
Unit 1 Test Review Guide: 5 pts Extra Credit on Summative Category
... Homeostasis & Feedback 14. What is homeostasis? What is one mechanism our body uses to maintain homeostasis? Explain why this mechanism is successful at maintaining homeostasis. ...
... Homeostasis & Feedback 14. What is homeostasis? What is one mechanism our body uses to maintain homeostasis? Explain why this mechanism is successful at maintaining homeostasis. ...
Tissues: Four classes Epithelium Connective Muscle Nervous
... o Composed of one cell type … the neuron o Neurons have Nucleus Several dendrites One or several axons o Normal pathway follows: Dendrite to Cell body to Axon • Produces a substance called a neurotransmitter • Allows impulse to jump o Neuron to neuron o Neuron to muscle o Neuron to gland ...
... o Composed of one cell type … the neuron o Neurons have Nucleus Several dendrites One or several axons o Normal pathway follows: Dendrite to Cell body to Axon • Produces a substance called a neurotransmitter • Allows impulse to jump o Neuron to neuron o Neuron to muscle o Neuron to gland ...
Body Systems Vocabulary
... Endocrine System – A chemical communication system that regulates many body functions Gland – A group of cells, or an organ, that secretes a chemical substance Pituitary Gland – A gland signaling other endocrine glands to produce hormones when needed Reproductive System – The organs that make possib ...
... Endocrine System – A chemical communication system that regulates many body functions Gland – A group of cells, or an organ, that secretes a chemical substance Pituitary Gland – A gland signaling other endocrine glands to produce hormones when needed Reproductive System – The organs that make possib ...
HumanBodyVocabulary
... 33. Depressant: An agent, especially a drug, that decreases the rate of vital physiological activities 34. Drug abuse: Habitual use of drugs to alter one's mood, emotion, or state of consciousness. 35. Addiction: condition of being habitually or compulsively occupied with or or involved in something ...
... 33. Depressant: An agent, especially a drug, that decreases the rate of vital physiological activities 34. Drug abuse: Habitual use of drugs to alter one's mood, emotion, or state of consciousness. 35. Addiction: condition of being habitually or compulsively occupied with or or involved in something ...
Ch 15 Notes
... • Resistance due to physiological processes of humans that are incompatible with those of the pathogen (species resistance) – Correct chemical receptors not present on human cells – Temperature and pH may be incompatible with those necessary for the pathogen’s survival • Number of pathogens for whic ...
... • Resistance due to physiological processes of humans that are incompatible with those of the pathogen (species resistance) – Correct chemical receptors not present on human cells – Temperature and pH may be incompatible with those necessary for the pathogen’s survival • Number of pathogens for whic ...
Unit IV- Nervous System
... Embryo - a fertilized egg from conception to the eighth embryonic week Fetus - A developing human from approximately eight weeks after conception until the time of its birth ...
... Embryo - a fertilized egg from conception to the eighth embryonic week Fetus - A developing human from approximately eight weeks after conception until the time of its birth ...
PowerPoint - Bryn Mawr School Faculty Web Pages
... your blood) due to their high content of the iron protein complex called hemoglobin. Hemoglobin is the molecule that allows erythrocytes to bind oxygen and carry it throughout the body. ...
... your blood) due to their high content of the iron protein complex called hemoglobin. Hemoglobin is the molecule that allows erythrocytes to bind oxygen and carry it throughout the body. ...
Human Body Systems – Level 1
... Bronchi – the two large passageways that lead from the trachea to your lungs (one for each lung) -- the bronchi are further subdivided into bronchioles -- eventually, the further subdivisions lead to tiny air sacs called alveoli -- alveoli are in clusters, like grapes -- capillaries surrounding eac ...
... Bronchi – the two large passageways that lead from the trachea to your lungs (one for each lung) -- the bronchi are further subdivided into bronchioles -- eventually, the further subdivisions lead to tiny air sacs called alveoli -- alveoli are in clusters, like grapes -- capillaries surrounding eac ...
Anatomy and Physiology Unit 1 - Organization - mics-bio2
... addition to basic process of life) 1. Special functions discussed later ( nerve cells, muscle, etc.) ...
... addition to basic process of life) 1. Special functions discussed later ( nerve cells, muscle, etc.) ...
The Tiny Living World Around Us
... • Except in cells we call them organelles • Nucleus, Golgi apparatus (Golgi body), smooth/rough endoplasmic reticulum, ribosomes, lysosomes, mitochondria, cell membrane, chloroplast in plant cells, and others • A cell is eukaryotic if it has a nucleus (plant and animal cells) • A cell is prokaryotic ...
... • Except in cells we call them organelles • Nucleus, Golgi apparatus (Golgi body), smooth/rough endoplasmic reticulum, ribosomes, lysosomes, mitochondria, cell membrane, chloroplast in plant cells, and others • A cell is eukaryotic if it has a nucleus (plant and animal cells) • A cell is prokaryotic ...
[pdf]
... program highlighted both the physical forces exerted during migration and the signaling pathways involved in the process. Celeste Nelson (Princeton University) presented results suggesting that cells migrate collectively through fibrous extracellular matrix (ECM) by exerting tensile forces at the le ...
