UPcellprepro.10131154
... meiosis results in the formation of haploid cells. Explain the importance of this process in sexual reproduction, and how gametes form diploid zygotes in the process of fertilization. ...
... meiosis results in the formation of haploid cells. Explain the importance of this process in sexual reproduction, and how gametes form diploid zygotes in the process of fertilization. ...
Ch 2 ppt - Dover High School
... Organic molecules • contain C and H • usually larger than inorganic molecules • dissolve in water and organic liquids • carbohydrates, proteins, lipids, and nucleic acids Inorganic molecules • generally do not contain C • usually smaller than organic molecules • usually dissociate in water, forming ...
... Organic molecules • contain C and H • usually larger than inorganic molecules • dissolve in water and organic liquids • carbohydrates, proteins, lipids, and nucleic acids Inorganic molecules • generally do not contain C • usually smaller than organic molecules • usually dissociate in water, forming ...
Intro to Anatomy and Physiology
... 5. Adaptation- Populations of living organisms are able to adapt to changing environmental conditions 6. Growth and Development- Organisms grow from a single cell as an egg, to an adult with millions (or more) cells. Living organisms also develop into a mature adult form, which is much different fro ...
... 5. Adaptation- Populations of living organisms are able to adapt to changing environmental conditions 6. Growth and Development- Organisms grow from a single cell as an egg, to an adult with millions (or more) cells. Living organisms also develop into a mature adult form, which is much different fro ...
Eukaryotic Cells
... complex in secretory vesicles, which detach from the Golgi membrane and deliver the proteins to the plasma membrane, where they are discharged from the cell. Some of the processed proteins leave the Golgi complex in vesicles that are called storage vesicles. The major storage vesicle is a lysosome. ...
... complex in secretory vesicles, which detach from the Golgi membrane and deliver the proteins to the plasma membrane, where they are discharged from the cell. Some of the processed proteins leave the Golgi complex in vesicles that are called storage vesicles. The major storage vesicle is a lysosome. ...
Lecture 3
... Dynamic proteins : Catalytic proteins; catalysts for chemical reactions, cell metabolism (hormones , insulin, erthrproetin and thyroxine, hemoglobinhemocyanin-myoglobin ...
... Dynamic proteins : Catalytic proteins; catalysts for chemical reactions, cell metabolism (hormones , insulin, erthrproetin and thyroxine, hemoglobinhemocyanin-myoglobin ...
Organ Systems - BartlettsBiology11C
... surface area of small intestine x 10… Each villus has a capillary network, nutrients travel through circulatory system and delivered to cells ...
... surface area of small intestine x 10… Each villus has a capillary network, nutrients travel through circulatory system and delivered to cells ...
Biology Summary
... down the captured material a lysosome fuses with and digests worn out organelles recycle their components back to cytoplasm enzymes make possible reaction that would otherwise not proceed ...
... down the captured material a lysosome fuses with and digests worn out organelles recycle their components back to cytoplasm enzymes make possible reaction that would otherwise not proceed ...
Glossary
... acquired immune response a response through which the body’s resistance to a specific pathogen is built up over time. (9.2) actin filaments long, thin, flexible protein cables that can contract; part of the cytoskeleton and a major component of muscle fibres. (2.1) active transport cellular process ...
... acquired immune response a response through which the body’s resistance to a specific pathogen is built up over time. (9.2) actin filaments long, thin, flexible protein cables that can contract; part of the cytoskeleton and a major component of muscle fibres. (2.1) active transport cellular process ...
- Lincoln University
... Students will learn that science is a more a Verb than a Noun: How one comes to know something is as valuable as what is learned. Science is a process involving reasoning and experimental design techniques. Statistical analysis of collected data is an integral part of science technique. Students wil ...
... Students will learn that science is a more a Verb than a Noun: How one comes to know something is as valuable as what is learned. Science is a process involving reasoning and experimental design techniques. Statistical analysis of collected data is an integral part of science technique. Students wil ...
File - Science with Snyder
... pH homeostasis can be maintained. 3. A ____________ is a substance that changes the rate of a chemical reaction or allows a chemical reaction to occur (activate) at a lower than normal temperature. a. Catalysts work by lowering the _________ energy of a chemical reaction. b. not consumed or changed ...
... pH homeostasis can be maintained. 3. A ____________ is a substance that changes the rate of a chemical reaction or allows a chemical reaction to occur (activate) at a lower than normal temperature. a. Catalysts work by lowering the _________ energy of a chemical reaction. b. not consumed or changed ...
