Organ Systems of the Body
... Organs: mouth – pharynx- esophagusstomach- small intestine – large intestine, rectum- anal canal Accessory organs – teeth, salivary glands, tongue, liver, gall bladder, pancreas, appendix ...
... Organs: mouth – pharynx- esophagusstomach- small intestine – large intestine, rectum- anal canal Accessory organs – teeth, salivary glands, tongue, liver, gall bladder, pancreas, appendix ...
Ch. 21 TheGeneticBasisofDevelopment
... As the dividing cells begin to take form, they are undergoing morphogenesis which means the “creation of form.” Morphogenetic events lay out the development very early on in development. These morphogenetic events “tell” the organism where the head and tail are, which is the front and back, and what ...
... As the dividing cells begin to take form, they are undergoing morphogenesis which means the “creation of form.” Morphogenetic events lay out the development very early on in development. These morphogenetic events “tell” the organism where the head and tail are, which is the front and back, and what ...
Organ Systems Presentation
... Function: allows the body to breathe in oxygen and breathe out carbon dioxide ...
... Function: allows the body to breathe in oxygen and breathe out carbon dioxide ...
Cells Cells are the basic units of all living things Cells are composed
... Body systemsorgans acting together to perform a function ...
... Body systemsorgans acting together to perform a function ...
Unit 2 Exam Cell Cell organelles Plant and Animal Tissue
... The cytoskeleton is an interior network to hold organelles and proteins in place, as well as keeping the cells structure. It is made of these three substances. ...
... The cytoskeleton is an interior network to hold organelles and proteins in place, as well as keeping the cells structure. It is made of these three substances. ...
Phylum Porifera
... • They are the simplest of multicellular animals. • Their bodies are an assemblage of cells embedded in a gelatinous mass and supported by a skeleton of minute needlelike spicules and proteins. • They are filter feeders that are attached to the bottom of a river or the sea. • They depend on currents ...
... • They are the simplest of multicellular animals. • Their bodies are an assemblage of cells embedded in a gelatinous mass and supported by a skeleton of minute needlelike spicules and proteins. • They are filter feeders that are attached to the bottom of a river or the sea. • They depend on currents ...
Sex Differentiation
... • Frogs, chicken, fish (zebrafish) – Develop in eggs outside the mother’s body • Mouse – Identifying the gene function using genetically modified mice – Use information from other model systems ...
... • Frogs, chicken, fish (zebrafish) – Develop in eggs outside the mother’s body • Mouse – Identifying the gene function using genetically modified mice – Use information from other model systems ...
Topic 1 - Basic Biological Principles
... – The oldest type of cell dating back to 3.5 bya – DNA is free floating in the cytoplasm – Examples include bacteria and archaea ...
... – The oldest type of cell dating back to 3.5 bya – DNA is free floating in the cytoplasm – Examples include bacteria and archaea ...
Life Science
... • All living things are composed of one or more cells • All cells come from other cells • All functions may be carried out by cells ...
... • All living things are composed of one or more cells • All cells come from other cells • All functions may be carried out by cells ...
Conditioning Cells to the Compliance of the Soft Underlying
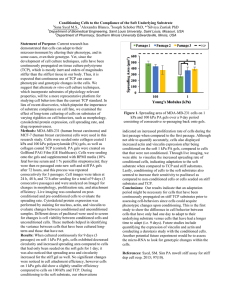
... indicated an increased proliferation rate of cells during the last passage when compared to the first passage. Although not able to quantify accurately, cells also displayed increased actin and vinculin expression after being conditioned on the soft 1 kPa PA gels, compared to cells that that were no ...
... indicated an increased proliferation rate of cells during the last passage when compared to the first passage. Although not able to quantify accurately, cells also displayed increased actin and vinculin expression after being conditioned on the soft 1 kPa PA gels, compared to cells that that were no ...
Cardiovascular System Kanwal Seireen Lemia Danya
... carries all of the oxygen, nutrients, hormones, etc to the cells and carries away all the toxins and carbon dioxide away from the cells. Cardiovascular disease is the leading cause of death in the United States. Without the cardiovascular system's functions, we would die in a matter of minutes (in f ...
... carries all of the oxygen, nutrients, hormones, etc to the cells and carries away all the toxins and carbon dioxide away from the cells. Cardiovascular disease is the leading cause of death in the United States. Without the cardiovascular system's functions, we would die in a matter of minutes (in f ...
Invertebrate Power Point Sponges to Earthworms File
... 4. Cells are organized into tissues 5. Some animals have organs and organ systems ...
... 4. Cells are organized into tissues 5. Some animals have organs and organ systems ...