... program highlighted both the physical forces exerted during migration and the signaling pathways involved in the process. Celeste Nelson (Princeton University) presented results suggesting that cells migrate collectively through fibrous extracellular matrix (ECM) by exerting tensile forces at the le ...
Transport Phenomena in Cell Biology - Thermal
... • Transcription networks regulate the production of proteins at longer timescales • Signaling networks process information from the environment at shorter timescales Ben-Schorr et al, Nature Genetics 31564 ...
... • Transcription networks regulate the production of proteins at longer timescales • Signaling networks process information from the environment at shorter timescales Ben-Schorr et al, Nature Genetics 31564 ...
Midterm Review: Living Environment Enzymes
... After a short period of time, you should observe the following under the microscope: ...
... After a short period of time, you should observe the following under the microscope: ...
Presentations : Cells
... Some tissues have more than one type of cell. These are called complex tissues. Heart muscle tissue: Formed by heart muscle cells, this tissue contracts and relaxes rhythmically at a steady rate. ...
... Some tissues have more than one type of cell. These are called complex tissues. Heart muscle tissue: Formed by heart muscle cells, this tissue contracts and relaxes rhythmically at a steady rate. ...
Cells Unit Study Guide
... 19. What is the cell theory? It explains the relationship between cells and living things and states that (1) all living things are composed of cells; (2) Cells are the basic units of structure and function in all living things; (3) all cells are produced from other cells (mitosis and meiosis). 20. ...
... 19. What is the cell theory? It explains the relationship between cells and living things and states that (1) all living things are composed of cells; (2) Cells are the basic units of structure and function in all living things; (3) all cells are produced from other cells (mitosis and meiosis). 20. ...
Cancer - is it merely a nutrient deficiency disease
... Cancer is the word used to describe the growth of excessive immature cells in the body, which form a lump or mass that can invade other tissue, and spread to other areas. There are several theories about causes of cancer, some causes and risk factors are known – such as UV rays inducing melanoma. So ...
... Cancer is the word used to describe the growth of excessive immature cells in the body, which form a lump or mass that can invade other tissue, and spread to other areas. There are several theories about causes of cancer, some causes and risk factors are known – such as UV rays inducing melanoma. So ...
Human Body Systems Study Guide KEY!! System Main Function
... Match systems to their function. Match organs to their systems and functions. Label organs in a diagram. Write about connections between systems. ( I will give you the systems, you tell me how they are connected.) Discuss the levels of organization and how they apply to the human body and its s ...
... Match systems to their function. Match organs to their systems and functions. Label organs in a diagram. Write about connections between systems. ( I will give you the systems, you tell me how they are connected.) Discuss the levels of organization and how they apply to the human body and its s ...
Animal Cells/ Cellular Function
... Students describe the general structure and function of cells. They can explain that all living systems are composed of cells and that organisms may be unicellular or multicellular. They understand that cells are composed of biological macromolecules and that the complex processes of the cell allow ...
... Students describe the general structure and function of cells. They can explain that all living systems are composed of cells and that organisms may be unicellular or multicellular. They understand that cells are composed of biological macromolecules and that the complex processes of the cell allow ...
Name: Standard 4.2: Grade ____/5 The Circulatory System
... 1. The heart is referred to as what of the circulatory system? Describe how the heart is divided into sections? ...
... 1. The heart is referred to as what of the circulatory system? Describe how the heart is divided into sections? ...
Glossary - The Polesworth School
... One form of a gene. Different alleles of the same gene produce slightly different characteristics, such as different eye colours. A person carrying one allele for a recessive disorder, so they do not have the disorder themselves but could pass it on to their children. An inherited disorder caused by ...
... One form of a gene. Different alleles of the same gene produce slightly different characteristics, such as different eye colours. A person carrying one allele for a recessive disorder, so they do not have the disorder themselves but could pass it on to their children. An inherited disorder caused by ...
“Open” circulatory system
... Again, any animal with a body (made of water) radius > 1 mm cannot obtain (or release) gases simply by diffusion, so you need a circulatory system and a medium in that system, i.e. blood. ...
... Again, any animal with a body (made of water) radius > 1 mm cannot obtain (or release) gases simply by diffusion, so you need a circulatory system and a medium in that system, i.e. blood. ...
Dentistry college - first class Medical biology
... The shape of the cells are highly variable , the bacterial cell could be rod , cocci or spiral shape ,the different cells in multicellular organisms are flat or sequamous as in endothelium of the artery ,cuboidal as in kidney tubules or bile ducts of the liver , columnar as in mucosa of the alimenta ...
... The shape of the cells are highly variable , the bacterial cell could be rod , cocci or spiral shape ,the different cells in multicellular organisms are flat or sequamous as in endothelium of the artery ,cuboidal as in kidney tubules or bile ducts of the liver , columnar as in mucosa of the alimenta ...






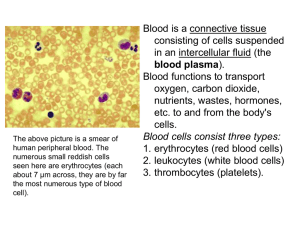



![[pdf]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008789103_1-746b7a86138a2a5bab5758b7de85a178-300x300.png)












