File
... To make ATP energy, water, and carbon dioxide waste Golgi bodies – modifies and packages proteins and lipids; gets them ready for export so they can move to where they n To go in order to carry out their function Lysosome – vesicle that contains digestive enzymes ...
... To make ATP energy, water, and carbon dioxide waste Golgi bodies – modifies and packages proteins and lipids; gets them ready for export so they can move to where they n To go in order to carry out their function Lysosome – vesicle that contains digestive enzymes ...
A-3 Notes
... produced and then attaches itself to the outside of the organism. When it is completely developed, it detaches itself and becomes its own organism. Some buds may remain attached to each other and form a superorganism: a collection of organisms which act together as a single organism. ...
... produced and then attaches itself to the outside of the organism. When it is completely developed, it detaches itself and becomes its own organism. Some buds may remain attached to each other and form a superorganism: a collection of organisms which act together as a single organism. ...
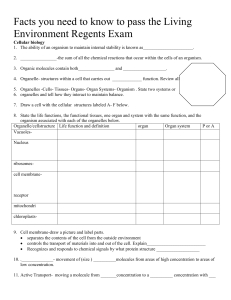
Facts you need to know to pass the Living
... prompts glucose to move from the blood into body cells, resulting in a lower glucose level in the blood. Another hormone secreted by the pancreas works in the opposite way. When the glucose level in the blood is too low, this hormone prompts the release of ____________. 26.___________ is caused by c ...
... prompts glucose to move from the blood into body cells, resulting in a lower glucose level in the blood. Another hormone secreted by the pancreas works in the opposite way. When the glucose level in the blood is too low, this hormone prompts the release of ____________. 26.___________ is caused by c ...
Cell Specialisation - NCEA Level 2 Biology
... 1. What are the beating hairs for movement of a unicellular organism called? Cilia 2. What organism uses these? Paramecium 3. These structures also help with feeding by moving food into a specialised area, what is this called? Cilia 4. Amoeba use extensions of the flexible cell membrane to move, wha ...
... 1. What are the beating hairs for movement of a unicellular organism called? Cilia 2. What organism uses these? Paramecium 3. These structures also help with feeding by moving food into a specialised area, what is this called? Cilia 4. Amoeba use extensions of the flexible cell membrane to move, wha ...
AP Exam Additional Content Information
... - Oogenesis: formation of eggs; stars in embryonic development and doesn’t finish for each egg until that egg matures during a menstrual cycle (hence, an egg could wait 40 years to finish maturation) - Meiosis II: oocytes undergo this process only after fertilization by a sperm in the oviduct - Sper ...
... - Oogenesis: formation of eggs; stars in embryonic development and doesn’t finish for each egg until that egg matures during a menstrual cycle (hence, an egg could wait 40 years to finish maturation) - Meiosis II: oocytes undergo this process only after fertilization by a sperm in the oviduct - Sper ...
Cell: basic unit of structure and function of life. Prokaryotic: cells that
... Mitochondria: use oxygen to transfer energy in food to a form that the cell can use to carry out its activities. Endoplasmic reticulum: produce important products for the cell, including proteins and lipids. Golgi bodies: Help package products from the endoplasmic reticulum and distribute them aroun ...
... Mitochondria: use oxygen to transfer energy in food to a form that the cell can use to carry out its activities. Endoplasmic reticulum: produce important products for the cell, including proteins and lipids. Golgi bodies: Help package products from the endoplasmic reticulum and distribute them aroun ...
PDQ1
... 3. Why are certain cellular structures unable to be observed with a light microscope? 4. How does the ratio of a cell’s surface area to volume place upward and downward limits on cell size? 5. How do organelles allow for increased complexity in cells? 6. Provide four examples of cell tasks that are ...
... 3. Why are certain cellular structures unable to be observed with a light microscope? 4. How does the ratio of a cell’s surface area to volume place upward and downward limits on cell size? 5. How do organelles allow for increased complexity in cells? 6. Provide four examples of cell tasks that are ...
Biology_Review_2012
... 26. During ____________________ the nucleus of the cell divides 27. Water moves through a cell membrane by a process called __________________________ 28. _________________________ is the longest stage of cell division 29. A ______________________ is a test in which a sample of living cells is remov ...
