...
Name Period ______ Date ______ Mrs. Levin Review Questions 1
... 15. What is the smallest unit of life? ____________________the cell___ ...
... 15. What is the smallest unit of life? ____________________the cell___ ...
Mader/Biology, 11/e – Chapter Outline
... e. Prevention of polyspermy depends on changes in the egg plasma membrane when the sperm touches the egg and depolarizes the egg plasma membrane; this is called “fast block.” f. Vesicles in the egg called cortical granules secrete enzymes that turn the zona pellucida, forming an impenetrable fertili ...
... e. Prevention of polyspermy depends on changes in the egg plasma membrane when the sperm touches the egg and depolarizes the egg plasma membrane; this is called “fast block.” f. Vesicles in the egg called cortical granules secrete enzymes that turn the zona pellucida, forming an impenetrable fertili ...
MIGORI SUB COUNTY JOINT EVALUATION EXAM BIOLOGY 231/1
... Deals with inheritance of genetically acquired characteristics States that characteristcs ...
... Deals with inheritance of genetically acquired characteristics States that characteristcs ...
meiosis - TeacherWeb
... Remember, meiosis only occurs in the _______________ to produce gametes The disadvantage of ASEXUAL reproduction is that there is _____ variation SEXUAL reproduction, however, relies on genetic contributions from __________ parents (instead of just one) There is also variation in the gametes pro ...
... Remember, meiosis only occurs in the _______________ to produce gametes The disadvantage of ASEXUAL reproduction is that there is _____ variation SEXUAL reproduction, however, relies on genetic contributions from __________ parents (instead of just one) There is also variation in the gametes pro ...
Reproduction Unit Review
... 13. How is the zygote, produced by sexual reproduction, different from daughter cells, produced by asexual reproduction? 14. List 5 types of asexual reproduction. Briefly explain each type. 15. Identify the type of asexual reproduction in each of the following situation; a) Multicellular algae is st ...
... 13. How is the zygote, produced by sexual reproduction, different from daughter cells, produced by asexual reproduction? 14. List 5 types of asexual reproduction. Briefly explain each type. 15. Identify the type of asexual reproduction in each of the following situation; a) Multicellular algae is st ...
Science NIOS - WordPress.com
... Centrosome(in animal cells only):It is located near the nucleus and contains 1 or 2 centrioles. • It initiates and regulates cell division. Plastids(in plant cells only):These are of various shapes – oval, spherical or disc-like. The most common ones are chloroplasts that contain chlorophyll Parts o ...
... Centrosome(in animal cells only):It is located near the nucleus and contains 1 or 2 centrioles. • It initiates and regulates cell division. Plastids(in plant cells only):These are of various shapes – oval, spherical or disc-like. The most common ones are chloroplasts that contain chlorophyll Parts o ...
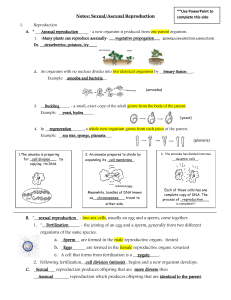
B. *__sexual reproduction_ - two sex cells, usually an egg and a
... 1. *__Fertilization_____ - the joining of an egg and a sperm, generally from two different organisms of the same species. a. _Sperm__ are formed in the male reproductive organs. (testes) b. _Eggs______ are formed in the female reproductive organs. (ovaries) c. A cell that forms from fertilization is ...
... 1. *__Fertilization_____ - the joining of an egg and a sperm, generally from two different organisms of the same species. a. _Sperm__ are formed in the male reproductive organs. (testes) b. _Eggs______ are formed in the female reproductive organs. (ovaries) c. A cell that forms from fertilization is ...
Developmental biology

Developmental biology is the study of the process by which animals and plants grow and develop, and is synonymous with ontogeny. In animals most development occurs in embryonic life, but it is also found in regeneration, asexual reproduction and metamorphosis, and in the growth and differentiation of stem cells in the adult organism. In plants, development occurs in embryos, during vegetative reproduction, and in the normal outgrowth of roots, shoots and flowers.Practical outcomes from the study of animal developmental biology have included in vitro fertilization, now widely used in fertility treatment, the understanding of risks from substances that can damage the fetus (teratogens), and the creation of various animal models for human disease which are useful in research. Developmental Biology has also help to generate modern stem cell biology which promises a number of important practical benefits for human health.Many of the processes of development are now well understood, and some major textbooks of the subject are