TWO TYPES OF CELLS
... 1. You will be able to explain what cells are and 2. You will be able to differentiate between the 2 types of cells. ...
... 1. You will be able to explain what cells are and 2. You will be able to differentiate between the 2 types of cells. ...
What are the different types of joints?
... provide shape & support aid in movement produce red blood cells protect vital organs • Skull – brain • Ribs – heart and lungs • Vertebrae – spinal cord ...
... provide shape & support aid in movement produce red blood cells protect vital organs • Skull – brain • Ribs – heart and lungs • Vertebrae – spinal cord ...
Embryonic Development
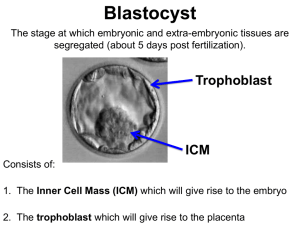
... dorsal lip is called the primary organizer of the embryo F. Pattern and position – determination is a result of a cell’s position 1.regeneration in animals (amphibians, planaria) starts with the formation at the site of injury of a blastema ( a mass of similar cells resembling each other). 2.later ...
... dorsal lip is called the primary organizer of the embryo F. Pattern and position – determination is a result of a cell’s position 1.regeneration in animals (amphibians, planaria) starts with the formation at the site of injury of a blastema ( a mass of similar cells resembling each other). 2.later ...
Lessons 8-10 Vocabulary Answers
... organ system-- a group of organs that work together to perform a complex function ex. digestive system Complete the Lesson Review questions on p. 56 1. A ...
... organ system-- a group of organs that work together to perform a complex function ex. digestive system Complete the Lesson Review questions on p. 56 1. A ...
SECOND TRIMESTER Unit Two: Human Body Systems Standards
... in end of bones produces blood cells. Yellow marrow in the middle has fat cells. B. Bone connectors 1. cartilage – rubbery tissue between bones; acts as a cushion 2. ligament – strands of tough tissue 3. joints – point at which two bones move against each other 4. tendons – connect muscle to the bon ...
... in end of bones produces blood cells. Yellow marrow in the middle has fat cells. B. Bone connectors 1. cartilage – rubbery tissue between bones; acts as a cushion 2. ligament – strands of tough tissue 3. joints – point at which two bones move against each other 4. tendons – connect muscle to the bon ...
Immunity - 1st and 2nd lines of defense
... Anti-microbial proteins Complement system ~20 proteins circulating in blood plasma attack bacterial & fungal cells ...
... Anti-microbial proteins Complement system ~20 proteins circulating in blood plasma attack bacterial & fungal cells ...
Part I: Levels of Biological Organization
... By now, you should be able to describe the basic structures and functions of a cell, but what happens when cells function or work together? A collection of cells all performing simi ...
... By now, you should be able to describe the basic structures and functions of a cell, but what happens when cells function or work together? A collection of cells all performing simi ...
Chapter 1 Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology Outline
... 1. Integumentary a. skin, sweat glands, oil glands 2. Skeletal: 206 bones and associated joints 3. Muscular ...
... 1. Integumentary a. skin, sweat glands, oil glands 2. Skeletal: 206 bones and associated joints 3. Muscular ...
The Human Body
... Smooth are found in hollow organs Involuntary muscles ex. Stomach and blood vessels Skeletal attached to bones made of fiber voluntary muscles ...
... Smooth are found in hollow organs Involuntary muscles ex. Stomach and blood vessels Skeletal attached to bones made of fiber voluntary muscles ...
Chapter 37- The Circulatory System
... Chapter 37- The Circulatory System Actually 2 Systems in 1 1. Circulatory System- composed of heart, arteries, veins, capillaries and blood 2. Lymphatic System- composed of lymph and interstial fluid, fights disease and infection Functions 1. Carry nutrients from small intestine and oxygen from lung ...
... Chapter 37- The Circulatory System Actually 2 Systems in 1 1. Circulatory System- composed of heart, arteries, veins, capillaries and blood 2. Lymphatic System- composed of lymph and interstial fluid, fights disease and infection Functions 1. Carry nutrients from small intestine and oxygen from lung ...
Student`s Name
... without being colorblind herself because a) the gene for colorblindness is recessive b) the gene for colorblindness is dominant c) colorblindness is an acquired trait d) she selected the trait for colorblindness ...
... without being colorblind herself because a) the gene for colorblindness is recessive b) the gene for colorblindness is dominant c) colorblindness is an acquired trait d) she selected the trait for colorblindness ...
organisation of living beings2016
... If all our body cells have the same genetic information, why do different specialised cells have different shape and perform different functions? Because each type of specialised cell only use the genetic information that they need to perform their specialised function and shape. TYPES OF TISSUES Al ...
