* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Reproduction Unit Review
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
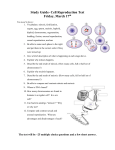
Science 9 Exam Review Package: Reproduction Name: ________________________________ Miss Slipp 1. List the parts of the animal and plant cell. (Know what each of these parts do and be able to label them on a diagram.) 2. What is the function of a) The cell membrane of a cell? b) The cytoplasm? 3. Where is the genetic information found in the cell? 4. How does the structure of a plant cell differ from that of an animal cell? 5. Why is cell division important? 6. Describe the cell cycle (mitosis). 7. What is interphase? 8. Why does the genetic material need to be duplicated during the cell cycle? 9. After mitosis, how do the daughter cells compare to the mother cell? 10. List and describe the 4 phases of mitosis. 11. A somatic human cell has 46 chromosomes. After the cell has undergone mitosis, how many chromosomes would you expect to find in each cell? 12. How is asexual reproduction different from sexual reproduction? 13. How is the zygote, produced by sexual reproduction, different from daughter cells, produced by asexual reproduction? 14. List 5 types of asexual reproduction. Briefly explain each type. 15. Identify the type of asexual reproduction in each of the following situation; a) Multicellular algae is struck by a wave. The algae breaks up and each new piece grew into a new organism. b) A new tree starts to grow from the root of a nearby tree. c) A small cell begins to grow on the outside of another cell. Eventually, it breaks away from the larger cell and continues to grow. 16. What advantages does an organism have when it reproduced asexually? What disadvantages does it have? 17. What advantages does an organism have when it reproduced sexually? What disadvantages does it have? 18. What does DNA stand for? What does DNA do? 19. What are the 4 nitrogen bases that make up DNA? 20. What molecules make up the sides of the DNA strands? 21. Why are organisms so different if all living organisms are made up of the same 4 bases? 22. What is cancer? 23. What are carcinogens? List the 3 types of carcinogens. 24. What is a mutation? 25. How do cancer cells differ from other cells? 26. List and describe 3 types of sexual reproduction. 27. What is a zygote? 28. Explain external and internal fertilization. 29. In terms of chromosomes, how do female mammals differ from male mammals? 30. A muscle cell from a mouse has 22 chromosomes. How many chromosomes would you expect in: a) An unfertilized egg cell? b) A zygote? c) A brain cell? d) A sperm cell? 31. What are somatic cells? What are reproductive cells? 32. What are homologous chromosomes? Science 9 Exam Review Package: Reproduction Name: ________________________________ Miss Slipp 33. Why is meiosis necessary? 34. What is a diploid chromosome number? What is a haploid chromosome number? 35. Name the male and female sex cells of the flower. Name the male and female parts of the flower. 36. What is pollination? How is fruit formed? 37. What is nondisjunction? In what stage does nondisjunction occur? 38. If a zygote has 45 chromosomes, how many chromosomes would you expect to find in nerve cells as they develop? Why? 39. What is genetic screening? In what type of chart are chromosomes arranged in to help determine if a fetus has a genetic disorder? 40. Do a Venn diagram comparing meiosis and mitosis.