Biology Final Exam Review Topic 4: The Human Body I
... Organization: The human body is made up of_________. A) All humans (and most other organisms) begin life as a __________cell. 1. The nucleus of this cell has _______the genes needed to become a complete organism. B) As cells divide, they begin to develop into specialized_________. C) As the body con ...
... Organization: The human body is made up of_________. A) All humans (and most other organisms) begin life as a __________cell. 1. The nucleus of this cell has _______the genes needed to become a complete organism. B) As cells divide, they begin to develop into specialized_________. C) As the body con ...
Animals
... • Most animals develop from a fertilized egg cell called a zygote. In animals, fertilization may be internal (inside the body) or external (outside the body). • After fertilization, the zygote of different animal species all have similar, genetically determined stages of development. • Fertilization ...
... • Most animals develop from a fertilized egg cell called a zygote. In animals, fertilization may be internal (inside the body) or external (outside the body). • After fertilization, the zygote of different animal species all have similar, genetically determined stages of development. • Fertilization ...
Stem Cells - University of California, Irvine
... products and minimize rejection of transplants • Works in rodents and large mammals (sheep, dogs) but not yet in humans • Claims of SCNT success from South Korea now completely discounted as fraudulent • Induced pluripotent stem cells largely supplant SCNT although successful cell fusion with oocyte ...
... products and minimize rejection of transplants • Works in rodents and large mammals (sheep, dogs) but not yet in humans • Claims of SCNT success from South Korea now completely discounted as fraudulent • Induced pluripotent stem cells largely supplant SCNT although successful cell fusion with oocyte ...
Respiratory system - simonbaruchcurriculum
... thin laminar blood flow and inspired air are separated only by a thin tissue layer. Gas exchange takes 0.25 seconds or 1/3 of the total transit time of a red cell. The entire blood volume of the body passes through the lungs each minute in the resting state, that is 5 liters per minute. The total su ...
... thin laminar blood flow and inspired air are separated only by a thin tissue layer. Gas exchange takes 0.25 seconds or 1/3 of the total transit time of a red cell. The entire blood volume of the body passes through the lungs each minute in the resting state, that is 5 liters per minute. The total su ...
Kingdom Animalia Notes
... cavity partly lined with mesoderm enables fast movement due to the muscles bracing themselves against the fluid-filled cavity ex: roundworms ...
... cavity partly lined with mesoderm enables fast movement due to the muscles bracing themselves against the fluid-filled cavity ex: roundworms ...
The Triploblasitc, Acoelomate Body Plan
... number of developmental stages, including two types of free-living larvae (most complex in the animal kingdom) The definitive (final) host of adult is always a vertebrate Snails are common intermediate hosts ...
... number of developmental stages, including two types of free-living larvae (most complex in the animal kingdom) The definitive (final) host of adult is always a vertebrate Snails are common intermediate hosts ...
Flash Cards
... It is in the nasal passage, consists of cells that have hair-like projections on them. These cells transmit “smell” to your brain. ...
... It is in the nasal passage, consists of cells that have hair-like projections on them. These cells transmit “smell” to your brain. ...
File
... 38 million times a year. Oven an average lifetime it will beat 2.8 billion times. A single drop of blood contains 5 million red blood cells, 5000 white blood cells, 250,000 platelets, and some proteins There are about 62,000 miles of arteries, veins, and capillaries in the body. An adult has about 1 ...
... 38 million times a year. Oven an average lifetime it will beat 2.8 billion times. A single drop of blood contains 5 million red blood cells, 5000 white blood cells, 250,000 platelets, and some proteins There are about 62,000 miles of arteries, veins, and capillaries in the body. An adult has about 1 ...
1.09_B_Aamazing Human Body Facts
... blood vessels. 14. The body produces over a quart of saliva day. It even helps heal mouth wounds. 15. Human bone has a compressive strength that is greater than reinforced concrete or marble. After all calcium is a metal! 16. An average, healthy male produces over 2 billion sperm per month. 17. A fe ...
... blood vessels. 14. The body produces over a quart of saliva day. It even helps heal mouth wounds. 15. Human bone has a compressive strength that is greater than reinforced concrete or marble. After all calcium is a metal! 16. An average, healthy male produces over 2 billion sperm per month. 17. A fe ...
E2 – Perception of Stimuli
... E.2.7 Explain how sound is perceived by the ear, including the roles of the eardrum, bones of the middle ear, oval and round windows, and the hair cells of the cochlea. ...
... E.2.7 Explain how sound is perceived by the ear, including the roles of the eardrum, bones of the middle ear, oval and round windows, and the hair cells of the cochlea. ...