1. Egg, 2. Larva, 3. Pupa, 4. adult
... 4. _Epidermis___ _tissue__ is the outside layer of cells on the top and bottom of a leaf. 5. There are _3___ stages in an incomplete metamorphosis. 6. The process by which cells break down sugar to release energy is _cellular respiration___. 7. There are ___4_____ stages in a complete metamorphosis. ...
... 4. _Epidermis___ _tissue__ is the outside layer of cells on the top and bottom of a leaf. 5. There are _3___ stages in an incomplete metamorphosis. 6. The process by which cells break down sugar to release energy is _cellular respiration___. 7. There are ___4_____ stages in a complete metamorphosis. ...
Nucleic acids and their protein partners
... The interactions between proteins and nucleic acids guide the flow of genetic information between DNA, RNA, and protein. The reviews in this issue of Current Opinion in Structural Biology discuss some of the most fundamental aspects of RNA folding and dynamics, modes of nucleic acid recognition, and ...
... The interactions between proteins and nucleic acids guide the flow of genetic information between DNA, RNA, and protein. The reviews in this issue of Current Opinion in Structural Biology discuss some of the most fundamental aspects of RNA folding and dynamics, modes of nucleic acid recognition, and ...
snews
... sugar cane. In the future scientists may be able to use any part of any plant to make bioplastics, including the leaves. It is claimed that this process is better for the environment as it emits less carbon dioxide than other ways of making plastic. These new plastics are also supposed to biodegrade ...
... sugar cane. In the future scientists may be able to use any part of any plant to make bioplastics, including the leaves. It is claimed that this process is better for the environment as it emits less carbon dioxide than other ways of making plastic. These new plastics are also supposed to biodegrade ...
Slide 1
... – glucose + oxygen carbon dioxide + water • This is a simplified version and does not show all the intermediate rxns involved • Key: respiration converts chemical energy of glucose into a form which can be used by organisms (for muscle contraction, growth, etc) • All heterotrophic organisms obtain ...
... – glucose + oxygen carbon dioxide + water • This is a simplified version and does not show all the intermediate rxns involved • Key: respiration converts chemical energy of glucose into a form which can be used by organisms (for muscle contraction, growth, etc) • All heterotrophic organisms obtain ...
0011657857 - University of Oxford
... The University of Oxford is a complex and stimulating organisation, which enjoys an international reputation as a world-class centre of excellence in research and teaching. It employs over 10,000 staff and has a student population of over 22,000. Most staff are directly appointed and managed by one ...
... The University of Oxford is a complex and stimulating organisation, which enjoys an international reputation as a world-class centre of excellence in research and teaching. It employs over 10,000 staff and has a student population of over 22,000. Most staff are directly appointed and managed by one ...
biology sequencing
... The basic unit of structure and function for all living organisms. Cells have three common components: genetic material, cytoplasm, and a cell membrane. Eukaryotic cells also contain specialized organelles. ...
... The basic unit of structure and function for all living organisms. Cells have three common components: genetic material, cytoplasm, and a cell membrane. Eukaryotic cells also contain specialized organelles. ...
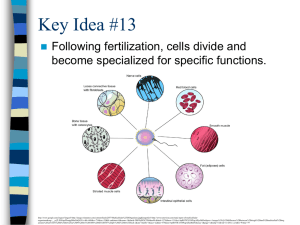
Key Idea #9 - Mona Shores Blogs
... learns a specific skill which they can then use to help everyone else. Just like people, cells specialize in important jobs. ...
... learns a specific skill which they can then use to help everyone else. Just like people, cells specialize in important jobs. ...
Chapter 1 The Framework of Biology
... Fermentation by fungi produces alcohol and carbon dioxide. Humans use fungi to ferment food sources producing bread, alcohol and cheese. Fungi are used for medicines. It was discovered that fungi produce a chemical which affects bacterial growth, now used by humans as antibiotics. 16.4 Animals are a ...
... Fermentation by fungi produces alcohol and carbon dioxide. Humans use fungi to ferment food sources producing bread, alcohol and cheese. Fungi are used for medicines. It was discovered that fungi produce a chemical which affects bacterial growth, now used by humans as antibiotics. 16.4 Animals are a ...
cells
... skin. -Information goes to the brain. -brain sends signals to muscles, skin and blood vessels. - they all work together to help your body perform properly. this system consists of the brain, spinal cord and the nerves. Diet, exercise, drugs, injury, and disease can affect body systems and disrup ...
