* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
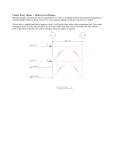
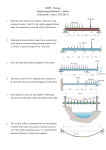
Download potential
Theoretical and experimental justification for the Schrödinger equation wikipedia , lookup
Relativistic mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear structure wikipedia , lookup
Shear wave splitting wikipedia , lookup
Eigenstate thermalization hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Work (thermodynamics) wikipedia , lookup