File
... Pangaea about 200 million years ago, before it began breaking up. Wegener named the southern portion of Pangaea Gondwana, and the northern portion Laurasia. ...
... Pangaea about 200 million years ago, before it began breaking up. Wegener named the southern portion of Pangaea Gondwana, and the northern portion Laurasia. ...
Divergent Margins
... Mid ocean ridge—the fracture zone along the ocean bottom where molten mantle material comes to the surface, thus creating new crust. This fracture can be seen beneath the ocean as a line of ridges that form as molten rock reaches the ocean bottom and solidifies. Plate Tectonics—the theory supported ...
... Mid ocean ridge—the fracture zone along the ocean bottom where molten mantle material comes to the surface, thus creating new crust. This fracture can be seen beneath the ocean as a line of ridges that form as molten rock reaches the ocean bottom and solidifies. Plate Tectonics—the theory supported ...
Lecture 15 - Empyrean Quest Publishers
... We also know core is denser iron and nickel because density of earth = 5.5 g/cm3, but surface rocks have a lower density than that. ...
... We also know core is denser iron and nickel because density of earth = 5.5 g/cm3, but surface rocks have a lower density than that. ...
Earth`s Interior PPT - Lyndhurst School District
... • Texture- The look and feel of a rock’s surface, determined by the size, shape, and pattern of a rock’s grains • Grains- The particles of minerals or other rocks that give a rock its texture. • Geologists look at grain shape, size, and pattern ...
... • Texture- The look and feel of a rock’s surface, determined by the size, shape, and pattern of a rock’s grains • Grains- The particles of minerals or other rocks that give a rock its texture. • Geologists look at grain shape, size, and pattern ...
Part B Continental Drift Slide Show
... fragile rock, fractured like the cracked shell of an egg. The pieces of the crust are Earth's tectonic plates -- there are 12 major ones -- and they float along on vast convection currents in the upper layer of the mantle called the asthenosphere. http://www.eas.purdue.edu/~braile/edumod/journey/jou ...
... fragile rock, fractured like the cracked shell of an egg. The pieces of the crust are Earth's tectonic plates -- there are 12 major ones -- and they float along on vast convection currents in the upper layer of the mantle called the asthenosphere. http://www.eas.purdue.edu/~braile/edumod/journey/jou ...
Chapter 33 Plate Tectonics
... – The movement of the magnetic pole over time(500 million years) suggests that either the pole moves around or the continents move ...
... – The movement of the magnetic pole over time(500 million years) suggests that either the pole moves around or the continents move ...
The Earth`s layers
... temperatures of the crust vary from air temperature on top to about 1600 degrees Fahrenheit (870 degrees Celsius) in the deepest parts of the crust. You can bake a loaf of bread in your oven at 350 degrees Fahrenheit, at 1600 degrees F. rocks begin to melt. The crust of the Earth is broken into many ...
... temperatures of the crust vary from air temperature on top to about 1600 degrees Fahrenheit (870 degrees Celsius) in the deepest parts of the crust. You can bake a loaf of bread in your oven at 350 degrees Fahrenheit, at 1600 degrees F. rocks begin to melt. The crust of the Earth is broken into many ...
plate tectonics
... • Slab-pull is a mechanism that contributes to plate motion in which cool, dense oceanic crust sinks into the mantle and “pulls” the trailing lithosphere along. It is thought to be the primary downward arm of convective flow in the mantle. • Ridge-push causes oceanic lithosphere to slide down the si ...
... • Slab-pull is a mechanism that contributes to plate motion in which cool, dense oceanic crust sinks into the mantle and “pulls” the trailing lithosphere along. It is thought to be the primary downward arm of convective flow in the mantle. • Ridge-push causes oceanic lithosphere to slide down the si ...
The Earth’s Layers - Welcome to Ms. George's Science Class
... Inner Core • Temperatures and pressures are so great here that the iron and nickel metals are squeezed together and vibrate in place as a solid. ...
... Inner Core • Temperatures and pressures are so great here that the iron and nickel metals are squeezed together and vibrate in place as a solid. ...
