* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Plate Tectonics
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
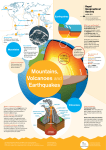
Name _______________________ Date ________________ Unit 6 Notes Packet: Plate Tectonics Block _____ Layers of the Earth 1. ____________________ Once you get past the soil of the earth, you hit the bedrock, known as the first layer of Earth called the _______________ Only about ______ miles thick and _______ miles at its thinnest part Found under our __________ and under the ______________ _____________ and _______________ Broken into large segments that move called __________________ 2. ________________________ Once you get past the crust, you end up in the second layer called the ___________________ __________________ layer of the Earth Contains the ________________________________ that raise hot mantle material up and allows cool mantle material to sink Creates the motions of ______________________________________ ____________________________________(TBD) 3. _____________________________ Third layer of the Earth is called the ___________________________ This a _____________ layer of the Earth made of ______________________ This spinning outer core is what makes the ___________________ that protects us from the dangerous ____________________________ of space It stays liquid because it is the perfect combination of ___________________ and _____________________ 4. ____________________________ The very center of our Earth is called the ___________________ This is a ________________ chunk of __________________________ that is the source of our ___________________ on Earth It stays solid because of all of the _____________________ that is pressing down on top of it from all the materials above it. The plates are not just made of crust The plates of the Earth are made of the _______________ and a the _______________________________________________ called the _______________________________ This plates are constantly moving and changing size and shape Under the lithosphere, there is a layer of mantle that is super soft (like ______________________________) that the plates _______________ on top of This layer is called the _______________________________ Activity 1: Follow along with the instructor as they diagram the layer of the Earth beneath us. Plate Movements The plates do not just move in one direction 3 Types of Movements 1. _______________________________ 2. _______________________________ 3. __________________________________________________ All plates are moving at _______________________ There are two types of plates: Continental Plates and Oceanic plates Each plate could be doing all three motions, just on ____________________ ______________________ These movements will create the _________________________ and _______________________________ that cover the lands and ocean floors, and other _______________________ that we come in contact with Types of Plate Boundaries 1. __________________________ Plate Boundaries Two plates _______________________________ Where the two plates meet, one is usually __________________________ Subducted means _______________________________ The plate that is subducted is ________________________ in the mantle This is why convergent plate boundaries are called _______________________ plate margins Examples ___________________________________________________ 2. _______________________ Plate Boundaries Two plates ____________________________ When the two plates separate, the crust is pulled thin and creates a hole in the crust called a __________ This rift will extend down to the mantle, allowing mantle material to rise and create ______________________________________ This is why divergent boundaries are called _____________________ plate margins Examples ____________________________________________________________ 3. ____________________________ Plate Boundaries This is where two plates are ________________________________________ Plates are neither ______________________ or _______________________ This can happen between ______________________ plates or between _________________________ plates Where the plates are sliding, they will create a fault, which is where many earthquakes happen all over the world Most active fault ________________________________________ Hazards of Plate Boundaries Earthquakes ______________________________________________________ Occurs at ___________ types of plate boundaries, but happens more often at ___________________________________ boundaries Volcanoes Expulsion of ___________ and ______________ from the Earth’s crust At convergent boundaries, they can happen _______________________ or on the ______________ At divergent boundaries, most of the volcanoes happen __________________ There are no ____________________________ at transform fault boundary If the eruptions or earthquakes happen underwater, there will be an _________________________ of the crust That will push the ocean water up and create a tsunami This is not a ___________________________ because there is nothing this wave has to do with the ___________________ All of these hazards will cause massive amounts of ___________________________ and ____________________________ if we are not prepared for the dangers of nature Activity 2: Fill in the missing information using the notes above. Motion Convergent Divergent Transform Fault Anything Destroyed or Created? Dangers as this Boundary? Real World Location Causes of Plate Motion The main theory believes that there is an __________________ distribution of heat in the mantle, caused by heat from the _____________. Hot mantle material will ____________ from near the core and _________ as it reaches near the lithosphere This motion of hot rising and cold sinking is known as a _______________________ cell Plate Motions Associated with Convection Cells 1. ______________________ When ocean lithosphere is being _______________________ beneath another plate, if _______________ the rest of the lithosphere behind is down as well. This slab pull is the _______________________ arm of the convection cell Found at ______________________ boundaries 2. _______________________ When oceanic crust is being made at ___________________ plate boundaries, it is pushing the oceanic lithosphere away from the _______________ arm of the convection cell This motion is found at ______________________ plate boundaries 3. _____________________________ The rising mantle materials is the upward arm of the convection cell can happen in a single place in the middle of a plate and create a ____________________________________ Example: _______________________ Models of the Mantle Convection Cell Activity 3: Answer the following questions about plate motions. 