CH 5 – THE FUNDAMENTAL UNIT OF LIFE
... 4. Draw and label the cells of an onion peel. 5. Why do we stain an object before observing it under microscope. Ans – By staining, the different parts of the object (cell) take up the stain at different rates. The rte of absorption of the stain depends on the chemical components in different parts. ...
... 4. Draw and label the cells of an onion peel. 5. Why do we stain an object before observing it under microscope. Ans – By staining, the different parts of the object (cell) take up the stain at different rates. The rte of absorption of the stain depends on the chemical components in different parts. ...
Chapter 1
... resources should be used and managed. • Scientists use an organized approach called the scientific method to investigate natural phenomena. • We will discuss this further later. ...
... resources should be used and managed. • Scientists use an organized approach called the scientific method to investigate natural phenomena. • We will discuss this further later. ...
Document
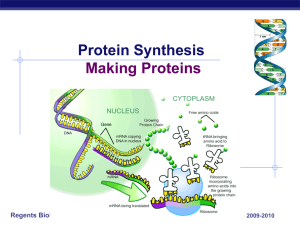
... Passing on DNA information Need to get DNA gene information from nucleus to cytoplasm ...
... Passing on DNA information Need to get DNA gene information from nucleus to cytoplasm ...
Chapter 2 Living Things and their Environment: Adaptations
... Below are examples of living things in the desert and how they have adapted to their environment. A. Creosote bush – have mainly shallow roots that help them take any rain that may fall. B. Barrel cactus – has thick waxy skin and thick round stem to help it collect and store water. C. Octillo – drop ...
... Below are examples of living things in the desert and how they have adapted to their environment. A. Creosote bush – have mainly shallow roots that help them take any rain that may fall. B. Barrel cactus – has thick waxy skin and thick round stem to help it collect and store water. C. Octillo – drop ...
Second Semester Vocab Review
... Cytoplasmic extensions that function in food ingestion and movement in certain amoebas ...
... Cytoplasmic extensions that function in food ingestion and movement in certain amoebas ...
Study Guide Ch - Cobb Learning
... 5. __________ is the diffusion of water molecules. 6. Both ____________ and __________ are examples of ________ transport because the do NOT require energy. 7. When a red blood cell has it’s normal doughnut shape, the concentration of water in the solution around the cell is the ______ as inside the ...
... 5. __________ is the diffusion of water molecules. 6. Both ____________ and __________ are examples of ________ transport because the do NOT require energy. 7. When a red blood cell has it’s normal doughnut shape, the concentration of water in the solution around the cell is the ______ as inside the ...
Practice Questions - the Elevate Student Portal.
... can find us on social media so you can stay up to date on any brand new tips we release throughout the year. ...
... can find us on social media so you can stay up to date on any brand new tips we release throughout the year. ...
Introduction to Life Sciences
... The course aims at introducing crucial concepts and insights in the origin and evolution of life on earth, the organisation of life, the building blocks of life, the energy conversions in life, inheritance and expression of genes. The course is situated at the interface between molecular biology, ge ...
... The course aims at introducing crucial concepts and insights in the origin and evolution of life on earth, the organisation of life, the building blocks of life, the energy conversions in life, inheritance and expression of genes. The course is situated at the interface between molecular biology, ge ...
circulation blood leaf sex cells images
... pairs of chromatids. Pairs of chromosomes arrange themselves in the centre of the cell. The chromosomes separate and move to opposite ends of the cell. The first cell division occurs. The chromosomes now separate from each other and move to opposite ends of the cells. The second cell division occurs ...
... pairs of chromatids. Pairs of chromosomes arrange themselves in the centre of the cell. The chromosomes separate and move to opposite ends of the cell. The first cell division occurs. The chromosomes now separate from each other and move to opposite ends of the cells. The second cell division occurs ...
B2 exam: Key words to understand
... A method of sampling where the samples are selected from the population at regular intervals (eg a sample every metre). The techniques / methods used by scientists studying ecology to get samples of the living organisms in an area. The preserved traces or remains of an organism which lived a very lo ...
... A method of sampling where the samples are selected from the population at regular intervals (eg a sample every metre). The techniques / methods used by scientists studying ecology to get samples of the living organisms in an area. The preserved traces or remains of an organism which lived a very lo ...
what is an infectious disease?
... Parasites can cause disease in humans. Some parasitic diseases are easily treated and some are not. Major types-protozoa, helminths or worms, and arthropods. ...
