* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Human Body Systems Study Guide KEY!! System Main Function
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
History of anatomy wikipedia , lookup
Animal nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Organisms at high altitude wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Gaseous signaling molecules wikipedia , lookup
Incomplete Nature wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Homeostasis wikipedia , lookup
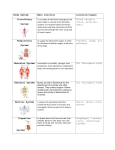
Human Body Systems Study Guide KEY!! System Main Function Major Organs Diagram Respiratory Obtain oxygen and release trachea Circulatory carbon dioxide. bronchi bronchioles alveoli pharynx larynx Transport materials through the body. heart veins arteries vena cava aorta Connections to Other Systems Other The oxygen and carbon dioxide are transported by blood in the blood vessels (circulatory systems). The oxygen obtained is combined with glucose (from the digestive system) to produce energy in cells. Know the path of an oxygen / carbon dioxide molecule through the system. trachea to bronchi to bronchioles to alveoli What gas exchange is. Diffusion of oxygen or carbon dioxide between blood vessels (capillaries) in the lungs and the alveoli at the end of the bronchioles. All happens by diffusion. Nutrients absorbed by the digestive system are transported by the circulatory system. Oxygen and carbon dioxide from the respiratory system are transported to and from the lungs, heart, and body. Difference between veins and arteries. Veins carry blood to the heart. Arteries carry blood Away from the heart. Path of blood through the heart, body, lungs. See diagram below. The blood only goes through 2 chambers of the heart at a time. Into the atria then to ventricle then out of heart. Nervous Excretory Control of the body and communication between body systems. brain spinal cord brain stem Eliminate wastes from blood, balance water and salt content in the body. kidneys bladder Controls ALL other systems. Signals from brain allow for voluntary movement. Involuntary control of heart beating, breathing, digestion, etc. What a neuron is. Nerve cells that make up the brain, spinal cord, and nerves. Send signals using chemicals, called neurotransmitters. Filters blood from circulatory system. Controlled by hormones produced by the endocrine system. Musculoskeletal Digestive** Since you were quizzed on most of this system already, you will not be quizzed on it again. You do need to know the organs we did not cover before and the connections to other systems. Support the body, protect internal organs, movement femur vertebrae skull ribs pelvis bones of arm & leg Break down food so nutrients can be absorbed by the body. liver pancreas gall bladder Marrow: Bone marrow produces red and white blood cells in your bones. Muscles and bones work together to allow for movement. You would be a jellylike blob without your bones. The products of digestion are transported by the circulatory system. Oxygen from the respiratory system are chemically combined with glucose from the digestive system to produce energy for cells. The raw materials for building cells like proteins (amino acids), lipids, & carbohydrates come from the food digested by this system. Levels of Organization On the Test you will have to: Circulatory System - Double Loop ● ● ● ● ● Match systems to their function. Match organs to their systems and functions. Label organs in a diagram. Write about connections between systems. ( I will give you the systems, you tell me how they are connected.) Discuss the levels of organization and how they apply to the human body and its systems. At the cellular level, diffusion happens to allow things into and out of cells like nutrients, oxygen, carbon dioxide. Tissues work together to form organs, organs work together to perform a function. Without coordination of all the organ systems, an organism could not stay alive.