Gymnosperms evolved seeds as a way to protect their young
... some of them extremely successful . Probably the bestknown arthropod group is the insects (grasshoppers, beetles, butterflies, and ants, among others), which have six legs and live on land . Whereas prokaryotes dominate Earth in sheer numbers of individuals, insects dominate in number of species, ha ...
... some of them extremely successful . Probably the bestknown arthropod group is the insects (grasshoppers, beetles, butterflies, and ants, among others), which have six legs and live on land . Whereas prokaryotes dominate Earth in sheer numbers of individuals, insects dominate in number of species, ha ...
education - Perelman School of Medicine
... interaction between the zinc finger domain of Nup153 and the small GTPase Ran. Single zinc fingers within the zinc finger domain of Nup153 were able to bind Ran with micromolar affinity, and the binding interface on the zinc finger surface was dependent on a three amino acid signature motif. Interes ...
... interaction between the zinc finger domain of Nup153 and the small GTPase Ran. Single zinc fingers within the zinc finger domain of Nup153 were able to bind Ran with micromolar affinity, and the binding interface on the zinc finger surface was dependent on a three amino acid signature motif. Interes ...
NGSS Levels of Organization
... 1. Describe and sequence the 5 levels of biological organization. ! 2. What must happen in the body to maintain homeostasis? Given an example of this.! 3. Describe the outcome of the two types of feedback, and give an example for each.! ...
... 1. Describe and sequence the 5 levels of biological organization. ! 2. What must happen in the body to maintain homeostasis? Given an example of this.! 3. Describe the outcome of the two types of feedback, and give an example for each.! ...
Answers to CSEC® Biology Examination Practice
... random mutations. Resistant bacteria will survive an antibiotic treatment and be able to reproduce more bacteria that are also resistant to the antibiotic. [4] iii Evolution is the slow process by which a species adapts to its environment and may eventually give rise to another species. Evolution m ...
... random mutations. Resistant bacteria will survive an antibiotic treatment and be able to reproduce more bacteria that are also resistant to the antibiotic. [4] iii Evolution is the slow process by which a species adapts to its environment and may eventually give rise to another species. Evolution m ...
Introduction To Animals
... - adult human has about 50 trillion cells - no cell walls Specialization – the differentiation of a cell for a particular function; such as cells designed for digestion or reproduction. Cell Junctions – connections between cells that hold the cells together as a unit; this leads to the formation tis ...
... - adult human has about 50 trillion cells - no cell walls Specialization – the differentiation of a cell for a particular function; such as cells designed for digestion or reproduction. Cell Junctions – connections between cells that hold the cells together as a unit; this leads to the formation tis ...
Chapter 3 The Basic Structure of a Cell
... • Robert Hooke (1635-1703) – invented the term cell; studied dead plant cells such as cork. ...
... • Robert Hooke (1635-1703) – invented the term cell; studied dead plant cells such as cork. ...
Cell Organelles and Biotechnology
... environment into simpler compounds such as water and carbon dioxide. This makes them important and beneficial decomposers. In a bioreactor, heterotrophic bacteria derive energy from organic waste — such as tree bark and fertilizer — that is dumped into the sludge tank (Figure 3.24). Certain species ...
... environment into simpler compounds such as water and carbon dioxide. This makes them important and beneficial decomposers. In a bioreactor, heterotrophic bacteria derive energy from organic waste — such as tree bark and fertilizer — that is dumped into the sludge tank (Figure 3.24). Certain species ...
No Slide Title
... light that can be used for identification or communication, to lure prey or confuse predators, or to help the fish see in total ...
... light that can be used for identification or communication, to lure prey or confuse predators, or to help the fish see in total ...
Metabolism Basics
... In addition to sugar, both amino acids and fatty acids can be used as energy sources by the body when needed. ...
... In addition to sugar, both amino acids and fatty acids can be used as energy sources by the body when needed. ...
Questions From Old Exams
... (abbreviated by their one-letter designation), draw a double-stranded DNA molecule with five base pairs below. Indicate covalent bonds between the P, S, and/or bases using solid lines and indicate hydrogen bonds with dotted or dashed lines. There should be 10 total nucleotides in your drawing. Examp ...