... Parasites can cause disease in humans. Some parasitic diseases are easily treated and some are not. Major types-protozoa, helminths or worms, and arthropods. ...
Levels of Organization
... 2. Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER) is a series of double membranes that ________ back and forth between the cell membrane and the _______________. These membranes fill the ____________________ but you cannot see them because they are very ___________________. The rough E.R. has ____________________ ...
... 2. Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER) is a series of double membranes that ________ back and forth between the cell membrane and the _______________. These membranes fill the ____________________ but you cannot see them because they are very ___________________. The rough E.R. has ____________________ ...
Levels of Organization
... 2. Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER) is a series of double membranes that ________ back and forth between the cell membrane and the _______________. These membranes fill the ____________________ but you cannot see them because they are very ___________________. The rough E.R. has ____________________ ...
... 2. Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER) is a series of double membranes that ________ back and forth between the cell membrane and the _______________. These membranes fill the ____________________ but you cannot see them because they are very ___________________. The rough E.R. has ____________________ ...
Six Grade Science Vocabulary
... A kingdom made up of complex, multicellular organisms that are usually green, have cell walls made of cellulose, cannot move around, and use the sun's energy to make sugar by photosynthesis. The location of an object. The energy that an object has because of the position, shape, or condition of the ...
... A kingdom made up of complex, multicellular organisms that are usually green, have cell walls made of cellulose, cannot move around, and use the sun's energy to make sugar by photosynthesis. The location of an object. The energy that an object has because of the position, shape, or condition of the ...
Midterm Review Cover page
... 35. Anaerobic respiration of glucose is a less efficient energy-releasing system than aerobic respiration of glucose. One of the reasons for this is that in anaerobic respiration (a) lactic acid contains much unreleased potential energy (b) water contains much released potential energy (c) oxygen se ...
... 35. Anaerobic respiration of glucose is a less efficient energy-releasing system than aerobic respiration of glucose. One of the reasons for this is that in anaerobic respiration (a) lactic acid contains much unreleased potential energy (b) water contains much released potential energy (c) oxygen se ...
Unit 7 - Cabarrus County Schools
... Describe the conditions necessary for natural selection (genetic variation, struggle for survival, fittest survive, reproduction which can lead to change in population frequency). Explain how various disease agents (bacteria, viruses, chemicals) can influence natural selection. Construct and use a d ...
... Describe the conditions necessary for natural selection (genetic variation, struggle for survival, fittest survive, reproduction which can lead to change in population frequency). Explain how various disease agents (bacteria, viruses, chemicals) can influence natural selection. Construct and use a d ...
Learning Objectives Chapter One
... 1. Briefly describe the unifying themes that characterize the biological sciences. 2. Diagram the hierarchy of structural levels in biological organization. 3. Explain how novel properties of life emerge from complex organization. 4. Describe the dilemma of reductionism. 5. Describe the two major dy ...
... 1. Briefly describe the unifying themes that characterize the biological sciences. 2. Diagram the hierarchy of structural levels in biological organization. 3. Explain how novel properties of life emerge from complex organization. 4. Describe the dilemma of reductionism. 5. Describe the two major dy ...
Syllabus - A Local Ecosystem
... The environment has an impact on all organisms in ways that a Biology student will learn to recognise and explain. Students are able to draw on existing knowledge of their own local area and expand on their understanding of biological concepts that can be identified through careful analysis of the b ...
... The environment has an impact on all organisms in ways that a Biology student will learn to recognise and explain. Students are able to draw on existing knowledge of their own local area and expand on their understanding of biological concepts that can be identified through careful analysis of the b ...
B - Sewanhaka Central High School District
... • Cells are the basic unit of structure for all living things. • Cells are the basic unit of function for all living things. • All cells come from pre-existing cells. ...
... • Cells are the basic unit of structure for all living things. • Cells are the basic unit of function for all living things. • All cells come from pre-existing cells. ...
pictures/graphs, etc. EOC Biology Rview Packet 2012-2013
... S. We found that methane, ammonia, hydrogen gases from early earth charged with electricity can form amino acids. T. I coined the term “cells” by looking at cork in the microscope. Goal 2: Learner will develop an understanding of the physical, chemical and cellular basis of life. Analyze the matter- ...
... S. We found that methane, ammonia, hydrogen gases from early earth charged with electricity can form amino acids. T. I coined the term “cells” by looking at cork in the microscope. Goal 2: Learner will develop an understanding of the physical, chemical and cellular basis of life. Analyze the matter- ...