... skin. -Information goes to the brain. -brain sends signals to muscles, skin and blood vessels. - they all work together to help your body perform properly. this system consists of the brain, spinal cord and the nerves. Diet, exercise, drugs, injury, and disease can affect body systems and disrup ...
Levels of Organization - Flipped Out Science with Mrs. Thomas!
... Within multi-cellular organisms there is division of labor. Division of labor means that the work (labor) of keeping the organism alive is divided (division) among the different parts of the body. Each part has a job to do and as each part does its special job, it works in harmony with all the other ...
... Within multi-cellular organisms there is division of labor. Division of labor means that the work (labor) of keeping the organism alive is divided (division) among the different parts of the body. Each part has a job to do and as each part does its special job, it works in harmony with all the other ...
Jack Bowers` Chapter 2 Biology Notes
... phenotype. Two alleles of autosomal genes interact to produce phenotype. 7.2: Phenotype is affected by many different factors. It is rarely the result of a simple dominant/recessive between two alleles of a gene. Often, there are more than two possible alleles of a gene. Incomplete dominance produce ...
... phenotype. Two alleles of autosomal genes interact to produce phenotype. 7.2: Phenotype is affected by many different factors. It is rarely the result of a simple dominant/recessive between two alleles of a gene. Often, there are more than two possible alleles of a gene. Incomplete dominance produce ...
Stage 3
... This unequal ability of individuals to survive and reproduce will cause a gradual change in the population Favorable characteristics will accumulate in the population over time ...
... This unequal ability of individuals to survive and reproduce will cause a gradual change in the population Favorable characteristics will accumulate in the population over time ...
Life

Life is a characteristic distinguishing physical entities having biological processes (such as signaling and self-sustaining processes) from those that do not, either because such functions have ceased (death), or because they lack such functions and are classified as inanimate. Various forms of life exist such as plants, animals, fungi, protists, archaea, and bacteria. The criteria can at times be ambiguous and may or may not define viruses, viroids or potential artificial life as living. Biology is the primary science concerned with the study of life, although many other sciences are involved.The smallest contiguous unit of life is called an organism. Organisms are composed of one or more cells, undergo metabolism, maintain homeostasis, can grow, respond to stimuli, reproduce (either sexually or asexually) and, through evolution, adapt to their environment in successive generations. A diverse array of living organisms can be found in the biosphere of Earth, and the properties common to these organisms—plants, animals, fungi, protists, archaea, and bacteria—are a carbon- and water-based cellular form with complex organization and heritable genetic information.Abiogenesis is the natural process of life arising from non-living matter, such as simple organic compounds. The age of the Earth is about 4.54 billion years. The earliest life on Earth arose at least 3.5 billion years ago, during the Eoarchean Era when sufficient crust had solidified following the molten Hadean Eon. The earliest physical evidence of life on Earth is biogenic graphite from 3.7 billion-year-old metasedimentary rocks found in Western Greenland and microbial mat fossils in 3.48 billion-year-old sandstone found in Western Australia. Some theories, such as the Late Heavy Bombardment theory, suggest that life on Earth may have started even earlier, and may have begun as early as 4.25 billion years ago according to one study, and even earlier yet, 4.4 billion years ago, according to another. The mechanism by which life began on Earth is unknown, although many hypotheses have been formulated. Since emerging, life has evolved into a variety of forms, which have been classified into a hierarchy of taxa. Life can survive and thrive in a wide range of conditions. Nonetheless, more than 99 percent of all species, amounting to over five billion species, that ever lived on Earth are estimated to be extinct. Estimates on the number of Earth's current species range from 10 million to 14 million, of which about 1.2 million have been documented and over 86 percent have not yet been described.The chemistry leading to life may have begun shortly after the Big Bang, 13.8 billion years ago, during a habitable epoch when the Universe was only 10–17 million years old. Though life is confirmed only on the Earth, many think that extraterrestrial life is not only plausible, but probable or inevitable. Other planets and moons in the Solar System and other planetary systems are being examined for evidence of having once supported simple life, and projects such as SETI are trying to detect radio transmissions from possible alien civilizations.The meaning of life—its significance, origin, purpose, and ultimate fate—is a central concept and question in philosophy and religion. Both philosophy and religion have offered interpretations as to how life relates to existence and consciousness, and on related issues such as life stance, purpose, conception of a god or gods, a soul or an afterlife. Different cultures throughout history have had widely varying approaches to these issues.