* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cell Specialization and Organization
Embryonic stem cell wikipedia , lookup
Artificial cell wikipedia , lookup
Cell (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Induced pluripotent stem cell wikipedia , lookup
Dictyostelium discoideum wikipedia , lookup
Hematopoietic stem cell wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Chimera (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Human embryogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Neuronal lineage marker wikipedia , lookup
Microbial cooperation wikipedia , lookup
State switching wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Adoptive cell transfer wikipedia , lookup
Cell theory wikipedia , lookup
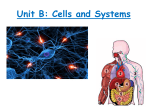
September 17, 2012 The Cell Theory states the following: zation i l a i c pe Cell S and tion a z i n Orga Organization of Living Things Vocab Cells: The smallest unit of life capable of carrying on life's functions Tissues: A group of similar cells that work together to perform a specific function Organs: Consists of different kinds of tissues that function together Organ Systems: A group of organs that work together to perform a major function Organism: A living thing. This type of cell is found all over the body, usually under the skin. We were born with the same number of this kind of cell as we have now. This cell's function is storage. When we exercise and eat healthy foods the storage gets depleted. When we don't exercise and we eat what we want these cells get bigger. What type of cells are shown? 1. All living things are composed of cells. 2. Cells are the basic units of structure and function in living things. 3. All cells are produced from other cells. CELLS: Plants and animals are made of cells. Cells form the basic "building blocks" for living things. Some cells have specialized functions. Let's look at various human cells. This type of human cell has long structures that connect to other's of it's kind. This cell's function is communication. What type of cell is this? What purpose do these long structures have? September 17, 2012 This cell's function is to carry oxygen, waste and nutrients throughout the body. It is circular to fit through a circular tube. What type of cell is it? EX S ' LET L E OR ! This cell's job is to destroy invading organisms. It also removes dead or damaged cells. What type of cell is shown? September 17, 2012 Why do cells have different sizes and shapes? CELLS: Plants and animals are made of cells. Cells form the basic "building blocks" for living things. Some cells have specialized functions. TISSUES: A GROUP OF SIMILAR CELLS WORKING TOGETHER TO PERFORM A SPECIFIC FUNCTION Muscle Tissue Connective Tissue Nervous Tissue Epithelial Tissue September 17, 2012 ORGANS: Consists of different kinds of tissues that function together Brain The brain consists of nervous tissue, as well as connective tissue that supports and protects. ORGANISM: Any living thing that is made up of cells and performs the 7 functions of life. Let's Review with Legos! From Cells to Systems BBC video clip: http://www.bbc.co.uk/schools/ks3bitesize/science/organisms_behaviour_health/cells_systems/ activity.shtml ORGAN SYSTEMS: A group of organs that work together to perform a major function. The Nervous System Consists of the brain, spinal cord and nerves throughout the body. It directs the body's activities and processes. Organization of Living Things Cells make tissues, tissues make organs, organs make systems, systems make the organism. Chris Thinks Of Spaghetti Often