14 - Plasticity
... Since no one has reached the mantle, scientists can only guess as to its actual make-up. All earthquake waves can pass through the mantle, which means it is a solid (S-waves cannot pass through liquids). Yet the tectonic plates of the earth “float” on the mantle, moving by convection currents in the ...
... Since no one has reached the mantle, scientists can only guess as to its actual make-up. All earthquake waves can pass through the mantle, which means it is a solid (S-waves cannot pass through liquids). Yet the tectonic plates of the earth “float” on the mantle, moving by convection currents in the ...
Seafloor Spreading - explained how continents could move
... Seafloor Spreading - explained how continents could move ocean floor young compared to land little sediment - igneous rock Midocean Ridge mountain range in center of oceans molten rock from mantle rises through crack spreads outward and hardens carries continents along record of Earth's magnetic fie ...
... Seafloor Spreading - explained how continents could move ocean floor young compared to land little sediment - igneous rock Midocean Ridge mountain range in center of oceans molten rock from mantle rises through crack spreads outward and hardens carries continents along record of Earth's magnetic fie ...
What Are Rocks - Lewiston School District
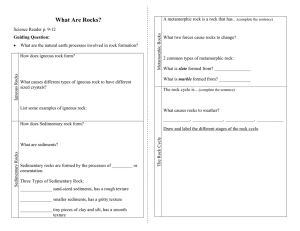
... What are the natural earth processes involved in rock formation? ...
... What are the natural earth processes involved in rock formation? ...
Lava
... Volcanic rock is rock that erupted on the surface and cooled quickly. This could take few minutes to a few hours. Volcanic rocks or extrusive rocks are Fine Grained or have small mineral crystals ...
... Volcanic rock is rock that erupted on the surface and cooled quickly. This could take few minutes to a few hours. Volcanic rocks or extrusive rocks are Fine Grained or have small mineral crystals ...
Rock Cycle Review
... ____ 25. model that illustrates the processes that create and change rocks ____ 26. magma that reaches Earth’s surface and flows from volcanoes ____ 27. a mixture of minerals, organic matter, volcanic glass, or other materials ____ 28. process by which sediments are pressed together to form rock ___ ...
... ____ 25. model that illustrates the processes that create and change rocks ____ 26. magma that reaches Earth’s surface and flows from volcanoes ____ 27. a mixture of minerals, organic matter, volcanic glass, or other materials ____ 28. process by which sediments are pressed together to form rock ___ ...
science questions
... The gravitational field of the Moon is only about 1.6 m/s2, compared to 9.8 m/s2 on Earth. This is about 1/6th as strong. The effect on our physiology is significant, especially for bones, which have developed on Earth in response to our gravity. Without this gravity (or with it largely diminished), ...
... The gravitational field of the Moon is only about 1.6 m/s2, compared to 9.8 m/s2 on Earth. This is about 1/6th as strong. The effect on our physiology is significant, especially for bones, which have developed on Earth in response to our gravity. Without this gravity (or with it largely diminished), ...
Homework01h - Kean University
... 7. Water driven out of a subducting ocean plate causes partial melting in the nearby mantle. The magma that may rise to form volcanoes. True or False? 8. The Himalayan Mountains are an example of a Collisional boundary. True or False? 9. When air is heated it contracts. True or False? 10. The Andes ...
... 7. Water driven out of a subducting ocean plate causes partial melting in the nearby mantle. The magma that may rise to form volcanoes. True or False? 8. The Himalayan Mountains are an example of a Collisional boundary. True or False? 9. When air is heated it contracts. True or False? 10. The Andes ...
Impact cratering
... • Molten rock rises for a number of reasons – It is of lower density than solid rock. – Most of Earth’s interior is NOT molten, so molten rock can be squeezed up to the surface. – Contains trapped gases that expand as it rises. ...
... • Molten rock rises for a number of reasons – It is of lower density than solid rock. – Most of Earth’s interior is NOT molten, so molten rock can be squeezed up to the surface. – Contains trapped gases that expand as it rises. ...