... 26. During ____________________ the nucleus of the cell divides 27. Water moves through a cell membrane by a process called __________________________ 28. _________________________ is the longest stage of cell division 29. A ______________________ is a test in which a sample of living cells is remov ...
B2 Revision - Tonypandy Community College
... Aerobic Respiration This is using oxygen- remember 'air'obic. It's the most efficient way to release energy from glucose. Glucose + Oxygen -> Carbon Dioxoide + Water (+ Energy) Anaerobic Respiration This is without oxygen when there is not enough available. It's not the most efficient way. Glucose - ...
... Aerobic Respiration This is using oxygen- remember 'air'obic. It's the most efficient way to release energy from glucose. Glucose + Oxygen -> Carbon Dioxoide + Water (+ Energy) Anaerobic Respiration This is without oxygen when there is not enough available. It's not the most efficient way. Glucose - ...
Unit C Section Review
... Unit C: Biology (Cycling of Matter in Living Systems) – Assignment Answer Key Section Review Questions #1 – 5, 7, 8, 10 – 12, 14 – 22 1. The benefits of being multicellular are that different functions can be performed by specialized groups of cells. Each cell is not responsible for carrying out all ...
... Unit C: Biology (Cycling of Matter in Living Systems) – Assignment Answer Key Section Review Questions #1 – 5, 7, 8, 10 – 12, 14 – 22 1. The benefits of being multicellular are that different functions can be performed by specialized groups of cells. Each cell is not responsible for carrying out all ...
Laboratory Exercise 20: Embryology and Fetology
... As the embryo passes its 8th week, it is called a fetus. The placenta becomes fully functional by this time. The placenta, a vascular organ formed by the chorion, the embryonic part of the placenta and the decidua basalis, the maternal part of the placenta. The decidua basalis is the endometrium of ...
... As the embryo passes its 8th week, it is called a fetus. The placenta becomes fully functional by this time. The placenta, a vascular organ formed by the chorion, the embryonic part of the placenta and the decidua basalis, the maternal part of the placenta. The decidua basalis is the endometrium of ...
Name_________________________________ Thompson 211
... The invader first finds refuge in Holly’s nose. The hairs in her nose are the first line of defense Influenza B is one of the more common viruses. It needs to hijack a special cell in her throat. Winding nasal passages are designed to trap invaders. The virus cell then takes advantage of how human c ...
... The invader first finds refuge in Holly’s nose. The hairs in her nose are the first line of defense Influenza B is one of the more common viruses. It needs to hijack a special cell in her throat. Winding nasal passages are designed to trap invaders. The virus cell then takes advantage of how human c ...
Anatomia I - univr dsnm
... molecules, enzymes and proteins involved in contraction of the muscle fiber. The muscle fiber types and their characteristics, the growth of muscle mass related to training, the function of satellite cells, the function of myostatin and its inhibitors. ...
... molecules, enzymes and proteins involved in contraction of the muscle fiber. The muscle fiber types and their characteristics, the growth of muscle mass related to training, the function of satellite cells, the function of myostatin and its inhibitors. ...
Semester Review
... A trait that will only show up in the phenotype if two recessive traits exist in the genotype (tt) Heredity The passing of genetic material from parents to offspring Genotype The combination of genes for one or more specific traits Phenotype How the trait shows out in the organism. The physical appe ...
... A trait that will only show up in the phenotype if two recessive traits exist in the genotype (tt) Heredity The passing of genetic material from parents to offspring Genotype The combination of genes for one or more specific traits Phenotype How the trait shows out in the organism. The physical appe ...
TAKS Obj 2 -BIOLOGY
... In order to raise it, it must be attached, so its not 1 or 2. 4 is a bone not a muscle, so its answer: ...
... In order to raise it, it must be attached, so its not 1 or 2. 4 is a bone not a muscle, so its answer: ...
Facts you need to know to pass the Living Environment
... glucose to move from the blood into body cells, resulting in a lower glucose level in the blood. Another hormone secreted by the pancreas works in the opposite way. When the glucose level in the blood is too low, this hormone prompts the release of glucose stored in the ___________. 25.___________ i ...