Biology STAAR Review #4 – Body systems
... What is the function of enzymes? ___Catalyze or speed up chemical reactions__________ What would cause an enzyme to not function? __Extreme heat/pH – denatures enzyme (shape changes)_ Will most substrates will bind to most enzymes? __No, has to be the right shape___________ ...
... What is the function of enzymes? ___Catalyze or speed up chemical reactions__________ What would cause an enzyme to not function? __Extreme heat/pH – denatures enzyme (shape changes)_ Will most substrates will bind to most enzymes? __No, has to be the right shape___________ ...
File
... When we are growing, we need to make new big macromolecules for our body. Monomers join together to form ___________________by removing water. When you pull the water out, it allows the two parts to join together. This process is called: _____________________. When joining two monomers together, you ...
... When we are growing, we need to make new big macromolecules for our body. Monomers join together to form ___________________by removing water. When you pull the water out, it allows the two parts to join together. This process is called: _____________________. When joining two monomers together, you ...
BIOL 105 S 2012 QZ2 Q 120204.2
... 1. Characteristics of most living organisms include the ability to A) grow and reproduce. B) respond and adapt to their environment. C) control the external environment. D) A and B only E) all of the above 2. The waste products of metabolism are eliminated through the process of A) assimilation. B) ...
... 1. Characteristics of most living organisms include the ability to A) grow and reproduce. B) respond and adapt to their environment. C) control the external environment. D) A and B only E) all of the above 2. The waste products of metabolism are eliminated through the process of A) assimilation. B) ...
Life

Life is a characteristic distinguishing physical entities having biological processes (such as signaling and self-sustaining processes) from those that do not, either because such functions have ceased (death), or because they lack such functions and are classified as inanimate. Various forms of life exist such as plants, animals, fungi, protists, archaea, and bacteria. The criteria can at times be ambiguous and may or may not define viruses, viroids or potential artificial life as living. Biology is the primary science concerned with the study of life, although many other sciences are involved.The smallest contiguous unit of life is called an organism. Organisms are composed of one or more cells, undergo metabolism, maintain homeostasis, can grow, respond to stimuli, reproduce (either sexually or asexually) and, through evolution, adapt to their environment in successive generations. A diverse array of living organisms can be found in the biosphere of Earth, and the properties common to these organisms—plants, animals, fungi, protists, archaea, and bacteria—are a carbon- and water-based cellular form with complex organization and heritable genetic information.Abiogenesis is the natural process of life arising from non-living matter, such as simple organic compounds. The age of the Earth is about 4.54 billion years. The earliest life on Earth arose at least 3.5 billion years ago, during the Eoarchean Era when sufficient crust had solidified following the molten Hadean Eon. The earliest physical evidence of life on Earth is biogenic graphite from 3.7 billion-year-old metasedimentary rocks found in Western Greenland and microbial mat fossils in 3.48 billion-year-old sandstone found in Western Australia. Some theories, such as the Late Heavy Bombardment theory, suggest that life on Earth may have started even earlier, and may have begun as early as 4.25 billion years ago according to one study, and even earlier yet, 4.4 billion years ago, according to another. The mechanism by which life began on Earth is unknown, although many hypotheses have been formulated. Since emerging, life has evolved into a variety of forms, which have been classified into a hierarchy of taxa. Life can survive and thrive in a wide range of conditions. Nonetheless, more than 99 percent of all species, amounting to over five billion species, that ever lived on Earth are estimated to be extinct. Estimates on the number of Earth's current species range from 10 million to 14 million, of which about 1.2 million have been documented and over 86 percent have not yet been described.The chemistry leading to life may have begun shortly after the Big Bang, 13.8 billion years ago, during a habitable epoch when the Universe was only 10–17 million years old. Though life is confirmed only on the Earth, many think that extraterrestrial life is not only plausible, but probable or inevitable. Other planets and moons in the Solar System and other planetary systems are being examined for evidence of having once supported simple life, and projects such as SETI are trying to detect radio transmissions from possible alien civilizations.The meaning of life—its significance, origin, purpose, and ultimate fate—is a central concept and question in philosophy and religion. Both philosophy and religion have offered interpretations as to how life relates to existence and consciousness, and on related issues such as life stance, purpose, conception of a god or gods, a soul or an afterlife. Different cultures throughout history have had widely varying approaches to these issues.