Energy - Maples Elementary School
... energy because of where it is. It has the potential to move because it is above the ground and has somewhere to go. ...
... energy because of where it is. It has the potential to move because it is above the ground and has somewhere to go. ...
Notes on Energy
... 2. If the mass is doubled, the KE is doubled 3. If the velocity is doubled, the KE is quadrupled. B. Gravitational Potential Energy – stored energy due to position of an object. 1. As height above the ground increases (or other arbitrary point), the gravitational potential energy increases. 2. PE = ...
... 2. If the mass is doubled, the KE is doubled 3. If the velocity is doubled, the KE is quadrupled. B. Gravitational Potential Energy – stored energy due to position of an object. 1. As height above the ground increases (or other arbitrary point), the gravitational potential energy increases. 2. PE = ...
Chapter-9-Energy-notes
... Work is done when a force _______ causes an object to ____________. The force must act against _________________ or __________________. The motion has to be the same ___________________ as the force. Is the female walking up the stairs a force against friction or against gravity? Write an example of ...
... Work is done when a force _______ causes an object to ____________. The force must act against _________________ or __________________. The motion has to be the same ___________________ as the force. Is the female walking up the stairs a force against friction or against gravity? Write an example of ...
Mechanical & Thermal Energy Energy
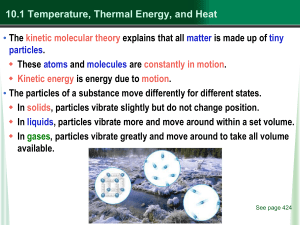
... The sum of all kinetic energies of all the particles comprising an object is thermal energy. (most matter expands as its thermal energy increases) The faster molecules are moving, the more thermal energy they have; which is why balls go farther in warm weather than cold. ...
... The sum of all kinetic energies of all the particles comprising an object is thermal energy. (most matter expands as its thermal energy increases) The faster molecules are moving, the more thermal energy they have; which is why balls go farther in warm weather than cold. ...
Physics_files/Unit 6 Review Part 3
... 6. A bowling ball has 1000J of kinetic energy and 8kg of mass. What is its velocity? 7. A ball sits on top of a pole 6m above the ground. Its mass is 3kg.’ a) What is its potential energy? b) If dropped off the top of the pole, how much potential energy does it have 3m from the ground? c) How much k ...
... 6. A bowling ball has 1000J of kinetic energy and 8kg of mass. What is its velocity? 7. A ball sits on top of a pole 6m above the ground. Its mass is 3kg.’ a) What is its potential energy? b) If dropped off the top of the pole, how much potential energy does it have 3m from the ground? c) How much k ...
Sample outline for Cornell Notes
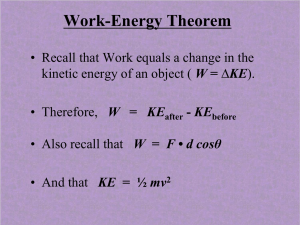
... 1) Work is done an object is caused to move a certain distance 2) Energy is the ability to do work or cause change I. Kinetic Energy 3) Kinetic Energy of an object due to its motion ...
... 1) Work is done an object is caused to move a certain distance 2) Energy is the ability to do work or cause change I. Kinetic Energy 3) Kinetic Energy of an object due to its motion ...
Energy
... Types of Energy 1) kinetic- energy of an object in motion 2) potential- the energy of an object’s position or shape. ...
... Types of Energy 1) kinetic- energy of an object in motion 2) potential- the energy of an object’s position or shape. ...
State Variables
... evaluated between the initial and final states – This is true whether or not the pressure ...
... evaluated between the initial and final states – This is true whether or not the pressure ...
Name: Period:______ Date:______ Infinite Potential Forms of
... 10. What types of properties do electromagnetic waves have? Do they need a medium through which to travel? Electromagnetic waves have electric and magnetic properties. They do not need a medium. 11. What is the unit for all forms of energy? The joule (J) 12. What is work? Work is the energy needed t ...
... 10. What types of properties do electromagnetic waves have? Do they need a medium through which to travel? Electromagnetic waves have electric and magnetic properties. They do not need a medium. 11. What is the unit for all forms of energy? The joule (J) 12. What is work? Work is the energy needed t ...
1. Discuss the following concepts
... 1. Discuss the following concepts (just writing formulas is not enough, use words) Enthropic principle Closed system Subsystem Distribution function Microcanonical distribution function 2. Consider N identical non-interacting 1D harmonic oscillators. The energy levels of the system will be given by: ...
... 1. Discuss the following concepts (just writing formulas is not enough, use words) Enthropic principle Closed system Subsystem Distribution function Microcanonical distribution function 2. Consider N identical non-interacting 1D harmonic oscillators. The energy levels of the system will be given by: ...
SCCS Physics Chapter 11 Study Guide Name
... 10. Describe an object that has rotational KE but no translational KE. 11. Describe an object that has translational KE but no rotational KE. 12. At what point in a pendulum’s swing are the the following quantities at maximum values? a) velocity b) potential energy c)kinetic energy PROBLEMS: (Draw a ...
... 10. Describe an object that has rotational KE but no translational KE. 11. Describe an object that has translational KE but no rotational KE. 12. At what point in a pendulum’s swing are the the following quantities at maximum values? a) velocity b) potential energy c)kinetic energy PROBLEMS: (Draw a ...
Solutions to Unit Conversion Practice Problems
... ME 201 Thermodynamics Practice Problems: Unit Manipulations Perform the following unit manipulations. a. A jet engine provides a thrust (force) of 2,000 lbf with a velocity of 600 km/hr. What is the power produced in horsepower? Solution Power = Force x Velocity Convert to SI Force = 2000 (lbf) x 4. ...
... ME 201 Thermodynamics Practice Problems: Unit Manipulations Perform the following unit manipulations. a. A jet engine provides a thrust (force) of 2,000 lbf with a velocity of 600 km/hr. What is the power produced in horsepower? Solution Power = Force x Velocity Convert to SI Force = 2000 (lbf) x 4. ...