... glucose to move from the blood into body cells, resulting in a lower glucose level in the blood. Another hormone secreted by the pancreas works in the opposite way. When the glucose level in the blood is too low, this hormone prompts the release of glucose stored in the ___________. 25.___________ i ...
Cells - Dr Magrann
... 30) What is the function of cell surfaces? 31) What do plant cell walls consist of? 32) The cell wall of one plant cell is separated from the cell wall of another by what? 33) Are plant cell walls one layer thick or more than ...
... 30) What is the function of cell surfaces? 31) What do plant cell walls consist of? 32) The cell wall of one plant cell is separated from the cell wall of another by what? 33) Are plant cell walls one layer thick or more than ...
List and tell the function of the parts of a cell
... 28. List and explain the 4 types of asexual reproduction. a. Budding – exact replica, but smaller at first b. Binary fission sometimes called fragmentation – exact replica, equal sizes c. Regeneration – usually involves growing new body parts to replace damaged ones (starfish) but can be used for re ...
... 28. List and explain the 4 types of asexual reproduction. a. Budding – exact replica, but smaller at first b. Binary fission sometimes called fragmentation – exact replica, equal sizes c. Regeneration – usually involves growing new body parts to replace damaged ones (starfish) but can be used for re ...
plants - Images
... Characteristics: • Eukaryotic, multicellular, heterotrophic, ingest food, specialized cells ...
... Characteristics: • Eukaryotic, multicellular, heterotrophic, ingest food, specialized cells ...
Strand A - Life Processes and Living Things
... stomach, or brain; in some plants, the root or flower). In complex organisms, organs work together in a system (recall, for example, from earlier studies of the human body, the digestive, circulatory, and respiratory systems). Plant Structures and Processes Structure: Vascular and Non Vascular Pla ...
... stomach, or brain; in some plants, the root or flower). In complex organisms, organs work together in a system (recall, for example, from earlier studies of the human body, the digestive, circulatory, and respiratory systems). Plant Structures and Processes Structure: Vascular and Non Vascular Pla ...
Section 4- Microscopes, Cells and Reproduction: Summary Sheets
... The new cells (often called daughter cells) contain exact copies of the genetic information found in the parent cell. New cells are required for growth (e.g. embryo to baby or child to adult) and also for repair e.g. skin damaged by a burn or fall. ...
... The new cells (often called daughter cells) contain exact copies of the genetic information found in the parent cell. New cells are required for growth (e.g. embryo to baby or child to adult) and also for repair e.g. skin damaged by a burn or fall. ...
Cell Specialization and Organization
... Cells: The smallest unit of life capable of carrying on life's functions Tissues: A group of similar cells that work together to perform a specific function Organs: Consists of different kinds of tissues that function ...
... Cells: The smallest unit of life capable of carrying on life's functions Tissues: A group of similar cells that work together to perform a specific function Organs: Consists of different kinds of tissues that function ...
Tissues, Organs, Systems Review 2013
... 10. Draw the stages of mitosis in animal and plant cells. Use these diagrams to compare mitosis in plant and animal cells. Identify differences between animal and plant cell mitosis. 11. In what type of climate would you be likely to find a plant with a very thick cuticle around its leaves and stem? ...
... 10. Draw the stages of mitosis in animal and plant cells. Use these diagrams to compare mitosis in plant and animal cells. Identify differences between animal and plant cell mitosis. 11. In what type of climate would you be likely to find a plant with a very thick cuticle around its leaves and stem? ...
Developmental biology

Developmental biology is the study of the process by which animals and plants grow and develop, and is synonymous with ontogeny. In animals most development occurs in embryonic life, but it is also found in regeneration, asexual reproduction and metamorphosis, and in the growth and differentiation of stem cells in the adult organism. In plants, development occurs in embryos, during vegetative reproduction, and in the normal outgrowth of roots, shoots and flowers.Practical outcomes from the study of animal developmental biology have included in vitro fertilization, now widely used in fertility treatment, the understanding of risks from substances that can damage the fetus (teratogens), and the creation of various animal models for human disease which are useful in research. Developmental Biology has also help to generate modern stem cell biology which promises a number of important practical benefits for human health.Many of the processes of development are now well understood, and some major textbooks of the subject are