... If all our body cells have the same genetic information, why do different specialised cells have different shape and perform different functions? Because each type of specialised cell only use the genetic information that they need to perform their specialised function and shape. TYPES OF TISSUES Al ...
Ancient Art of Biblical Healing 50-Hour ModuleAroma Hut Institute
... could not be considered alive. It is accurate then to say essentially cells are life itself. By contrast, if there is a breakdown of cells for any reason, whether that be by injury or genetic disorder, then disease occurs. ...
... could not be considered alive. It is accurate then to say essentially cells are life itself. By contrast, if there is a breakdown of cells for any reason, whether that be by injury or genetic disorder, then disease occurs. ...
Cell: basic unit of structure and function of life. Prokaryotic: cells that
... Cell: basic unit of structure and function of life. Prokaryotic: cells that do not have membrane bound structures. Eukaryotic: cells that have membrane bound structures Unicellular: made of only one cell Multicellular: made of many cells Cell membrane: encloses the cell and acts like a gatekeeper-al ...
... Cell: basic unit of structure and function of life. Prokaryotic: cells that do not have membrane bound structures. Eukaryotic: cells that have membrane bound structures Unicellular: made of only one cell Multicellular: made of many cells Cell membrane: encloses the cell and acts like a gatekeeper-al ...
Nervous System Section 35–1 Human Body Systems (pages 891
... a. Stores mineral reserves and provides a site for blood cell formation. ...
... a. Stores mineral reserves and provides a site for blood cell formation. ...
Homework Exercise 1 - Cells, Tissues and Organs 1. Place the
... A human body is made up of small building blocks called cells. Muscle cells and nerve cells are two of many types of cells found in the body. These cells are specialised i.e. they have a specific structure to allow them to do a specific task in the body e.g. red blood cells contain haemoglobin to he ...
... A human body is made up of small building blocks called cells. Muscle cells and nerve cells are two of many types of cells found in the body. These cells are specialised i.e. they have a specific structure to allow them to do a specific task in the body e.g. red blood cells contain haemoglobin to he ...
Cells Study Guide
... o Larger organisms are made of more cells, not larger cells. o Unicellular organisms have only one cell and life is limited to the life of that cell. o Multicellular organisms are made of many cells and their lifespan is not limited to the life of only one cell. o Multicellular organisms grow when c ...
... o Larger organisms are made of more cells, not larger cells. o Unicellular organisms have only one cell and life is limited to the life of that cell. o Multicellular organisms are made of many cells and their lifespan is not limited to the life of only one cell. o Multicellular organisms grow when c ...
ANSWERS TO REVIEW QUESTIONS – CHAPTER 38
... List the main features that characterise members of the animal kingdom compared with those from the other eukaryotic kingdoms. What are the advantages of multicellularity for animals? (pp. 933–934) Basic characteristics of animals include multicellularity, embryonic development where a multicellular ...
... List the main features that characterise members of the animal kingdom compared with those from the other eukaryotic kingdoms. What are the advantages of multicellularity for animals? (pp. 933–934) Basic characteristics of animals include multicellularity, embryonic development where a multicellular ...
Cells and Organs
... circulatory system moves all these substances to or from cells where they are needed, or produced, responding to changing demands. Circulatory system ...
... circulatory system moves all these substances to or from cells where they are needed, or produced, responding to changing demands. Circulatory system ...
Embryonic Stem Cells
... "In recent years when it comes to stem cell research, rather than furthering discovery, our government has forced what I believe is a false choice between sound science and moral values... ...
... "In recent years when it comes to stem cell research, rather than furthering discovery, our government has forced what I believe is a false choice between sound science and moral values... ...
Function - Webster Elementary School
... Saturated Fats and / or lack of exercise. - Saturated Fats (plaque) build up and block the arteries that bring oxygen to the heart muscle (Coronary Arteries). - Lack of oxygen causes the heart muscle to die which really hurts a lot! - If enough of the heart muscle dies, the heart cannot function and ...
... Saturated Fats and / or lack of exercise. - Saturated Fats (plaque) build up and block the arteries that bring oxygen to the heart muscle (Coronary Arteries). - Lack of oxygen causes the heart muscle to die which really hurts a lot! - If enough of the heart muscle dies, the heart cannot function and ...
Chapter 1 Review and Test Preparation Vocabulary Review Use the
... B. maple tree C. moss D. oak tree Inquiry Skills 16. Which major organs are pictured above? F. arteries G. heart H. lungs J. stomach ...
... B. maple tree C. moss D. oak tree Inquiry Skills 16. Which major organs are pictured above? F. arteries G. heart H. lungs J. stomach ...