... (abbreviated by their one-letter designation), draw a double-stranded DNA molecule with five base pairs below. Indicate covalent bonds between the P, S, and/or bases using solid lines and indicate hydrogen bonds with dotted or dashed lines. There should be 10 total nucleotides in your drawing. Examp ...
Word Roots - Jennifer`s e
... aux- = grow, enlarge (auxins: a class of plant hormones, including indoleacetic acid, having a variety of effects, such as phototropic response through the stimulation of cell elongation, stimulation of secondary growth, and the development of leaf traces and fruit) bacul- = a rod (baculum: a bone t ...
... aux- = grow, enlarge (auxins: a class of plant hormones, including indoleacetic acid, having a variety of effects, such as phototropic response through the stimulation of cell elongation, stimulation of secondary growth, and the development of leaf traces and fruit) bacul- = a rod (baculum: a bone t ...
基础医学英语Unit 14
... Microorganisms are beneficial for microbial biodegradation or bioremediation(生物修复) of domestic, agricultural and industrial wastes and subsurface pollution in soils, sediments and marine (海洋) environments. The ability of each microorganism to degrade toxic waste depends on the nature of each contam ...
... Microorganisms are beneficial for microbial biodegradation or bioremediation(生物修复) of domestic, agricultural and industrial wastes and subsurface pollution in soils, sediments and marine (海洋) environments. The ability of each microorganism to degrade toxic waste depends on the nature of each contam ...
Chapter 3 The Basic Structure of a Cell
... Introduction to Cells Cells are the basic units of organisms Cells can only be observed under microscope Basic types of cells: ...
... Introduction to Cells Cells are the basic units of organisms Cells can only be observed under microscope Basic types of cells: ...
Structure
... Multicellular – organisms made up of many independent cells working together (plants and animals) ...
... Multicellular – organisms made up of many independent cells working together (plants and animals) ...
Cells→ Tissues → Organs → Organ Systems
... fresh oxygen (O2) from the air. When the blood reaches the lungs, part of the respiratory system, the blood is re-oxygenated. Your stomach, part of the digestive system, constantly interacts with your endocrine system and spreads hormones throughout your body. Examples of Systems It's easy to point ...
... fresh oxygen (O2) from the air. When the blood reaches the lungs, part of the respiratory system, the blood is re-oxygenated. Your stomach, part of the digestive system, constantly interacts with your endocrine system and spreads hormones throughout your body. Examples of Systems It's easy to point ...
Name - Spring Branch ISD
... radish seeds. Sam thought that if vitamins helped the nutrition and growth of humans, then vitamins would help the growth of the radish seeds by making more of the seed sprout. Sam planted 5 radish seeds in 100 grams of soil and added 10 ml of water to the soil. In his second group, Sam planted 5 mo ...
... radish seeds. Sam thought that if vitamins helped the nutrition and growth of humans, then vitamins would help the growth of the radish seeds by making more of the seed sprout. Sam planted 5 radish seeds in 100 grams of soil and added 10 ml of water to the soil. In his second group, Sam planted 5 mo ...
Levels of Organization
... *A living thing that can carry out all life processes *Most complex level of organization *Some organisms are made of only one cell (like bacteria & paramecium) ...
... *A living thing that can carry out all life processes *Most complex level of organization *Some organisms are made of only one cell (like bacteria & paramecium) ...
Chapter 1 - Maintaining Life
... • Catabolism- breakdown of “stuff” into simpler parts • Anabolism – synthesizing more complex cellular structures from simpler substances • Cellular respiration – using nutrients and oxygen to ...
... • Catabolism- breakdown of “stuff” into simpler parts • Anabolism – synthesizing more complex cellular structures from simpler substances • Cellular respiration – using nutrients and oxygen to ...
2.1 Cells, tissues and organs
... Multicellular organisms • Multicellular organisms are made up of more than one cell. • These cells can be organised into tissues and organs. ...
... Multicellular organisms • Multicellular organisms are made up of more than one cell. • These cells can be organised into tissues and organs. ...
Printable PDF
... which simple substances are synthesized into the complex materials of living tissue. ...
... which simple substances are synthesized into the complex materials of living tissue. ...
Review Keystone Biology Multiple choice
... Which of the following is NOT found in all cells? a. cytoplasm b. genetic material c. mitochondria d. plasma membrane ...
