Cells and Systems Notes
... have much oxygen Arteries – Arteries carry blood away from the heart. Arteries carry bright red blood that is high in oxygen Blood – Carries food and oxygen to cells as well as carrying wastes away from cells. Blood also carries disease fighting white blood cells through the body. ...
... have much oxygen Arteries – Arteries carry blood away from the heart. Arteries carry bright red blood that is high in oxygen Blood – Carries food and oxygen to cells as well as carrying wastes away from cells. Blood also carries disease fighting white blood cells through the body. ...
8838083
... the throat. Normally, in children, it forms a soft mound in the roof and posterior wall of the nasopharynx, just above and behind the uvula. Often adenoids A mass of lymphoid tissue located at the back of the nose in the upper partof the throat, normally present only in children, that when infected ...
... the throat. Normally, in children, it forms a soft mound in the roof and posterior wall of the nasopharynx, just above and behind the uvula. Often adenoids A mass of lymphoid tissue located at the back of the nose in the upper partof the throat, normally present only in children, that when infected ...
Overview of Anatomy Slides
... Connective Tissue gives shape to organs and holds them together. It is made out of cells like bone and cartilage. ...
... Connective Tissue gives shape to organs and holds them together. It is made out of cells like bone and cartilage. ...
Cells - College of Science | Oregon State University
... since many cells are quite small after mitosis. There are cells found throughout the body that can grow quite large if a human consumes an excess of calories. These are __________ (or adipose) cells. 4. Most cells have a finite life span, and are genetically programmed to die at a specific time. Thi ...
... since many cells are quite small after mitosis. There are cells found throughout the body that can grow quite large if a human consumes an excess of calories. These are __________ (or adipose) cells. 4. Most cells have a finite life span, and are genetically programmed to die at a specific time. Thi ...
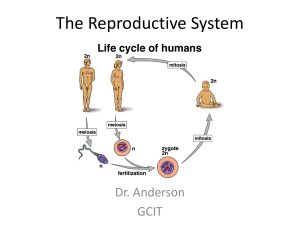
The Reproductive System
... • At least four (probably more) of these are known to be associated with cervical cancer ...
... • At least four (probably more) of these are known to be associated with cervical cancer ...
What is the Digestive System?
... Circulatory Systems in this unit – that’s it!! It’s going to be wonderful ...
... Circulatory Systems in this unit – that’s it!! It’s going to be wonderful ...
Structural levels of organization:
... body has many levels of organization simplest level is the chemical level (study on your own in ch.2) Atoms o Tiny building blocks come together to form molecules o come together to form cells o smallest unit of living things o basic structure of all living things cellular level examined in chapter ...
... body has many levels of organization simplest level is the chemical level (study on your own in ch.2) Atoms o Tiny building blocks come together to form molecules o come together to form cells o smallest unit of living things o basic structure of all living things cellular level examined in chapter ...
The Cell The Discovery of the Cell The Discovery of
... within the cell. – Organelles are specialized organs that have different roles within the cell. – The Eukaryotic cell is generally broken down into two parts: • Nucleus • Cytoplasm The Nora School 955 Sligo Avenue Silver Spring, Maryland 20910 ...
... within the cell. – Organelles are specialized organs that have different roles within the cell. – The Eukaryotic cell is generally broken down into two parts: • Nucleus • Cytoplasm The Nora School 955 Sligo Avenue Silver Spring, Maryland 20910 ...
cells - AHS
... Cells come only from other cells (Biogenesis) Before this, spontaneous generation was the accepted idea Hey…Mice are always coming out of the hay! ...
... Cells come only from other cells (Biogenesis) Before this, spontaneous generation was the accepted idea Hey…Mice are always coming out of the hay! ...
Chapter Review
... Sample answer: Alveoli are tiny sacs whose function is to contain and exchange gases such as oxygen and carbon dioxide. The structure of alveoli, as tiny sacs surrounded by tiny blood vessels, includes the cells that make up the tissue of the alveoli and the tissue that joins the alveoli to the bron ...
... Sample answer: Alveoli are tiny sacs whose function is to contain and exchange gases such as oxygen and carbon dioxide. The structure of alveoli, as tiny sacs surrounded by tiny blood vessels, includes the cells that make up the tissue of the alveoli and the tissue that joins the alveoli to the bron ...
Respiratory and Excretory Systems
... Lungs are a respiratory organ because they take in oxygen and an excretory organ because they get rid of carbon dioxide ...
... Lungs are a respiratory organ because they take in oxygen and an excretory organ because they get rid of carbon dioxide ...
Kingdom Animalia
... Asexually – fission – when damaged, regenerates new body parts. Proglottids – found in tapeworms – each is shed off individually. ...
... Asexually – fission – when damaged, regenerates new body parts. Proglottids – found in tapeworms – each is shed off individually. ...
Body Systems
... for the body providing its shape • Protection for internal organs • Blood cell production • Made in red bone marrow • Stores calcium and phosphorous ...
... for the body providing its shape • Protection for internal organs • Blood cell production • Made in red bone marrow • Stores calcium and phosphorous ...
Anatomy Systems summary
... organ systems. • A cell is the basic unit of structure and function in living things. Specialized cells are suited to perform a particular function. • Groups of similar cells work together to form tissues. • Groups of tissues that work together to perform complex functions are called organs. • Organ ...
