Name: ____________ Date: 8th Grade Science Earth Surface Mr
... hardens. This process may take place inside Earth or on the surface. Inside Earth, magma cools so slowly that is may take a thousand years for a rock to form. One of the most common kinds of igneous rocks is granite. Granite is made by magma cooling inside Earth. Granite is light colored with large ...
... hardens. This process may take place inside Earth or on the surface. Inside Earth, magma cools so slowly that is may take a thousand years for a rock to form. One of the most common kinds of igneous rocks is granite. Granite is made by magma cooling inside Earth. Granite is light colored with large ...
TEK 8.9B: Formation of Crustal Features
... slowly over millions of years, opening up gaps that fill with lava, colliding plates together to build mountains, and subducting ocean crust to form volcanic mountains. (Tutorial 38 describes the historic development of the plate tectonic theory.) The USGS diagram below shows the major plate boundar ...
... slowly over millions of years, opening up gaps that fill with lava, colliding plates together to build mountains, and subducting ocean crust to form volcanic mountains. (Tutorial 38 describes the historic development of the plate tectonic theory.) The USGS diagram below shows the major plate boundar ...
Formation of Crustal Features - Flipped Out Science with Mrs. Thomas!
... slowly over millions of years, opening up gaps that fill with lava, colliding plates together to build mountains, and subducting ocean crust to form volcanic mountains. (Tutorial 38 describes the historic development of the plate tectonic theory.) The USGS diagram below shows the major plate boundar ...
... slowly over millions of years, opening up gaps that fill with lava, colliding plates together to build mountains, and subducting ocean crust to form volcanic mountains. (Tutorial 38 describes the historic development of the plate tectonic theory.) The USGS diagram below shows the major plate boundar ...
Earth`s Interior
... Volcanism brings material to Earth’s surface Other processes (subduction) return more dense material to interior Conclusion: Earth is still under construction! ...
... Volcanism brings material to Earth’s surface Other processes (subduction) return more dense material to interior Conclusion: Earth is still under construction! ...
Inside the Earth
... Next, calculate the time it would take the object to get 240 miles if it traveled at that same speed. Show your work!!!! ...
... Next, calculate the time it would take the object to get 240 miles if it traveled at that same speed. Show your work!!!! ...
Slide 1
... ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________ ...
... ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________ ...
Earth
... Liquid outer core (2,885 - 5,155 km); Solid inner core (5,155 - 7,371 km). Inner core is hotter than the outer core, but intense pressure ...
... Liquid outer core (2,885 - 5,155 km); Solid inner core (5,155 - 7,371 km). Inner core is hotter than the outer core, but intense pressure ...
Volcanoes and mountains
... Landform changes • Landforms on Earth can be created or changed by volcanic eruptions and mountain building forces ...
... Landform changes • Landforms on Earth can be created or changed by volcanic eruptions and mountain building forces ...
NEW ZEALAND ROCkS AND LANDFORMS
... Tapuaenuku. Volcanism associated with mantle ‘hot–spots’ under southern New Zealand, away from the plate boundary subduction zones, has resulted in a broad volcanic province stretching from the Campbell Plateau, through eastern South Island to the Chatham Islands. The mainly basaltic volcanic activi ...
... Tapuaenuku. Volcanism associated with mantle ‘hot–spots’ under southern New Zealand, away from the plate boundary subduction zones, has resulted in a broad volcanic province stretching from the Campbell Plateau, through eastern South Island to the Chatham Islands. The mainly basaltic volcanic activi ...
Earth`s Surface Vocabulary
... Rock that is formed when heat and pressure change the minerals in the igneous or sedimentary rocks; examples are marble, soapstone, and slate. ...
... Rock that is formed when heat and pressure change the minerals in the igneous or sedimentary rocks; examples are marble, soapstone, and slate. ...
Module E: Unit 4, Lesson 1 – Earth`s Layers
... Module E: Unit 4, Lesson 1 – Earth’s Layers What is inside Earth? • Earth is made of several layers. • Each layer has its own characteristic properties. • Scientists think about Earth’s layers in two ways—in terms of chemical composition and in terms of physical properties. What are Earth’s composit ...
... Module E: Unit 4, Lesson 1 – Earth’s Layers What is inside Earth? • Earth is made of several layers. • Each layer has its own characteristic properties. • Scientists think about Earth’s layers in two ways—in terms of chemical composition and in terms of physical properties. What are Earth’s composit ...
lab case for pacific plate motion.pub
... Lab: A Case for Pacific Plate Motion COORDINATED SCIENCE 1 Background: To measure motion you have to have a starting and an ending point. You must also know the time it took to get from start to end. Volcanic activity associated with a hot spot beneath Hawaii gives geologists exactly that. How can s ...
