* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Midterm Review Cover page
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Polyclonal B cell response wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Neuronal lineage marker wikipedia , lookup
Human genetic resistance to malaria wikipedia , lookup
Regeneration in humans wikipedia , lookup
Human embryogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Cell-penetrating peptide wikipedia , lookup
Artificial cell wikipedia , lookup
State switching wikipedia , lookup
Microbial cooperation wikipedia , lookup
Cell (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Adoptive cell transfer wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
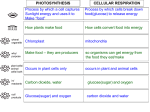
Midterm Review Sheet Chapters 1 Topics 8 Life functions 2 Diversity of life classification 4 Tools of Biologists The Cell 5 Basic Chemistry 3 6 Biochemistry 7 7B Nutrition Examples nutrition, transport, excretion, regulation, respiration, reproduction, synthesis, growth Homeostasis and Metabolism Kingdom, phylum, class, order, family genus, Species, 5 kingdoms, scientific names, Carolus Linnaeus Binomial Nomenclature microscopes, scientific method, electrophoresis, chromatography, cemtrifuge Animal vs. Plant Cells, organelles (cell wall, Centrioles, chloroplasts), Cell Theory, three exception to the cell theory Plasma Membrane *Passive transport, Mvmt w/o expenditure of energy HCLC, with the Concentration Gradient Ex. diffusion, Plasmolysis, osmosis, CYCLOSIS *Active transport Mvmt of materials using energy LCHC, against the concentration gradient Ex. Actions of the Contractile Vacuole, Endocytosis: Phagocytosis, Pinocytosis, Exocytosis Radioactive Isotope Acids (H+) and Bases(OH-) pH Scale, Acid Rain Organic vs inorganic Dehydration synthesis, hydrolysis Enzyme, three things that affect them Carbohydrates Proteins glucose mono, di amino acids polysaccarides Lipids Nucleic Acids 3 fatty acids glycerol nucleotides Autotrophic Nutrition *Photosynthesis, Light and Dark reactions, chloroplasts three things affecting photosynthesis, best +worst wavelengths *Chemosynthesis Heterotrophic Nutrition Amoeba, paramecium, Hydra, Yeast, Earthworm, Grasshopper, human, Human Digestive Malfunctions Transport: Amoeba, paramecium, Hydra, Earthworm, Grasshopper, IF time permits Human circulation and Malfunctions all 10 15% trace 20% trace 20% 40% BIOLOGY PRACTICE QUESTIONS GROUP III 1. Which process would include a net movement of sugar molecules through a membrane from a region of lower concentration to a region of higher concentration? (a) osmosis (b) cyclosis (c) active transport (d) passive transport 2. In the human body, the potassium ion can pass easily through cell membranes, yet the potassium ion concentration is higher inside many cells than it is outside these cells. This condition is mainly a result of the process of (a) passive transport (b) active transport (c) osmosis (d) pinocytosis 3. Chemical analysis indicates that the cell membrane is composed mainly of (a) proteins and starch (b) proteins and cellulose (c) lipids and starch (d) lipids and proteins 4. The net flow of materials through the membrane of a cell against a concentration gradient is known as (a) passive transport (b) active transport (c) osmosis (d) pinocytosis 5. The natural streaming of the cytoplasm that occurs within all cells is called (a) pinocytosis (b) phagocytosis (c) osmosis (d) cyclosis 6. When a cell uses energy to move materials across a cell membrane, the process is known as (a) osmosis (b) active transport (c) diffusion (d) passive transport 7. The diffusion of water molecules into and out of cells is called (a) cyclosis (b) pinocytosis (c) osmosis (d) homeostasis 8. The net movement of molecules into cells is most dependent upon the (a) selectivity of the plasma membrane (b) selectivity of the cell wal (c) number of nucleoli (d) number of chromosomes 9. A red blood cell placed in distilled water will swell and burst due to the diffusion of (a) salt from the red blood cell into the water (b) water into the red blood cel (c) water from the blood cell into its environmen (d) salts from the water into the red blood cell 10.The primary function of root hairs in a plant is to (a) prevent excessive loss of water (b) provide increased surface area for absorption (c) conduct water and minerals upward (d) conduct organic food materials upward and downward 11. Which structures are found in the veins of a maple leaf? (a) phloem cells (b) guard cells (c) chloroplasts (d) capillaries 12. The mechanism by which water moves from the roots to the leaves of a tall tree is known as (a) evaporation (b) transpiration (c) adhesion (d) transpirational pull 13.The destruction of xylem tissues in a maple tree most directly interferes with the movement of (a) carbon dioxide out of the leaves (b) water to the leaves (c) oxygen out of the leaves (d) nutrients down to the roots 14. The tissue that conducts organic food throughout a vascular plant is composed of (a) cambium cells (b) xylem cells (c) phloem cells (d) epidermal cells 15. The process by which water evaporates from the leaves of a plant is called (a) cohesion (b) respiration (c) active transport (d) transpiration 16. The dissolved sugars produced in the leaves of a maple tree move to the tree's roots through the (a) xylem (b) phloem (c) epidermis (d) guard cells 17. When a living geranium plant is enclosed in a large jar, water droplets appear on the inner surface of the jar. These water droplets are most likely the direct result of (a) hydrolysis and photosynthesis (b) light absorption and reflection (c) transpiration and condensation (d)intracellular and extracellular digestion 18. The circulatory system of the earthworm is most similar in structure and function to that of a (a) hydra (b) protozoan (c) grasshopper (d) human 19. Which organism contains an open circulatory system? (a) earthworm (b) grasshopper (c) hydra (d) ameba 20.How are nutrients transported from the blood of an earthworm to the muscle cells of its body wall? (a) The blood flows directly into the muscle cells. (b) The nutrients diffuse through capillary walls and through the cell membranes. (c) The nutrients pass through pores at the ends of nephridia. (d) The nutrients diffuse through the skin from the outside environment. 