* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download potential
Theoretical and experimental justification for the Schrödinger equation wikipedia , lookup
Relativistic mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear structure wikipedia , lookup
Shear wave splitting wikipedia , lookup
Eigenstate thermalization hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Work (thermodynamics) wikipedia , lookup
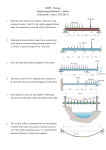
Ideal Mechanical Strength Lindsay O’Brien, Course 22 9/27/12 Clarification of Variables Variable Units Description eV/atom Binding energy per atom -- Shear elastic strain -- Hydrostatic invariant GPa Shear modulus GPa Bulk modulus m2 Slip plane area -- Bravais translational vector energy/area Generalized stacking fault energy/area Unstable stacking energy Potential Learning Landscape Metallic Bonding Ideal Strength Dislocations • Explanation of Metal Properties • Metastable State of Matter • Binding Energy • Potential Energy Landscape • Thought Experiment Versus Frenkel Sinusoidal • Shear Modulus G, Bulk Modulus B • Types of Dislocations • Explanation of Strength Discrepancies Potential Energy Landscape Activation Energy Turning Point Things to Remember: • First derivative of potential is force • Force = 0 corresponds to minimum or saddle point • When the second derivative of potential is zero, you’re at a turning point Concave Convex http://www.engr.ucsb.edu/~shell/che210d/Exploring_the_energy_landscape.pdf Shear and Bulk Moduli Hydrostatic! Measurement of Ideal Stress • Assumptions • Perfect lattice with no defects • Temperature = 0 K Oh no! ɛ hydro ɛ shear Prove it! • Electron glue is local (only care about atomic planes directly below and above) Further Simplification Small Deformation (Small x) Large Deformation (Large x) Thanks!