... Lab: A Case for Pacific Plate Motion COORDINATED SCIENCE 1 Background: To measure motion you have to have a starting and an ending point. You must also know the time it took to get from start to end. Volcanic activity associated with a hot spot beneath Hawaii gives geologists exactly that. How can s ...
Plate Tectonic Test Review
... due to extremely high temperature • Inner core (1200km) is solid due to extremely high pressure. Return to Quiz ...
... due to extremely high temperature • Inner core (1200km) is solid due to extremely high pressure. Return to Quiz ...
Slide 1
... There can never be any gaps on Earth so when tectonic plates pull apart magma from the mantle rises up and solidifies to fill the space. If oceanic crust is pulling apart from oceanic crust then new crust will made. This means that in some places the sea floor is actually growing! This is a process ...
... There can never be any gaps on Earth so when tectonic plates pull apart magma from the mantle rises up and solidifies to fill the space. If oceanic crust is pulling apart from oceanic crust then new crust will made. This means that in some places the sea floor is actually growing! This is a process ...
Plate Tectonics
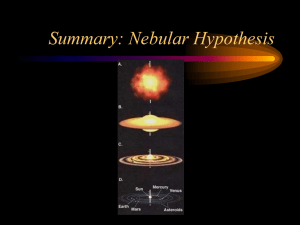
... – Planets 1. accretion of Heavy elements 2. attraction of Light gases to dense nucleus ...
... – Planets 1. accretion of Heavy elements 2. attraction of Light gases to dense nucleus ...
Plate Tectonics
... All plates are moving at _______________________ There are two types of plates: Continental Plates and Oceanic plates Each plate could be doing all three motions, just on ____________________ ______________________ These movements will create the _________________________ and _____________ ...
... All plates are moving at _______________________ There are two types of plates: Continental Plates and Oceanic plates Each plate could be doing all three motions, just on ____________________ ______________________ These movements will create the _________________________ and _____________ ...
Volcanoes Post-lab Lesson Plan
... explosive eruptions or the effusion of large volumes of lava flows. Cinder cone: A steep-sided volcano formed by the explosive eruption of cinders that pile up around a vent. Cinders are lava fragments a few centimeters in diameter. Hot spot: An area in the middle of a lithospheric plate where m ...
... explosive eruptions or the effusion of large volumes of lava flows. Cinder cone: A steep-sided volcano formed by the explosive eruption of cinders that pile up around a vent. Cinders are lava fragments a few centimeters in diameter. Hot spot: An area in the middle of a lithospheric plate where m ...
Notes: Plate Tectonics - Riverdale Middle School
... recorded by rocks in strips parallel to ridges ...
... recorded by rocks in strips parallel to ridges ...
Lab 3&4 PowerPoint
... When comparing our model to the earth, what do the following parts of your model represent? • The heat source (candle): Core • The moving syrup: Mantle Convection • The cardboard pieces: pieces of the Earth’s crust ...
... When comparing our model to the earth, what do the following parts of your model represent? • The heat source (candle): Core • The moving syrup: Mantle Convection • The cardboard pieces: pieces of the Earth’s crust ...
The top layer of the earth is the Crust made of mostly
... The top layer of the earth is the Crust made of mostly soil and rocks. Smaller rocks come from the breakage and weathering of larger rocks. The second layer is the Mantle made of hot rocks and metals. Geologists believe the Core is made of a solid ball of metal. ...
... The top layer of the earth is the Crust made of mostly soil and rocks. Smaller rocks come from the breakage and weathering of larger rocks. The second layer is the Mantle made of hot rocks and metals. Geologists believe the Core is made of a solid ball of metal. ...
Week 3 (Norton), part b (pdf, 5.7 MB)
... zone being experienced by the edges of the Eurasian Plate is where the Indian Plate is jamming into its southern edge, where the Himalayan upthrust is taking place. Major convergences where marine crust is subducted beneath continental crust are confined to the Pacific Ocean and its rim, such as in ...
... zone being experienced by the edges of the Eurasian Plate is where the Indian Plate is jamming into its southern edge, where the Himalayan upthrust is taking place. Major convergences where marine crust is subducted beneath continental crust are confined to the Pacific Ocean and its rim, such as in ...
Large igneous province

A large igneous province (LIP) is an extremely large accumulation of igneous rocks, including liquid rock (intrusive) or volcanic rock formations (extrusive), when hot magma extrudes from inside the Earth and flows out. The source of many or all LIPs is variously attributed to mantle plumes or to processes associated with plate tectonics. Types of LIPs can include large volcanic provinces (LVP), created through flood basalt and large plutonic provinces (LPP). Eleven distinct flood basalt episodes occurred in the past 250 million years, creating volcanic provinces, which coincided with mass extinctions in prehistoric times. Formation depends on a range of factors, such as continental configuration, latitude, volume, rate, duration of eruption, style and setting (continental vs. oceanic), the preexisting climate state, and the biota resilience to change.