Chapter 18/19 Review Game Questions What are 3 types of
... What are 3 types of volcanism? A: Convergent, Divergent, Hot Spots What do you call the part of a volcano that collapses when the magma chamber empties? A: Caldera What do you call cracks in the Earth’s crust that magma flows in? A: Fissure 2/3 of all volcanism occurs where? A: At Divergent Boundari ...
... What are 3 types of volcanism? A: Convergent, Divergent, Hot Spots What do you call the part of a volcano that collapses when the magma chamber empties? A: Caldera What do you call cracks in the Earth’s crust that magma flows in? A: Fissure 2/3 of all volcanism occurs where? A: At Divergent Boundari ...
Plate Tectonics
... Mid-ocean ridges (rifts) normally form where tectonic plates are (1) converging (3) stationary (2) diverging (4) sliding past each other The motion of the convection currents in the mantle beneath the Atlantic Ocean appears to be mainly making this ocean basin (1) deeper (3) wider (2) shallower (4) ...
... Mid-ocean ridges (rifts) normally form where tectonic plates are (1) converging (3) stationary (2) diverging (4) sliding past each other The motion of the convection currents in the mantle beneath the Atlantic Ocean appears to be mainly making this ocean basin (1) deeper (3) wider (2) shallower (4) ...
Unit 5: Plate Tectonics Review Guide Things you need to know for
... Theory of Continental Drift and Pangaea What are layers of earth and what the Lithosphereic plates move on What are the two types of lithospheric plates? Explain the difference between each (at least 3 differences)? What types of rocks make up continental and oceanic crust? What is a mid-ocean ridge ...
... Theory of Continental Drift and Pangaea What are layers of earth and what the Lithosphereic plates move on What are the two types of lithospheric plates? Explain the difference between each (at least 3 differences)? What types of rocks make up continental and oceanic crust? What is a mid-ocean ridge ...
Name: Date: Chapter 9 Changes to Earth`s Surface Study Guide
... Chapter 9 Changes to Earth’s Surface Study Guide When preparing for this test make sure you study…. Three packets from this chapter This study guide Vocab Words listed below: landform topography glacier ...
... Chapter 9 Changes to Earth’s Surface Study Guide When preparing for this test make sure you study…. Three packets from this chapter This study guide Vocab Words listed below: landform topography glacier ...
CONSTRUCTING A SEA-FLOOR SPREADING MODEL
... The lithosphere is composed of the crust and upper mantle and is broken into large pieces know as plates. The lithospheric plates, carrying both oceanic and continental rock, “float” on the plastic part of the mantle below the lithosphere. Plates move together, separate, and slide past each other cr ...
... The lithosphere is composed of the crust and upper mantle and is broken into large pieces know as plates. The lithospheric plates, carrying both oceanic and continental rock, “float” on the plastic part of the mantle below the lithosphere. Plates move together, separate, and slide past each other cr ...
Portraying the Earth
... continental crust, it comes in contact with the asthenosphere, creating magma The magma begins to rise, the continental crust is pushed up and volcanoes are formed Earthquakes occur when the relatively cooler sinking lithosphere comes in contact with the hot asthenosphere This contact causes t ...
... continental crust, it comes in contact with the asthenosphere, creating magma The magma begins to rise, the continental crust is pushed up and volcanoes are formed Earthquakes occur when the relatively cooler sinking lithosphere comes in contact with the hot asthenosphere This contact causes t ...
ch9
... • Slab-pull is a mechanism that contributes to plate motion in which cool, dense oceanic crust sinks into the mantle and “pulls” the trailing lithosphere along. It is thought to be the primary downward arm of convective flow in the mantle. • Ridge-push causes oceanic lithosphere to slide down the si ...
... • Slab-pull is a mechanism that contributes to plate motion in which cool, dense oceanic crust sinks into the mantle and “pulls” the trailing lithosphere along. It is thought to be the primary downward arm of convective flow in the mantle. • Ridge-push causes oceanic lithosphere to slide down the si ...