... organ systems. • A cell is the basic unit of structure and function in living things. Specialized cells are suited to perform a particular function. • Groups of similar cells work together to form tissues. • Groups of tissues that work together to perform complex functions are called organs. • Organ ...
Bone - Baldwin Schools Teachers
... Striated complex mesh involuntary …reacts quickly… never tires ...
... Striated complex mesh involuntary …reacts quickly… never tires ...
Grade 8 Science Cells and Systems
... Include: all living things are composed of one or more cells; cells are the basic unit of structure and function of any organism; all cells come from pre-existing cells; the activity of an organism as a whole depends on the total activity of all its cells ...
... Include: all living things are composed of one or more cells; cells are the basic unit of structure and function of any organism; all cells come from pre-existing cells; the activity of an organism as a whole depends on the total activity of all its cells ...
Cell
... any type of cell, it is not specialised • All animal cells originate from embryo stem cells. During the development of an embryo, most of these cells become specialised. They cannot later change to become a different type of cell. This process is called cell differentiation. • Adult stem cells can g ...
... any type of cell, it is not specialised • All animal cells originate from embryo stem cells. During the development of an embryo, most of these cells become specialised. They cannot later change to become a different type of cell. This process is called cell differentiation. • Adult stem cells can g ...
Chapter 21 Presentation-The Genetic Basis of Development
... encoded region is part of the protein that functions as a transcription regulator. The shape of the encoded region allows it to bind to any DNA segment, but by itself, it cannot select a specific sequence. The variable regions within the whole protein allow it to interact with other transcription ...
... encoded region is part of the protein that functions as a transcription regulator. The shape of the encoded region allows it to bind to any DNA segment, but by itself, it cannot select a specific sequence. The variable regions within the whole protein allow it to interact with other transcription ...
Snímek 1 - Hotelová škola Poděbrady
... Blood - our blood is on a 19,000 km journey per day – our body creates 100 billion red cells every day – our body has about 5.6 liters of blood. This 5.6 liters of blood circulates through the body three times every minute Cells - it takes about 20 seconds for a red blood cell to circle the whole bo ...
... Blood - our blood is on a 19,000 km journey per day – our body creates 100 billion red cells every day – our body has about 5.6 liters of blood. This 5.6 liters of blood circulates through the body three times every minute Cells - it takes about 20 seconds for a red blood cell to circle the whole bo ...
Germ cell transplantation and testicular xenografting in
... generate transgenic animals are inefficient. Introduction of a genetic change prior to fertilization will circumvent problems associated with manipulation of early embryos and nuclear reprogramming. In addition, if a genetic modification is introduced into male germline stem cells prior to transplan ...
... generate transgenic animals are inefficient. Introduction of a genetic change prior to fertilization will circumvent problems associated with manipulation of early embryos and nuclear reprogramming. In addition, if a genetic modification is introduced into male germline stem cells prior to transplan ...
What is a cell? - Epiphany Catholic School
... • controls materials moving into and out of the cell. • cytoplasm - region inside the cell that includes the fluid and all the organelles except for the nucleus. • organelle - small body in the cytoplasm • specialized to perform a specific function • DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid)- genetic material tha ...
... • controls materials moving into and out of the cell. • cytoplasm - region inside the cell that includes the fluid and all the organelles except for the nucleus. • organelle - small body in the cytoplasm • specialized to perform a specific function • DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid)- genetic material tha ...
Unit 2 - St. John Paul II Collegiate
... *Be able to identify the different types of cells Pg. 138, 139. The disadvantage of being unicellular -Unicellular organisms have to be able to move, eat, reproduce and respond to environments. Because they depend on cell membranes they can only live in watery, food rich environments. Multi-cellula ...
... *Be able to identify the different types of cells Pg. 138, 139. The disadvantage of being unicellular -Unicellular organisms have to be able to move, eat, reproduce and respond to environments. Because they depend on cell membranes they can only live in watery, food rich environments. Multi-cellula ...
Blood and Oxygen - science-teachers
... Veins carry blood back from the cells and tissues to the heart so it can be pumped into the lungs for re-oxygenation. Veins have thinner walls than arteries, which contain less elastic tissue and muscle. Veins contain one way valves which prevent blood flowing the wrong way. ...
... Veins carry blood back from the cells and tissues to the heart so it can be pumped into the lungs for re-oxygenation. Veins have thinner walls than arteries, which contain less elastic tissue and muscle. Veins contain one way valves which prevent blood flowing the wrong way. ...
Science - edl.io
... 1. What are the structures of the circulatory system? 2. What is the function of the circulatory system? 3. What is blood and why does it circulate throughout our body? 4. How do the circulatory and respiratory systems work together? ...
... 1. What are the structures of the circulatory system? 2. What is the function of the circulatory system? 3. What is blood and why does it circulate throughout our body? 4. How do the circulatory and respiratory systems work together? ...
Vocabulary for 9
... 1. cartilage- tough, flexible tissue similar to bone but is softer and less brittle. 2. joint- any place where two or more bones come together; can be movable or immovable. 3. ligament- touch band of tissue that holds bones together at joints. 4. periosteum- tough, tight-fitting membrane that conver ...
... 1. cartilage- tough, flexible tissue similar to bone but is softer and less brittle. 2. joint- any place where two or more bones come together; can be movable or immovable. 3. ligament- touch band of tissue that holds bones together at joints. 4. periosteum- tough, tight-fitting membrane that conver ...