Sedimentary = Intrusive Igneous = Extrusive Igneous = Sedimentary
... Intrusive = slow cooling; formation of large crystals Extrusive = fast cooling; formation of s mall to No crystals Sedimentary = ● weathering, erosion, sediments in water to cementation of sediments ● components: pieces of rock, minerals, fossils, etc. ● mechanical, chemical or organic processes ...
... Intrusive = slow cooling; formation of large crystals Extrusive = fast cooling; formation of s mall to No crystals Sedimentary = ● weathering, erosion, sediments in water to cementation of sediments ● components: pieces of rock, minerals, fossils, etc. ● mechanical, chemical or organic processes ...
Name Period Study Guide for 7th Grade Science Final Exam
... 16. The ______________ ________________ of a rock is determined through radioactive dating. 17. The geological time scale is record of __________________ _________________ and the ______________ ___ _____________ forms as shown in the fossil record. 18. Early Earth was very hot and had very little _ ...
... 16. The ______________ ________________ of a rock is determined through radioactive dating. 17. The geological time scale is record of __________________ _________________ and the ______________ ___ _____________ forms as shown in the fossil record. 18. Early Earth was very hot and had very little _ ...
Petrology
... Igneous petrology focuses on the composition and texture of igneous rocks (rocks such as granite or basalt which have crystallized from molten rock or magma). Igneous rocks include volcanic and plutonic rocks. Sedimentary petrology focuses on the composition and texture of sedimentary rocks (rocks s ...
... Igneous petrology focuses on the composition and texture of igneous rocks (rocks such as granite or basalt which have crystallized from molten rock or magma). Igneous rocks include volcanic and plutonic rocks. Sedimentary petrology focuses on the composition and texture of sedimentary rocks (rocks s ...
plate tectonics
... • Slab-pull is a mechanism that contributes to plate motion in which cool, dense oceanic crust sinks into the mantle and “pulls” the trailing lithosphere along. It is thought to be the primary downward arm of convective flow in the mantle. • Ridge-push causes oceanic lithosphere to slide down the si ...
... • Slab-pull is a mechanism that contributes to plate motion in which cool, dense oceanic crust sinks into the mantle and “pulls” the trailing lithosphere along. It is thought to be the primary downward arm of convective flow in the mantle. • Ridge-push causes oceanic lithosphere to slide down the si ...
as a PDF
... Earth’s mantle and the history of continental movement around Australia, which was determined from geological evidence, as guidelines for their computer simulations. From the models, they found that Australia had an inland sea 120mya ago when the global sea levels were low, because Australia, which ...
... Earth’s mantle and the history of continental movement around Australia, which was determined from geological evidence, as guidelines for their computer simulations. From the models, they found that Australia had an inland sea 120mya ago when the global sea levels were low, because Australia, which ...
Geol 101: Physical Geology Spring 2002
... A. the Earth is comprised of many layers with different densities B. the deep interior of the Earth must have a density greater than 5.5 g/cm 3 C. the deep interior of the Earth must have a density less than 5.5 g/cm 3 D. the deep interior of the Earth must have a density less than 2.5 g/cm3 E. meas ...
... A. the Earth is comprised of many layers with different densities B. the deep interior of the Earth must have a density greater than 5.5 g/cm 3 C. the deep interior of the Earth must have a density less than 5.5 g/cm 3 D. the deep interior of the Earth must have a density less than 2.5 g/cm3 E. meas ...
Igneous rocks
... more minerals • The rock cycle shows how one type of rocky material gets transformed into another – Representation of how rocks are formed, broken down, and processed in response to changing conditions – Processes may involve interactions of geosphere with hydrosphere, atmosphere and/or biosphere – ...
... more minerals • The rock cycle shows how one type of rocky material gets transformed into another – Representation of how rocks are formed, broken down, and processed in response to changing conditions – Processes may involve interactions of geosphere with hydrosphere, atmosphere and/or biosphere – ...