... Which of the following is NOT found in all cells? a. cytoplasm b. genetic material c. mitochondria d. plasma membrane ...
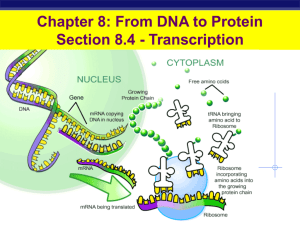
Transcription/translation
... How do cells control Gene Expression? For RNA Polymerase to do its job it has to attach to the DNA molecule ...
... How do cells control Gene Expression? For RNA Polymerase to do its job it has to attach to the DNA molecule ...
Ch. 19 Bacteria and Viruses
... chopping up the cell DNA, a process that shuts down the infected host cell – In this lytic infection, the virus then uses the materials of the host cell to make thousands of copies of its own DNA molecule ...
... chopping up the cell DNA, a process that shuts down the infected host cell – In this lytic infection, the virus then uses the materials of the host cell to make thousands of copies of its own DNA molecule ...
Tissues in the lungs
... activity and surface-area-to-volume ratios. Explain the meaning of the terms single and double circulatory systems with reference to the circulatory systems of fish and animals. Large animal transport systems All living cells need a supply of oxygen and nutrients to survive. They also need to remo ...
... activity and surface-area-to-volume ratios. Explain the meaning of the terms single and double circulatory systems with reference to the circulatory systems of fish and animals. Large animal transport systems All living cells need a supply of oxygen and nutrients to survive. They also need to remo ...
Life

Life is a characteristic distinguishing physical entities having biological processes (such as signaling and self-sustaining processes) from those that do not, either because such functions have ceased (death), or because they lack such functions and are classified as inanimate. Various forms of life exist such as plants, animals, fungi, protists, archaea, and bacteria. The criteria can at times be ambiguous and may or may not define viruses, viroids or potential artificial life as living. Biology is the primary science concerned with the study of life, although many other sciences are involved.The smallest contiguous unit of life is called an organism. Organisms are composed of one or more cells, undergo metabolism, maintain homeostasis, can grow, respond to stimuli, reproduce (either sexually or asexually) and, through evolution, adapt to their environment in successive generations. A diverse array of living organisms can be found in the biosphere of Earth, and the properties common to these organisms—plants, animals, fungi, protists, archaea, and bacteria—are a carbon- and water-based cellular form with complex organization and heritable genetic information.Abiogenesis is the natural process of life arising from non-living matter, such as simple organic compounds. The age of the Earth is about 4.54 billion years. The earliest life on Earth arose at least 3.5 billion years ago, during the Eoarchean Era when sufficient crust had solidified following the molten Hadean Eon. The earliest physical evidence of life on Earth is biogenic graphite from 3.7 billion-year-old metasedimentary rocks found in Western Greenland and microbial mat fossils in 3.48 billion-year-old sandstone found in Western Australia. Some theories, such as the Late Heavy Bombardment theory, suggest that life on Earth may have started even earlier, and may have begun as early as 4.25 billion years ago according to one study, and even earlier yet, 4.4 billion years ago, according to another. The mechanism by which life began on Earth is unknown, although many hypotheses have been formulated. Since emerging, life has evolved into a variety of forms, which have been classified into a hierarchy of taxa. Life can survive and thrive in a wide range of conditions. Nonetheless, more than 99 percent of all species, amounting to over five billion species, that ever lived on Earth are estimated to be extinct. Estimates on the number of Earth's current species range from 10 million to 14 million, of which about 1.2 million have been documented and over 86 percent have not yet been described.The chemistry leading to life may have begun shortly after the Big Bang, 13.8 billion years ago, during a habitable epoch when the Universe was only 10–17 million years old. Though life is confirmed only on the Earth, many think that extraterrestrial life is not only plausible, but probable or inevitable. Other planets and moons in the Solar System and other planetary systems are being examined for evidence of having once supported simple life, and projects such as SETI are trying to detect radio transmissions from possible alien civilizations.The meaning of life—its significance, origin, purpose, and ultimate fate—is a central concept and question in philosophy and religion. Both philosophy and religion have offered interpretations as to how life relates to existence and consciousness, and on related issues such as life stance, purpose, conception of a god or gods, a soul or an afterlife. Different cultures throughout history have had widely varying approaches to these issues.