Section 3 - Studying Life
... Made Up of Cells Living things, or organisms, are made up of small, self-contained units called cells. A cell is a collection of living matter enclosed by a barrier that separates the cell from its surroundings. Cells are the smallest units of an organism that can be considered alive. Cells can grow ...
... Made Up of Cells Living things, or organisms, are made up of small, self-contained units called cells. A cell is a collection of living matter enclosed by a barrier that separates the cell from its surroundings. Cells are the smallest units of an organism that can be considered alive. Cells can grow ...
Biochemistry of Cells - Lakewood City Schools
... Cellulose is the most abundant organic compound on Earth It forms cable-like fibrils in the tough walls that enclose plants It is a major component of wood It is also known as dietary fiber ...
... Cellulose is the most abundant organic compound on Earth It forms cable-like fibrils in the tough walls that enclose plants It is a major component of wood It is also known as dietary fiber ...
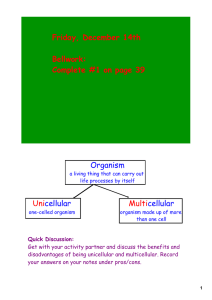
Friday, December 14th Bellwork: Complete #1 on page 39 Organism
... Cell - smallest functional and structural unit of all living ...
... Cell - smallest functional and structural unit of all living ...
Section 1: Human Body
... Chemical is when the enzymes in saliva begin to break down the chemical bonds in the carbohydrates into sugars. 9. At which stages in your life do you need to eat the most? Why do you need to eat so much at that point in your life? Explain. ...
... Chemical is when the enzymes in saliva begin to break down the chemical bonds in the carbohydrates into sugars. 9. At which stages in your life do you need to eat the most? Why do you need to eat so much at that point in your life? Explain. ...
trans nzoia west district mock examination – 2008 - KCPE-KCSE
... appendix, coccyx tail; vertebrate heart; The pendactyl limb/ any correct example; Analogous structures/ different structures performing the same function; e.g wings of insects bats and birds – show convergent evolution; Homologous structures/ structures with same origin but performing different func ...
... appendix, coccyx tail; vertebrate heart; The pendactyl limb/ any correct example; Analogous structures/ different structures performing the same function; e.g wings of insects bats and birds – show convergent evolution; Homologous structures/ structures with same origin but performing different func ...
STAR Testing - Mr. Stern's Virtual Classroom
... gaseous substances can change both shape and volume water changes from a solid to a liquid when ice is freezing water changes from a liquid to a gas when it is boiling All matter is made out atoms ...
... gaseous substances can change both shape and volume water changes from a solid to a liquid when ice is freezing water changes from a liquid to a gas when it is boiling All matter is made out atoms ...
2017 General externally set tasks Unit 3 content
... Unit 3 – Reproduction and inheritance Unit description Organisms exhibit a diverse and interesting range of reproductive structures and behaviours to ensure reproductive success. This unit explores the genetic basis for variation and inheritance of characteristics by the next generation. Environ ...
... Unit 3 – Reproduction and inheritance Unit description Organisms exhibit a diverse and interesting range of reproductive structures and behaviours to ensure reproductive success. This unit explores the genetic basis for variation and inheritance of characteristics by the next generation. Environ ...
Apple Molecular Biology: Animation 1
... Cloning can mean several things. Most people associate cloning with 'copying'. In molecular biology, cloning can be a process of recreating individuals from their own DNA but a more common use of cloning refers to the insertion of a short piece of DNA into a bacterial plasmid for replication purpose ...
... Cloning can mean several things. Most people associate cloning with 'copying'. In molecular biology, cloning can be a process of recreating individuals from their own DNA but a more common use of cloning refers to the insertion of a short piece of DNA into a bacterial plasmid for replication purpose ...
Honors Anatomy and Physiology
... Become familiar with the human body’s necessary life functions & survival needs. Define homeostasis & how it persists in the body. Differentiate between positive & negative feedback and provide examples ...
... Become familiar with the human body’s necessary life functions & survival needs. Define homeostasis & how it persists in the body. Differentiate between positive & negative feedback and provide examples ...
Word Format
... Unit 3 – Reproduction and inheritance Unit description Organisms exhibit a diverse and interesting range of reproductive structures and behaviours to ensure reproductive success. This unit explores the genetic basis for variation and inheritance of characteristics by the next generation. Environmen ...