Plate Boundaries-new
... § Define the theory of plate tectonics. § Explain how the Earth is divided into layers based on chemical and physical properties. § Define the asthenosphere and lithosphere. § Describe the plate motion at each of the three different plate boundaries. § Describe the features associated with each ...
... § Define the theory of plate tectonics. § Explain how the Earth is divided into layers based on chemical and physical properties. § Define the asthenosphere and lithosphere. § Describe the plate motion at each of the three different plate boundaries. § Describe the features associated with each ...
Study Guide: Plate Tectonics Test
... animal, were found in only two regions, southern Africa and the southern part of South America. These two regions are far from each other and separated by the Atlantic Ocean, further supporting that the continents were once joined. c. Climate Evidence: An island in the Arctic Ocean contain fossils o ...
... animal, were found in only two regions, southern Africa and the southern part of South America. These two regions are far from each other and separated by the Atlantic Ocean, further supporting that the continents were once joined. c. Climate Evidence: An island in the Arctic Ocean contain fossils o ...
C4 sciencespot.net center
... 8. In the diagram, what two types of plates are colliding? ________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ 9. What is happening to the continental plate? _________________________________ ________________________________________________________________ ...
... 8. In the diagram, what two types of plates are colliding? ________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ 9. What is happening to the continental plate? _________________________________ ________________________________________________________________ ...
Volcanism in Response to Plate Flexure
... a mantle plume) at a 410-km depth in this area was reported by Obayashi et al. (17); however, there is no evidence for a conduit or connection of any type between this low-velocity region and the shallower mantle. Our geochemical evidence strongly supports a depleted mantle (nonplume-like) source. F ...
... a mantle plume) at a 410-km depth in this area was reported by Obayashi et al. (17); however, there is no evidence for a conduit or connection of any type between this low-velocity region and the shallower mantle. Our geochemical evidence strongly supports a depleted mantle (nonplume-like) source. F ...
1.Beginning of the Earth
... layer of molten rock or magma, which is inside the circle slowly. Depths ranging from 3502900 kilometers, Temperatures will rise from about 2250 to about 4500 degrees C, The mantle and the lower support plate are the asthenosphere. ...
... layer of molten rock or magma, which is inside the circle slowly. Depths ranging from 3502900 kilometers, Temperatures will rise from about 2250 to about 4500 degrees C, The mantle and the lower support plate are the asthenosphere. ...
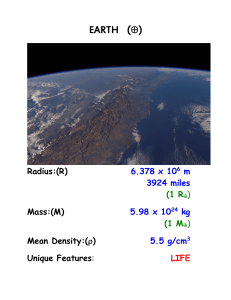
EARTH (¿)
... Structure of the Earth Deep Wells: - deepest is 12 km (7.5 miles) in Russia - temp at bottom = 190oC or 375oF ! Seismology - science of shock waves - caused by earthquakes, volcanoes, etc. - shows density and boundary of regions Two basic types of seismic waves: Shear (S) waves: - material displace ...
... Structure of the Earth Deep Wells: - deepest is 12 km (7.5 miles) in Russia - temp at bottom = 190oC or 375oF ! Seismology - science of shock waves - caused by earthquakes, volcanoes, etc. - shows density and boundary of regions Two basic types of seismic waves: Shear (S) waves: - material displace ...
Large igneous province

A large igneous province (LIP) is an extremely large accumulation of igneous rocks, including liquid rock (intrusive) or volcanic rock formations (extrusive), when hot magma extrudes from inside the Earth and flows out. The source of many or all LIPs is variously attributed to mantle plumes or to processes associated with plate tectonics. Types of LIPs can include large volcanic provinces (LVP), created through flood basalt and large plutonic provinces (LPP). Eleven distinct flood basalt episodes occurred in the past 250 million years, creating volcanic provinces, which coincided with mass extinctions in prehistoric times. Formation depends on a range of factors, such as continental configuration, latitude, volume, rate, duration of eruption, style and setting (continental vs. oceanic), the preexisting climate state, and the biota resilience to change.