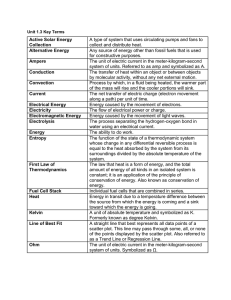
Unit 1.3 Key Terms Active Solar Energy Collection A type of system
... which all parts of the system have attained a uniform temperature which is the same as that of the system’s surroundings. A part of the physical world as described by its thermodynamic properties such as temperature, volume, pressure, concentration, surface tension, and viscosity. The study of the e ...
... which all parts of the system have attained a uniform temperature which is the same as that of the system’s surroundings. A part of the physical world as described by its thermodynamic properties such as temperature, volume, pressure, concentration, surface tension, and viscosity. The study of the e ...
potential energy
... potential energy: stored energy Chemical potential energy is due to electrostatic forces between charged particles. ...
... potential energy: stored energy Chemical potential energy is due to electrostatic forces between charged particles. ...
1. (a) Consider that an entropy S is as function of temperature T and
... temperature Ti,1 , whereas box 2 starts with Ti,2 . (The subscript “i” means “initial,” and “f ” will mean “final.”) Assume that both gases are ideal so that the internal energy is given by Ei (T ) = Ci T . Note that the boxes are neither permeable nor deformable. Now we put the boxes into thermal c ...
... temperature Ti,1 , whereas box 2 starts with Ti,2 . (The subscript “i” means “initial,” and “f ” will mean “final.”) Assume that both gases are ideal so that the internal energy is given by Ei (T ) = Ci T . Note that the boxes are neither permeable nor deformable. Now we put the boxes into thermal c ...
Chapter 2
... created nor destroyed but can be changed from one form to another. The quantity of energy remains the same. E = mc2 ...
... created nor destroyed but can be changed from one form to another. The quantity of energy remains the same. E = mc2 ...
Chemical Energy
... 1. Attracting – To draw by a physical force causing or tending to cause to approach, adhere, or unite; pull. 2. Chemical Energy – Energy which is stored within the bonds of atoms and molecules of a a. substance. Released when they are broken and the substance undergoes a chemical reaction. 3. Electr ...
... 1. Attracting – To draw by a physical force causing or tending to cause to approach, adhere, or unite; pull. 2. Chemical Energy – Energy which is stored within the bonds of atoms and molecules of a a. substance. Released when they are broken and the substance undergoes a chemical reaction. 3. Electr ...
A box is sitting on the floor
... 2) The normal force does work on the box, creating gravitational potential energy. 3) The cable pulling up the elevator does work on the box, creating gravitational potential energy. 4) The normal force must be larger than MAg in order to overcome gravity and create the upward energy. 5) The box has ...
... 2) The normal force does work on the box, creating gravitational potential energy. 3) The cable pulling up the elevator does work on the box, creating gravitational potential energy. 4) The normal force must be larger than MAg in order to overcome gravity and create the upward energy. 5) The box has ...
P2 Forces and energy Revision Sheet
... P2 Forces and energy Revision Sheet 1. What is the type of energy for objects that Kinetic energy are moving? [1] 2. What does momentum depend on? [2] ...
... P2 Forces and energy Revision Sheet 1. What is the type of energy for objects that Kinetic energy are moving? [1] 2. What does momentum depend on? [2] ...
Work and Energy
... (a) the weight of the box; (b) the potential energy lost by the box; (c) the kinetic energy gained by the box; (d) the work done against friction; (e) the size of the frictional force. Assume that the frictional force is constant and that no energy is lost in any other form. 7 A boy of mass 50 kg ru ...
... (a) the weight of the box; (b) the potential energy lost by the box; (c) the kinetic energy gained by the box; (d) the work done against friction; (e) the size of the frictional force. Assume that the frictional force is constant and that no energy is lost in any other form. 7 A boy of mass 50 kg ru ...
Energy Vocabulary
... absorption: the stopping of light by soaking it up sound energy: a form of energy made when something moves back and forth (vibration) vibrations: a rapid motion of the particles of an elastic body or substance back and forth chemical energy: energy that can be released by a chemical change fossil f ...
... absorption: the stopping of light by soaking it up sound energy: a form of energy made when something moves back and forth (vibration) vibrations: a rapid motion of the particles of an elastic body or substance back and forth chemical energy: energy that can be released by a chemical change fossil f ...
What is Energy?
... – The work done by a force of one newton (kg*m/s2)traveling through a distance of one meter; – The work required to move an electric charge of one coulomb through an electrical potential difference of one volt; or one coulomb volt, with the symbol C·V; – The work done to produce power of one watt co ...
... – The work done by a force of one newton (kg*m/s2)traveling through a distance of one meter; – The work required to move an electric charge of one coulomb through an electrical potential difference of one volt; or one coulomb volt, with the symbol C·V; – The work done to produce power of one watt co ...
Conservation of Energy
... Use the meter stick taped to the right door frame in the video for scaling purposes. Translate the origin to the lowest position marked in any frame so that the floor will be the zero reference point for potential energy. Plots of position-time, velocity-time, and acceleration-time are useful. ...
... Use the meter stick taped to the right door frame in the video for scaling purposes. Translate the origin to the lowest position marked in any frame so that the floor will be the zero reference point for potential energy. Plots of position-time, velocity-time, and acceleration-time are useful. ...
Atomic Structure
... a. Internal energy is related to temperature. The human body has fairly constant temperature, hence the internal energy does not decrease as described above. b. Internal energy is added to the body to balance the continual decrease due to heat flow from the body and work being done by the body. The ...
... a. Internal energy is related to temperature. The human body has fairly constant temperature, hence the internal energy does not decrease as described above. b. Internal energy is added to the body to balance the continual decrease due to heat flow from the body and work being done by the body. The ...
PEKE - Science
... • The ability to cause matter to move • The ability to cause matter to change • Measured in joules & calories ...
... • The ability to cause matter to move • The ability to cause matter to change • Measured in joules & calories ...
Work Review
... Potential Energy • Gravitational Potential Energy – PE due to an elevated position – Amount of PE is equal to the Work done in lifting it • W = Fd • The force (F) needed to lift it is the force equal and opposite to the objects weight Fw = mg • The distance (d) is the height, h above the Earth ...
... Potential Energy • Gravitational Potential Energy – PE due to an elevated position – Amount of PE is equal to the Work done in lifting it • W = Fd • The force (F) needed to lift it is the force equal and opposite to the objects weight Fw = mg • The distance (d) is the height, h above the Earth ...
Summary presentation 10.2 File
... transferred as heat and as work. It had its foundations with engineers in the 19th century who wanted to know what were the limitations of the Laws of physics with regard to the operation of steam engines and other machines that generate mechanical energy. ...
... transferred as heat and as work. It had its foundations with engineers in the 19th century who wanted to know what were the limitations of the Laws of physics with regard to the operation of steam engines and other machines that generate mechanical energy. ...