... Unit 3 – Reproduction and inheritance Unit description Organisms exhibit a diverse and interesting range of reproductive structures and behaviours to ensure reproductive success. This unit explores the genetic basis for variation and inheritance of characteristics by the next generation. Environmen ...
MS Green Final Review 2016 1. The smallest group in the
... MS Green Final Review 2016 1. The smallest group in the classification system used today is called a __________________. 2. Organisms that can mate and produce fertile offspring belong to the same ____________. 3. All of these are characteristics of living things EXCEPT _____________________________ ...
... MS Green Final Review 2016 1. The smallest group in the classification system used today is called a __________________. 2. Organisms that can mate and produce fertile offspring belong to the same ____________. 3. All of these are characteristics of living things EXCEPT _____________________________ ...
cell - Jordan High School
... 3-2: The Plasma Membrane Functions Separates inside of cell from outside Controls entry/exit of substances ...
... 3-2: The Plasma Membrane Functions Separates inside of cell from outside Controls entry/exit of substances ...
Dedham Middle School MCAS Science Review Book
... proteins are polymers of amino acids. Long chains of monosaccharide units bonded together; e.g., glycogen, starch, and cellulose. the group of organic compounds made up of chains of amino acids. Polymers made up of amino acids that perform a wide variety of cellular functions. One of the classes of ...
... proteins are polymers of amino acids. Long chains of monosaccharide units bonded together; e.g., glycogen, starch, and cellulose. the group of organic compounds made up of chains of amino acids. Polymers made up of amino acids that perform a wide variety of cellular functions. One of the classes of ...
Exam Summary Points 2013
... and descending colon AND the rectum). Storage of faeces is the role of the rectum and elimination is controlled by the anal sphincter muscle. ...
... and descending colon AND the rectum). Storage of faeces is the role of the rectum and elimination is controlled by the anal sphincter muscle. ...
Organ Systems and Life
... Flower: The flower is the reproductive organ of plants. It may contain the stamen and or the carpel. The stamen contains the pollen, which is brought to the carpel by insects. The carpel contains the ovaries. The receptor of pollen is called the stigma. Stem: The stem raises the leaves and flower, a ...
... Flower: The flower is the reproductive organ of plants. It may contain the stamen and or the carpel. The stamen contains the pollen, which is brought to the carpel by insects. The carpel contains the ovaries. The receptor of pollen is called the stigma. Stem: The stem raises the leaves and flower, a ...
Cells Practice Test - Crossroads Academy
... 45) To the first decimal place, how many billion years ago did life arise on Earth? ANSWER: 46) What is the plural of genus? 47) What is the meaning of the scientific term, endosymbiosis? ANSWER: 48) What are the three taxonomical Domains? ANSWER: 49) Proteins are most directly made from a temporar ...
... 45) To the first decimal place, how many billion years ago did life arise on Earth? ANSWER: 46) What is the plural of genus? 47) What is the meaning of the scientific term, endosymbiosis? ANSWER: 48) What are the three taxonomical Domains? ANSWER: 49) Proteins are most directly made from a temporar ...
Cell Biology - WEB . WHRSD . ORG
... (What must students know? What should they remember years from now?) Include a listing of vocabulary terms that will be assessed) ...
... (What must students know? What should they remember years from now?) Include a listing of vocabulary terms that will be assessed) ...
Proteins Large, complex polymer consists of carbon, oxygen
... Two general types: RNA and DNA Nucleic acids have just one function DNA and RNA work together to make proteins. DNA stores the information for putting the amino acids together RNA helps to build the proteins. ...
... Two general types: RNA and DNA Nucleic acids have just one function DNA and RNA work together to make proteins. DNA stores the information for putting the amino acids together RNA helps to build the proteins. ...
Chapter 2 Part 2
... membrane structure, vitamin D synthesis, and production of steroid hormones. *Hormones are chemicals which alter cell activity in order to maintain homeostasis. Can move through cell membranes easily. Part of endocrine system. Cortisol is an example. ...
... membrane structure, vitamin D synthesis, and production of steroid hormones. *Hormones are chemicals which alter cell activity in order to maintain homeostasis. Can move through cell membranes easily. Part of endocrine system. Cortisol is an example. ...
