* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download meiosis - TeacherWeb
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
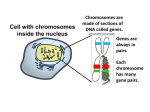
MITOSIS & ASEXUAL REPRODUCTION Reproduction – NOT essential to survival of an individual, BUT is essential to survival of the _______________ 2 Types of Reproduction a) Asexual – only ____ parent NO fusion of _______________ (sex cells) b) Sexual – involves ____ parents Fusion of gametes occurs to produce a new individual ASEXUAL REPRODUCTION Asexual reproduction is an example of ______ _______________ Cell division has 2 parts a) _______________ = the dividing of a _______________ to form ____ daughter nuclei (nuclear division) Involves separation of the hereditary material (______) b) _______________ = the division of the _______________ into 2 parts _______________ = the period “_______________” cell divisions The ________ replicates at this time --- The 2 identical strands of DNA are called _______________ chromatids The sister chromatids are held together at the _______________ MITOSIS is made up of 4 stages: 1) _______________ Chromatin _______________ and becomes visible as distinct rods --- These rods are called _______________ The 2 pairs of _______________ begin to separate --- But, the centrioles remain connected to each other by fine protein threads called _______________ _______________ (made up of microtubules) The _______________ disappears The _______________ membrane disappears 2) _______________ The 2 centrioles have moved toward opposite __________ (ends) of the cell Sister chromatids line up along the _______________ (equator) of the cell The microtubules of some _______________ fibers attach to the _______________ of various sister chromatids 3) _______________ All the _______________ divide The _______________ chromatids are PULLED, by the spindle fibers, toward opposite poles --- Each doubled chromosome is therefore split into ____ chromosomes Cytokinesis begins – the ______ _______________ begins to pinch inward 4) _______________ The chromosomes uncoil & elongate, forming _______________ Spindle fibers disappear A new _______________ membrane forms around each set of chromosomes The _______________ reappears Cytokinesis is complete, resulting in 2 _______________ ____________ (each of which is IDENTICAL to the original parent cell) Cell Division in PLANTS Plant cells lack _______________, BUT spindle fibers do form Plant cells have rigid ________ ________ and therefore cannot “pinch in half” like animal cells do --- Instead, a ________ __________ forms between the 2 daughter cells Results of Mitosis a) The chromosome number is retained from generation to generation --- This is due to __________________ of the DNA b) Each daughter cell receives an exact _______________ of the chromosomes present in the _______________ cell Cancer = _______________ cell division Methods of Asexual Reproduction 1) Binary Fission – when a one-celled organism undergoes cell division to form ____ one-celled organisms The 2 _______________ cells are exactly the same as the parent cell Ex. Bacteria, protozoa, algae Ex. Amoeba Nucleus & cytoplasm divide _______________ 2) Budding – a new individual develops as an _______________ of an older one The nucleus divides evenly (like in binary fission), BUT the _______________ does not Buds are therefore much _______________ Ex. Yeast (also reproduces sexually) Ex. Hydra (also reproduces sexually) 3) Sporulation – ____________ = asexually-formed cells with a protective outer covering to prevent _______________ out Ex. Fungi, algae, protozoa Ex. Bread mold (also reproduces sexually) 4) Regeneration = growing back of _______________ parts Invertebrates have more ______________________ (unspecialized) cells than vertebrates do They have a greater ability to regenerate Ex. Planaria, starfish, hydra, earthworm, snails, slugs 5) __________________ __________________ (Reproduction) Plants have 3 major vegetative structures that can give rise to a new plant ROOTS, STEMS & LEAVES A _______________ is a sexual reproductive structure that produces seeds Vegetative propagation = growth of a new plant from the root, stem, or leaf of a plant (via _______________ reproduction) 2 Types a) _______________ Vegetative Propagation Bulbs, Tubers & Runners b) _______________ Vegetative Propagation Cutting & Grafting Advantages of Vegetative Propagation NO _______________ (unlike with plants grown from seeds) ____________ It’s faster to graft than to start from a seed Formation of _______________ fruit MEIOSIS & SEXUAL REPRODUCTION MEIOSIS Occurs ONLY in the _______________ (sex glands) to produce _______________ (egg & sperm) --- Male gonads = _______________ --- Female gonads = _______________ Known as “reduction division” because each gamete produced by meiosis has _______________ the normal # of chromosomes --- Therefore, in sexually reproducing organisms, meiosis followed by __________________ maintains the _______________ number In HUMANS there are 46 chromosomes (called the _____ or diploid #) --- All ____________ cells have the diploid # of chromosomes The haploid # (____) is found ONLY in egg & sperm cells (gametes) Meiosis involves ____ CELL DIVISIONS: The following example is a cell with 6 chromosomes (3 chromosome pairs) 1. Primary sex cell of ovary or testis (2n = 6 in this case) Replication of each chromosome occurs Each chromosome is _______________ (2 chromatids) 2. The doubled chromosomes line up at the center (equator) in _______________ _______________ Each chromosome of a homologous pair has similar genetic content (DNA) There are ____ chromatids for each type of chromosome This is called a _______________ During the FIRST cell division, homologous pairs _______________ & are pulled toward opposite poles 3. ____ cells result from the 1st division Each chromosome is still connected to its sister chromatid 4. EACH cell in Step 3 undergoes a SECOND cell division The _______________ chromatids now separate & move toward opposite poles Each of the resulting 4 cells has the _______________ (n) number of chromosomes MITOSIS produces cells with the normal _______________ # of chromosomes (2n) WHILE MEIOSIS produces cells with the ______________ # (n) Remember, meiosis only occurs in the _______________ to produce gametes The disadvantage of ASEXUAL reproduction is that there is _____ variation SEXUAL reproduction, however, relies on genetic contributions from __________ parents (instead of just one) There is also variation in the gametes produced by each parent since “_______________ _______________” can occur during Meiosis I Variation allows a population, as a whole, to __________________ to a changing environment What is this called??? 2 Types of Sexual Reproduction __________________ = the _______________ of genetic material (DNA) between 2 different _______________ types of the same species Ex. Paramecium, spirogyra, bacteria __________________ = egg + sperm _______________ --- Fertilization occurs when the _______________ of an egg & sperm fuse, producing a zygote (= a single _______________ cell) --- Millions of sperm are attracted to an egg, but only ____ can fertilize it 2 Types of Fertilization a) External = gametes fuse _______________ the body of the female Occurs in many _______________ animals (fish, amphibians) Since the eggs have less chance of being fertilized, ____________ are produced b) Internal = gametes fuse _______________ the moist reproductive tract of the female Occurs in most ____________ animals (reptiles, birds , mammals) FEWER eggs are produced because they are well _____________ & have a greater chance of being fertilized Most animals have separate sexes (male & female), however… --- ____________________ = organisms that have both _______________ & _______________ --- Usually do NOT self-fertilize Ex. Hydra, earthworm, snails ____________________ = the development of an egg _______________ fertilization by sperm Ex. Insects (bees, wasps, ants, aphids), some lizards & snakes The queen honeybee lays both fertilized & unfertilized eggs The fertilized ones become _______________ & the unfertilized ones become ______________ ____________________ = the production of gametes (by _____________) ____________________ = production of sperm in the _______________ Cytoplasmic division is _______________ & each primary sperm cell produces ____ sperm cells, ALL of which are functional ____________________ = production of eggs in the _______________ Cytoplasmic division is _______________ Each primary egg cell produces 1 functional egg & ____ nonfunctional ____________ bodies (smaller) Disintegrate Human females are born with ALL the primary egg cells they will ever have