1. Are the convection cells under the crust perfect circles in the mantle? ______ 2. Where is crust destroyed, at slab pull or ridge push? _______________________ 3. What type of motion will create transform fault boundaries, slab pull, ridge push, mantle plume or none of the above? ____________________________________ 4. Where are all the convection cells located, in the crust or the mantle? _______________ 5. Which two types of motions are happening in between plates? ____________________________________________________________ 6. Which type of motion is happening in the middle of a plate? _______________________________ 7. A volcano is made at which plate motion(s)? __________________________________________________________________ Earthquakes ________________________________________________________________________ > Caused by a _____________________ or break in the Earth’s crust > Is it possible for an earthquake to happen in the mantle? ________ Why Not? ___________________________________________________ > The energy that is released when the rocks begin to move is called _________________ energy, much like when a rubber band is stretched and the tension ___________ up before it is released Locations of Earthquakes 1. ___________________________________________ have earthquakes because there is rock rubbing against rock, creating shockwaves through the crust 2. All other earthquakes will happen at _______________________, which are __________________________________________________ or cracks in the Earth that show movement > If the big earthquake is the initial shock, then what are the shakes after and before an earthquake? ________________________ Smaller earthquakes that occur before the big earthquake > Do these always happen ? _________ > How long before the earthquake do foreshocks happen? _________________ ________________________ Smaller earthquakes that occur after the big earthquake > Why would these cause more damage if they are smaller than the big earthquake? _____________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________ Parts of an Earthquake Focus __________________ point in the Earth where the earthquake started >Waves from this will travel in _____ ______________________ >If the focus is ___________________ underground, meaning it is closer to the surface, it is ______________ dangerous than an earthquake that is deep underground Epicenter Location on the Earth’s _______________directly above the focus of the Earth >Why would we care more about the epicenter of an earthquake than the focus? _________________________________ _________________________________ _________________________________ > _______________________ is the measure of how strong the earthquake is Higher numbers means that the earthquake is __________________________ 3 Types of Earthquake Waves 1. ________________ waves Waves that travel along the Earth’s surface >This causes everything on the surface and underground to move > ______________ wave, but they are the ___________________ of all waves >Most ___________________________ of the earthquake waves Why? ____________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________ > Can travel though ___________________ only 2. __________________ waves (AKA ___________________) > These waves will pull and push the ground underneath you > _______________________ waves, but not the ______________________ > P-waves can travel through ___________________ and ___________________ > Least destructive, but these are the ________ parts of an earthquake that you feel 3. __________________________ waves (AKA _______________________) > These waves will cause an up and down motion of the ground > __________________ waves, but second to the surface waves. > __________________ that p-waves, but faster than surface waves > Fairly __________________________, definitely more so than the p-waves > S-waves cannot travel through ________ and ____________________ *** Can these waves travel through the outer core then? _________** Seismogram _______________________________________________________________________ Seismograph ______________________________________________________________________ *** You need _____ of these to find an earthquake epicenter Activity 4: Using the notes, pick the correct answer choice for the following questions. 1. Which happens first, a p-wave or an s-wave? ____________________ 2. Which has more energy behind it, surface waves or s-waves? _________________ 3. What type of energy is released during an earthquake, convective energy or elastic energy? _______________________ 4. Which is going to cause more property damage, a p-wave or a surface wave? _______________________ 5. Which records an earthquake, a seismogram or a seismograph? ________________________ 6. How many seismograms do we need to triangulate an earthquake epicenter, 2 or 3? _________ 7. Which is located underground and is the origin point for an earthquake, an epicenter or a focus? ___________________ 8. Why are we more concerned with the epicenter of an earthquake than its focus, because a focus is farther away from us or because the epicenter is at the surface near our property? ___________________________________________________ 9. Which will travel faster, waves on the surface or waves underground? _____________________________ 10. Why are s-waves more dangerous than p-waves, because one stronger or because one deals with pre-broken foundations and cracks in walls? ________________ Volcano _____________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ Parts of a Volcano Magma Chamber _________________________ _________________________________________ _________________________________________ Conduit (Pipeline) ________________________ _________________________________________ _________________________________________ Vent __________________________________ _________________________________________ _________________________________________ Crater _________________________________ ________________________________________ Pyroclastics _____________________________ _________________________________________ _________________________________________ *** All volcanoes have some form of these structures.**** Where do we find volcanoes? 1. At ______________________________________ ____________________ boundaries will form more violent and explosive volcanoes At ___________________ boundaries, the volcanoes are less violent and less explosive 2. At __________________________ When the weakened lithosphere has allowed mantle material to rise through and creates ________________ in the middle of some oceans If they are on continents, then usually create _________________________ under the surface Dangers that happen because of Volcanic Eruptions Viscosity The ability to ____________ > When things flow fast, they have a _________ viscosity and the lava can move up to 50 mph > When things flow slow, they have a ________ viscosity and the lava moves as slowly as in inches per hour __________ and other aerosols can _______________ out the Sun, making temperatures _______on a global scale Ash can also combine with rain clouds and produce ____________________ Larger pyroclastics called volcanic ____________ will destroy property upon impact Lava flows will ____________ anything that they come in contact with until they have cooled enough to become _____________ rock 3 Major types of Volcanoes Activity 5: Use the answer bank to find the answers for the following questions. 1. 2. 3. 4. Where are most volcanoes located? _______________________________ What part of a volcano is going to turn magma into lava? __________________ What are some examples of pyroclastics? ___________________________ What is viscosity? ____________________________________________________ 5. Which type of volcano has the highest viscosity? _____________________ 6. Which type of volcano should we be worried about on the East Coast? _________________ 7. Which type of volcano is found in Hawaii? ____________________ 8. What are the associated dangers of a volcanic eruption? ________________________________________________________ 9. Which ocean has the most volcanoes located on it? _____________________ 10. Why does acid rain happen after a volcanic eruption? ________________________________________________________________ Answer Bank: Ash, lava bombs, and rock shards None Plate Boundaries Vent Gases combine with water vapor in the air Shield The ability to flow Composite Earthquakes and tsunamis Pacific