21. Which organism has an internal, closed circulatory system that brings materials from the external environment into contact with its cells? (a) ameba (b) paramecium (c) hydra (d) earthworm 22. Materials are circulated within the cells of a liydra by (a) osmosis, only (b) osmosis and diffusion (c) cyclosis and diffusion (d) a transport system 23. Hemoglobin is found in the blood of (a) humans and earthworms (b) earthworms and grasshoppers (c) grasshoppers and humans (d) humans, only 24. A circulatory system in which the blood remains within vessels is called a(n) (a)closed circulatory system (b)open circulatory system (c)internal circulatory system (d) external circulatory system 25. The intestinal fold of the earthworm and the villi of the human small intestine function primarily to (a) increase the surface area for absorption of digested nutrients (b) excrete metabolic wastes (c) circulate blood (d) force the movement of food in one direction through the digestive tract 26. Pairs of aortic arches are found in the circulatory system of the (a) hydra (b) grasshopper (c) earthworm (d) paramecium 27. Which compounds are produced in human muscle cells as a result of the oxidation of glucose in the absence of oxygen? (a) lipase and water (b) sucrase and carbon dioxide (c) ethyl alcohol and ATP (d) lactic acid and ATP 28. Most animals make energy available for cell activity by transferring the potential energy of glucose to ATP. This process occurs during (a) aerobic respiration, only (b) anaerobic respiration, only (c) both aerobic and anaerobic respiration (d) neither aerobic nor anaerobic respiration 29. Which of the following processes releases the greatest amount of energy? (a) the oxidation of one glucose molecule to lactic acid molecules (b) the oxidation of one glucose molecule to carbon dioxide and water molecules (c) the conversion of two glucose molecules to a maltose molecule (d) the conversion of one glucose molecule to alcohol and carbon dioxide molecules 30. Alcohol fermentation and aerobic respiration are similar in that both processes (a) utilize light (b) produce ethyl alcohol (c) require free oxygen (d) release carbon dioxide 31. Respiratory enzymes are present in (a) animal cells, but not plant cells (b) plant cells, but not animal cells (c) neither animal nor plant cells (d) both animal and plant cells 32. In animal cells, the energy to convert ADP to ATP comes directly from (a) hormones (b) sunlight (c) organic molecules (d) inorganic molecules 33. Vigorous activity of human voluntary muscle tissues may result in the production of lactic acid. Insufficient amount of which gas would result in the buildup of lactic acid in muscle cells? (a) carbon dioxide (b) nitrogen (c) oxygen (d) hydrogen 34. The organelles in which most of the reactions of aerobic cellular respiration take place are (a) ribosomes (b) chloroplasts (c) lysosomes (d) mitochondria 35. Anaerobic respiration of glucose is a less efficient energy-releasing system than aerobic respiration of glucose. One of the reasons for this is that in anaerobic respiration (a) lactic acid contains much unreleased potential energy (b) water contains much released potential energy (c) oxygen serves as the final hydrogen acceptor (d) chlorophyll is hydrolyzed into PGAL molecules 36. The tracheal tubes of the grasshopper and the air spaces of a geranium leaf are similar in that they both (a) regulate the flow of urea into and out of the organism (b) are the major sites for the ingestion of nutrients (c) contain enzymes that convert light energy to chemical bond energy (d) are surrounded by moist internal surfaces where gas exchange occurs 37. In the earthworm, the exchange of gases with the external environment occurs through the (a) skin (b) lungs (c) nephridia (d) pharynx 38. Protists obtain oxygen from the environment through (a) spiracles (b) cell membranes (c) contractile vacuoles (d) mitochondria 39. Openings in plant tissues that allow the exchange of respiratory gases are (a) tracheae and spiracles (b) spiracles and lenticels (c) lenticels and stomates (d) spiracles and stomates 40. The mucus secreted by cells of the external body wall of the earthworm (a) acts as a stimulus upon the paired nephridia (b) permits transpiration to be accomplished (c) is an excretory waste product (d) provides a moist surface for gas exchange 41. In the hydra, the exchange of respiratory gases takes place by (a) diffusion through the cell membranes (b)active transport through the skin (c)pinocytosis through the cell membranes (d) diffusion through lenticels BIOLOGY PRACTICE QUESTIONS GROUP III 1. c 11. A 21. D 31. D 41. a 2. b 12. D 22. C 32. c 3. d 13. B 23. A 33. c 4. b 14. C 24. A 34. d 5. d 15. D 25. A 35. a 6. b 16. B 26. C 36. d 7. c 17. C 27. D 37. a 8. a 18. D 28. C 38. b 9. b 19. B 29. B 39. c 10. b 20. B 30. D 40. D