Syllabus - Miami Dade College
... The student will be able to: A. explain the theory of evolution of life on Earth favored by modern scientists. B. describes and explain Darwin's basic concept of natural selection and how it relates to the theory of evolution. C. list and explain the several categories of evidence that support the t ...
... The student will be able to: A. explain the theory of evolution of life on Earth favored by modern scientists. B. describes and explain Darwin's basic concept of natural selection and how it relates to the theory of evolution. C. list and explain the several categories of evidence that support the t ...
Life Science: Cells
... transporters of oxygen and carbon dioxide. White blood cells attack invading germs. All reproduce by mitosis, or cell division. A glitch in this process can lead to the growth of cancerous cells that crowd out healthy ones. Cells’ ability to replicate is what keeps every living thing alive. But when ...
... transporters of oxygen and carbon dioxide. White blood cells attack invading germs. All reproduce by mitosis, or cell division. A glitch in this process can lead to the growth of cancerous cells that crowd out healthy ones. Cells’ ability to replicate is what keeps every living thing alive. But when ...
B2 revision questions
... What is the function of the oesophagus in digestion? What is the function of the stomach in digestion? What is the function of the small intestine in digestion? What is the function of the large intestine in digestion? What is the function of the pancreas in digestion? What is the function of the li ...
... What is the function of the oesophagus in digestion? What is the function of the stomach in digestion? What is the function of the small intestine in digestion? What is the function of the large intestine in digestion? What is the function of the pancreas in digestion? What is the function of the li ...
Life

Life is a characteristic distinguishing physical entities having biological processes (such as signaling and self-sustaining processes) from those that do not, either because such functions have ceased (death), or because they lack such functions and are classified as inanimate. Various forms of life exist such as plants, animals, fungi, protists, archaea, and bacteria. The criteria can at times be ambiguous and may or may not define viruses, viroids or potential artificial life as living. Biology is the primary science concerned with the study of life, although many other sciences are involved.The smallest contiguous unit of life is called an organism. Organisms are composed of one or more cells, undergo metabolism, maintain homeostasis, can grow, respond to stimuli, reproduce (either sexually or asexually) and, through evolution, adapt to their environment in successive generations. A diverse array of living organisms can be found in the biosphere of Earth, and the properties common to these organisms—plants, animals, fungi, protists, archaea, and bacteria—are a carbon- and water-based cellular form with complex organization and heritable genetic information.Abiogenesis is the natural process of life arising from non-living matter, such as simple organic compounds. The age of the Earth is about 4.54 billion years. The earliest life on Earth arose at least 3.5 billion years ago, during the Eoarchean Era when sufficient crust had solidified following the molten Hadean Eon. The earliest physical evidence of life on Earth is biogenic graphite from 3.7 billion-year-old metasedimentary rocks found in Western Greenland and microbial mat fossils in 3.48 billion-year-old sandstone found in Western Australia. Some theories, such as the Late Heavy Bombardment theory, suggest that life on Earth may have started even earlier, and may have begun as early as 4.25 billion years ago according to one study, and even earlier yet, 4.4 billion years ago, according to another. The mechanism by which life began on Earth is unknown, although many hypotheses have been formulated. Since emerging, life has evolved into a variety of forms, which have been classified into a hierarchy of taxa. Life can survive and thrive in a wide range of conditions. Nonetheless, more than 99 percent of all species, amounting to over five billion species, that ever lived on Earth are estimated to be extinct. Estimates on the number of Earth's current species range from 10 million to 14 million, of which about 1.2 million have been documented and over 86 percent have not yet been described.The chemistry leading to life may have begun shortly after the Big Bang, 13.8 billion years ago, during a habitable epoch when the Universe was only 10–17 million years old. Though life is confirmed only on the Earth, many think that extraterrestrial life is not only plausible, but probable or inevitable. Other planets and moons in the Solar System and other planetary systems are being examined for evidence of having once supported simple life, and projects such as SETI are trying to detect radio transmissions from possible alien civilizations.The meaning of life—its significance, origin, purpose, and ultimate fate—is a central concept and question in philosophy and religion. Both philosophy and religion have offered interpretations as to how life relates to existence and consciousness, and on related issues such as life stance, purpose, conception of a god or gods, a soul or an afterlife. Different cultures throughout history have had widely varying approaches to these issues.