Document
... you answer. Good Luck! Please keep this document when finished. Just return your scantron to me and the page with the bonus question. As you leave I will check to see that you are enrolled in this class. To save on paper, the format is squeezed together in some places. FIRST NAME____________________ ...
... you answer. Good Luck! Please keep this document when finished. Just return your scantron to me and the page with the bonus question. As you leave I will check to see that you are enrolled in this class. To save on paper, the format is squeezed together in some places. FIRST NAME____________________ ...
Cell Theory Cell Structure, Cell Transport and Mitosis
... Transport of organelles and molecules: Microtubules are the freeways used by organelles like lysosomes to move from one part of cell to another. Microfilaments are the roads/streets used by smaller things. Genes – DNA – Chromatin fiber – Chromosomes Fig. 3-17 Genes, the segments of DNA, are part of ...
... Transport of organelles and molecules: Microtubules are the freeways used by organelles like lysosomes to move from one part of cell to another. Microfilaments are the roads/streets used by smaller things. Genes – DNA – Chromatin fiber – Chromosomes Fig. 3-17 Genes, the segments of DNA, are part of ...
living environment
... answers for all multiple-choice questions, including those in Parts B–2 and D, on the separate answer sheet. Record your answers for all open-ended questions directly in this examination booklet. All answers in this examination booklet should be written in pen, except for graphs and drawings, which ...
... answers for all multiple-choice questions, including those in Parts B–2 and D, on the separate answer sheet. Record your answers for all open-ended questions directly in this examination booklet. All answers in this examination booklet should be written in pen, except for graphs and drawings, which ...
1. What is true of all fungi? They are a. eukaryotic, heterotrophic
... a. means that sexual reproduction can occur in specialized structures. b. results in more genetic variation during sexual reproduction. c. allows fungi to reproduce asexually most of the time. d. creates dikaryotic cells. e. is strong support for the claim that fungi are not truly eukaryotic. The qu ...
... a. means that sexual reproduction can occur in specialized structures. b. results in more genetic variation during sexual reproduction. c. allows fungi to reproduce asexually most of the time. d. creates dikaryotic cells. e. is strong support for the claim that fungi are not truly eukaryotic. The qu ...
1 Living things - Macmillan English
... All plants in the Plant Kingdom are multicellular organisms. They make their own food by taking energy from the Sun. This process is called photosynthesis. During photosynthesis, plants produce oxygen, which is released into the air. Plants can’t move around, but they can move certain parts, and the ...
... All plants in the Plant Kingdom are multicellular organisms. They make their own food by taking energy from the Sun. This process is called photosynthesis. During photosynthesis, plants produce oxygen, which is released into the air. Plants can’t move around, but they can move certain parts, and the ...
Organization of Living Organisms cell: basic unit of life all living
... regeneration: the ability to regrow body parts this is different than healing, characteristic of lower animals segmentation: a repetition of body parts a characteristic of more complex organisms do we have this? where? ectotherm: organism that cannot regulate its internal body temperature endotherm: ...
... regeneration: the ability to regrow body parts this is different than healing, characteristic of lower animals segmentation: a repetition of body parts a characteristic of more complex organisms do we have this? where? ectotherm: organism that cannot regulate its internal body temperature endotherm: ...
Revision
... (or why not) some of these technologies should (or should not) be used in light of social and ethical considerations Describe and discriminate between different forms of cell division Create novel pedigrees from provided gene and trait information Describe the impact of human populations on disease ...
... (or why not) some of these technologies should (or should not) be used in light of social and ethical considerations Describe and discriminate between different forms of cell division Create novel pedigrees from provided gene and trait information Describe the impact of human populations on disease ...
Taxonomy ppt
... species is not and both are italicized • Combines the genus and species of an animal to give it a name – man is known as Homo sapiens – domesticated dogs are known as Canis ...
... species is not and both are italicized • Combines the genus and species of an animal to give it a name – man is known as Homo sapiens – domesticated dogs are known as Canis ...
MAE Colloquium: Lonnie Shea, PhD (University of Michigan)
... dual need i) to develop systems capable of presenting combinations of factors that drive tissue growth, as well as ii) to incorporate systems biology approaches that can identify the appropriate combination of factors. Biomaterial scaffolds represent a central component of many approaches and provid ...