Pre-visit Lesson: Grades K-2 - Washington State Parks and
... Demonstration: Plate tectonics is the theory that the earth’s crust is made up of separate plates that are constantly moving on the mantle. Where plates meet there is a point where the crust can break apart, earthquakes can occur, and the crust can crumple forming mountains. This theory can be shown ...
... Demonstration: Plate tectonics is the theory that the earth’s crust is made up of separate plates that are constantly moving on the mantle. Where plates meet there is a point where the crust can break apart, earthquakes can occur, and the crust can crumple forming mountains. This theory can be shown ...
Getting to Know: Why Earthquakes Occur
... Tectonic plate movement is the primary cause of earthquakes. As tectonic plates move, they grind against each other or push into each other. The edges of the plates rub against each other with a lot of friction, and the edges can become stuck for awhile. If this happens, pressure builds up in the cr ...
... Tectonic plate movement is the primary cause of earthquakes. As tectonic plates move, they grind against each other or push into each other. The edges of the plates rub against each other with a lot of friction, and the edges can become stuck for awhile. If this happens, pressure builds up in the cr ...
Earth`s Layers
... •Thickness varies. Under mountains it can be as thick as 60 km and less than 5 km under the ocean. •It is the least dense of all the layers. (lightest layer) •It is made up of silicon and oxygen. ...
... •Thickness varies. Under mountains it can be as thick as 60 km and less than 5 km under the ocean. •It is the least dense of all the layers. (lightest layer) •It is made up of silicon and oxygen. ...
Earth`s Layers ppt
... •Thickness varies. Under mountains it can be as thick as 60 km and less than 5 km under the ocean. •It is the least dense of all the layers. (lightest layer) •It is made up of silicon and oxygen. ...
... •Thickness varies. Under mountains it can be as thick as 60 km and less than 5 km under the ocean. •It is the least dense of all the layers. (lightest layer) •It is made up of silicon and oxygen. ...
Volcanoes and Igneous Activity Earth
... • Slab-pull is a mechanism that contributes to plate motion in which cool, dense oceanic crust sinks into the mantle and “pulls” the trailing lithosphere along. It is thought to be the primary downward arm of convective flow in the mantle. • Ridge-push causes oceanic lithosphere to slide down the si ...
... • Slab-pull is a mechanism that contributes to plate motion in which cool, dense oceanic crust sinks into the mantle and “pulls” the trailing lithosphere along. It is thought to be the primary downward arm of convective flow in the mantle. • Ridge-push causes oceanic lithosphere to slide down the si ...
Igneous and Metamorphic Rock
... 1. What is extrusive igneous rock? 2. What is the most common extrusive rock and where is it found? 3. What is magma? 4. What is lava? 5. Where does intrusive igneous rock form? 6. Does intrusive igneous rock form from lava or magma? 7. When molten rock takes a long time to cool, are the crystals in ...
... 1. What is extrusive igneous rock? 2. What is the most common extrusive rock and where is it found? 3. What is magma? 4. What is lava? 5. Where does intrusive igneous rock form? 6. Does intrusive igneous rock form from lava or magma? 7. When molten rock takes a long time to cool, are the crystals in ...
chapter 4 study guide
... What are the seven physical properties used to identify minerals? Name and describe each. ...
... What are the seven physical properties used to identify minerals? Name and describe each. ...
Large igneous province

A large igneous province (LIP) is an extremely large accumulation of igneous rocks, including liquid rock (intrusive) or volcanic rock formations (extrusive), when hot magma extrudes from inside the Earth and flows out. The source of many or all LIPs is variously attributed to mantle plumes or to processes associated with plate tectonics. Types of LIPs can include large volcanic provinces (LVP), created through flood basalt and large plutonic provinces (LPP). Eleven distinct flood basalt episodes occurred in the past 250 million years, creating volcanic provinces, which coincided with mass extinctions in prehistoric times. Formation depends on a range of factors, such as continental configuration, latitude, volume, rate, duration of eruption, style and setting (continental vs. oceanic), the preexisting climate state, and the biota resilience to change.