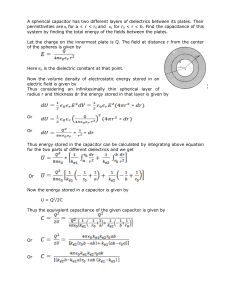
Motion, Forces and Energy Lecture 7: Potential Energy & Conservation
... Energy losses (non-conservative forces) Kinetic friction is an example of a non-conservative force. When a book slides across a surface which is not frictionless, it will eventually stop. But all the KE of the book is NOT transferred to internal energy of the book. We can find the speed of the mass ...
... Energy losses (non-conservative forces) Kinetic friction is an example of a non-conservative force. When a book slides across a surface which is not frictionless, it will eventually stop. But all the KE of the book is NOT transferred to internal energy of the book. We can find the speed of the mass ...
Intro to Energy - DuVall School News
... Energy can only be converted from one form to another (energy isn’t “lost”, it merely changes form) Energy conversions occur without loss or gain in energy (however, not all forms of energy are “useful”) ...
... Energy can only be converted from one form to another (energy isn’t “lost”, it merely changes form) Energy conversions occur without loss or gain in energy (however, not all forms of energy are “useful”) ...
Energy - Gyanpedia
... be obtained from the nucleus far exceed those that can be obtained from chemical processes, which involve only the outer regions of the atom. ...
... be obtained from the nucleus far exceed those that can be obtained from chemical processes, which involve only the outer regions of the atom. ...
Energy Forms - Greenwood County School District 52
... A. Mechanical Energy • 1. The total amount of kinetic and potential energy • 2. Anything in motion has mechanical energy! • Example – a toy wind up car ...
... A. Mechanical Energy • 1. The total amount of kinetic and potential energy • 2. Anything in motion has mechanical energy! • Example – a toy wind up car ...
Ideal Gas
... the amount of heat supplied to the system, minus the amount of work performed by the system on its surroundings. (Version of conservation of energy applied to thermodynamical systems. ...
... the amount of heat supplied to the system, minus the amount of work performed by the system on its surroundings. (Version of conservation of energy applied to thermodynamical systems. ...
work and energy - Indian School Al Wadi Al Kabir
... 9) Seema tried to push a heavy rock of mass 100 kg for 200 s, but could not move it. Find the work done by Seema at the end of 200s.Find out the power delivered by her. Give reason to justify the answer. 10) Distinguish between positive work and negative work. When you lift an object up, two forces ...
... 9) Seema tried to push a heavy rock of mass 100 kg for 200 s, but could not move it. Find the work done by Seema at the end of 200s.Find out the power delivered by her. Give reason to justify the answer. 10) Distinguish between positive work and negative work. When you lift an object up, two forces ...
verifying information
... 1. When an object has _______, it has the ability to cause __________. 2. ________ and ___________ energy are the two types of energy that relate to motion. 3. Potential energy is ________ energy that increases or decreases depending on an object’s ___________ and condition. 4. Kinetic energy is the ...
... 1. When an object has _______, it has the ability to cause __________. 2. ________ and ___________ energy are the two types of energy that relate to motion. 3. Potential energy is ________ energy that increases or decreases depending on an object’s ___________ and condition. 4. Kinetic energy is the ...
Energy Worksheet - Kinetic, Potential, and Elastic
... 8. The rock from question #7 falls to the bottom of the cliff. Just before it hits, its velocity is 18.25 m/s. What is it’s kinetic energy? ...
... 8. The rock from question #7 falls to the bottom of the cliff. Just before it hits, its velocity is 18.25 m/s. What is it’s kinetic energy? ...
Conservation of Mechanical Energy Law of Conservation of Energy
... of 80,000 km from the center of Earth. The meteorite is moving directly toward Earth with a velocity of 2000 m/s What will be the velocity of the meteorite when it hits Earth’s surface? Ignore all drag effects. ...
... of 80,000 km from the center of Earth. The meteorite is moving directly toward Earth with a velocity of 2000 m/s What will be the velocity of the meteorite when it hits Earth’s surface? Ignore all drag effects. ...
Slide 1
... A 50 kg Christina went running at 5 m/s and a gust of wind slowed her down to 3 m/s. What is the momentum of his new ...
... A 50 kg Christina went running at 5 m/s and a gust of wind slowed her down to 3 m/s. What is the momentum of his new ...
Conservation of Energy Worksheet
... The boulder begins to fall. What is its potential energy when it is 500-m above the ground? Where did the “lost” potential energy go? ...
... The boulder begins to fall. What is its potential energy when it is 500-m above the ground? Where did the “lost” potential energy go? ...