... dual need i) to develop systems capable of presenting combinations of factors that drive tissue growth, as well as ii) to incorporate systems biology approaches that can identify the appropriate combination of factors. Biomaterial scaffolds represent a central component of many approaches and provid ...
1 IntroBio
... Eight Properties of Living Things 1) Life is highly ordered and complex in structure. ...
... Eight Properties of Living Things 1) Life is highly ordered and complex in structure. ...
SAT Biology Review: Diversity of Life
... Have hair, produce milk to feed young. Most carry eggs to term internally (vivipary, or live birth). Four-chambered heart. Endothermic (warm-blooded) ...
... Have hair, produce milk to feed young. Most carry eggs to term internally (vivipary, or live birth). Four-chambered heart. Endothermic (warm-blooded) ...
EuroDYNA Activities - European Science Foundation
... Each time a cell divides its genetic information must be doubled in order for the genes to remain the same. A cell that is about to become tumorous can not make this genome replication and division without errors. To spot errors in the genetic material cells have evolved mechanisms to slow down or b ...
... Each time a cell divides its genetic information must be doubled in order for the genes to remain the same. A cell that is about to become tumorous can not make this genome replication and division without errors. To spot errors in the genetic material cells have evolved mechanisms to slow down or b ...
SAT Biology Review: Diversity of Life
... Have hair, produce milk to feed young. Most carry eggs to term internally (vivipary, or live birth). Four-chambered heart. Endothermic (warm-blooded) ...
... Have hair, produce milk to feed young. Most carry eggs to term internally (vivipary, or live birth). Four-chambered heart. Endothermic (warm-blooded) ...
Cell
... coli bacteria naturally live in the human intestine. E. coli is essential for digestion to occur. However, if E. coli enters the stomach through contaminated food, it can cause foodborne illness. ...
... coli bacteria naturally live in the human intestine. E. coli is essential for digestion to occur. However, if E. coli enters the stomach through contaminated food, it can cause foodborne illness. ...
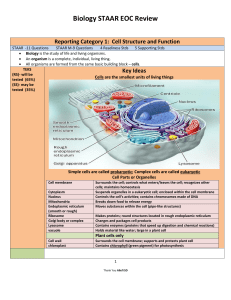
Alief ISD Biology STAAR EOC Review
... explain cellular processes, including homeostasis, energy conversions, transport of molecules, and synthesis of new materials (RS) ...
... explain cellular processes, including homeostasis, energy conversions, transport of molecules, and synthesis of new materials (RS) ...
Biology ORGANISMS Practice Test with Answer Key
... placed separately into the four jars. The jars are sealed and placed in direct sunlight for six months. After this period the jars are checked to see if there are living inhabitants. Which classification of organisms lacks the characteristics necessary to survive the conditions in the jar for six mo ...
... placed separately into the four jars. The jars are sealed and placed in direct sunlight for six months. After this period the jars are checked to see if there are living inhabitants. Which classification of organisms lacks the characteristics necessary to survive the conditions in the jar for six mo ...
AP Biology
... 1. How do single celled and ‘sac’ animals allow for each body cell to be in contact with an aqueous medium? How do more complex organisms solve this problem? (what is a common theme used to maximize SA:volume ratios?) ...
... 1. How do single celled and ‘sac’ animals allow for each body cell to be in contact with an aqueous medium? How do more complex organisms solve this problem? (what is a common theme used to maximize SA:volume ratios?) ...
Available - Ggu.ac.in
... cilia or flagellum. An organ of excretion in flatworms: a hollow cup-shaped cell containing a bunch of cilia or flagellum, whose movement draws in waste products and wafts them to the outside through a connecting tubule. ...
... cilia or flagellum. An organ of excretion in flatworms: a hollow cup-shaped cell containing a bunch of cilia or flagellum, whose movement draws in waste products and wafts them to the outside through a connecting tubule. ...
homologous structures
... Why is discussion of analogous structures inappropriate when detailing evidence of evolution? How are homologous structures evidence of evolution? Give an example of a human vestigial structure, and describe why it is evidence of evolution. ...
... Why is discussion of analogous structures inappropriate when detailing evidence of evolution? How are homologous structures evidence of evolution? Give an example of a human vestigial structure, and describe why it is evidence of evolution. ...
Downloaded - MsOttoliniBiology
... • A single-celled organism is called unicellular. Examples: bacteria, algae (plant), yeasts (fungi) • These organisms perform ALL of their functions in ONLY ONE CELL using different organelles!!! • Multicellular organisms are made up of MANY cells. • These organisms have cell specialization— differe ...
... • A single-celled organism is called unicellular. Examples: bacteria, algae (plant), yeasts (fungi) • These organisms perform ALL of their functions in ONLY ONE CELL using different organelles!!! • Multicellular organisms are made up of MANY cells. • These organisms have cell specialization— differe ...
concepts of matter and energy
... 22. For each true statement, insert T in the answer blank. If any are false, correct the underlined term and insert your correction in the answer blank. _________________________ 1. Phospholipids are polarized molecules. _________________________ 2. Steroids are the major form in which body fat is s ...
... 22. For each true statement, insert T in the answer blank. If any are false, correct the underlined term and insert your correction in the answer blank. _________________________ 1. Phospholipids are polarized molecules. _________________________ 2. Steroids are the major form in which body fat is s ...
Life

Life is a characteristic distinguishing physical entities having biological processes (such as signaling and self-sustaining processes) from those that do not, either because such functions have ceased (death), or because they lack such functions and are classified as inanimate. Various forms of life exist such as plants, animals, fungi, protists, archaea, and bacteria. The criteria can at times be ambiguous and may or may not define viruses, viroids or potential artificial life as living. Biology is the primary science concerned with the study of life, although many other sciences are involved.The smallest contiguous unit of life is called an organism. Organisms are composed of one or more cells, undergo metabolism, maintain homeostasis, can grow, respond to stimuli, reproduce (either sexually or asexually) and, through evolution, adapt to their environment in successive generations. A diverse array of living organisms can be found in the biosphere of Earth, and the properties common to these organisms—plants, animals, fungi, protists, archaea, and bacteria—are a carbon- and water-based cellular form with complex organization and heritable genetic information.Abiogenesis is the natural process of life arising from non-living matter, such as simple organic compounds. The age of the Earth is about 4.54 billion years. The earliest life on Earth arose at least 3.5 billion years ago, during the Eoarchean Era when sufficient crust had solidified following the molten Hadean Eon. The earliest physical evidence of life on Earth is biogenic graphite from 3.7 billion-year-old metasedimentary rocks found in Western Greenland and microbial mat fossils in 3.48 billion-year-old sandstone found in Western Australia. Some theories, such as the Late Heavy Bombardment theory, suggest that life on Earth may have started even earlier, and may have begun as early as 4.25 billion years ago according to one study, and even earlier yet, 4.4 billion years ago, according to another. The mechanism by which life began on Earth is unknown, although many hypotheses have been formulated. Since emerging, life has evolved into a variety of forms, which have been classified into a hierarchy of taxa. Life can survive and thrive in a wide range of conditions. Nonetheless, more than 99 percent of all species, amounting to over five billion species, that ever lived on Earth are estimated to be extinct. Estimates on the number of Earth's current species range from 10 million to 14 million, of which about 1.2 million have been documented and over 86 percent have not yet been described.The chemistry leading to life may have begun shortly after the Big Bang, 13.8 billion years ago, during a habitable epoch when the Universe was only 10–17 million years old. Though life is confirmed only on the Earth, many think that extraterrestrial life is not only plausible, but probable or inevitable. Other planets and moons in the Solar System and other planetary systems are being examined for evidence of having once supported simple life, and projects such as SETI are trying to detect radio transmissions from possible alien civilizations.The meaning of life—its significance, origin, purpose, and ultimate fate—is a central concept and question in philosophy and religion. Both philosophy and religion have offered interpretations as to how life relates to existence and consciousness, and on related issues such as life stance, purpose, conception of a god or gods, a soul or an afterlife. Different cultures throughout history have had widely varying approaches to these issues.