* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Plate Tectonics
Age of the Earth wikipedia , lookup
Deep sea community wikipedia , lookup
Geomagnetic reversal wikipedia , lookup
Post-glacial rebound wikipedia , lookup
Physical oceanography wikipedia , lookup
Anoxic event wikipedia , lookup
Great Lakes tectonic zone wikipedia , lookup
Geochemistry wikipedia , lookup
History of Earth wikipedia , lookup
History of geology wikipedia , lookup
Algoman orogeny wikipedia , lookup
Tectonic–climatic interaction wikipedia , lookup
Oceanic trench wikipedia , lookup
Mantle plume wikipedia , lookup
Abyssal plain wikipedia , lookup
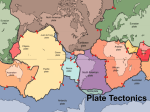
Continental Drift Evidence: Fossils Matching Mountain Ranges Glacier Evidence “Uh-Oh!”: Problems with Continental Drift…. …an alternate explanation? 1928: Arthur Holmes suggested magma rises toward the crust, spreads, and sinks again. (Convection current) 1930: Wegner dies, unable to adapt Holmes’ idea to his theory. Mantle/Crust Structure A new hope: Sea-Floor Spreading MID-ATLANTIC RIDGE 50,000 km. Long mountain range on the ocean floor Evidence for Plate Tectonics During WWII, the U.S. in an effort to find any advantage that would help out submarines in the war effort, scientists found that the iron in the rock at the mid-ocean ridge sometimes pointed North and sometimes pointed South How could this be? Basalt is iron rich and contains magnetite. Magnetite acts like a little magnet and aligns itself with the orientation of earth’s magnetic field. When magma solidifies, the alignment is “locked in” recording Earth’s magnetic orientation at the time of cooling. MAGNETIC STRIPE EVIDENCE North Oriented Rocks are said to have NORMAL POLARITY South Oriented Rocks are said to have REVERSED POLARITY The earth’s magnetic field has reversed hundreds of times POLARITY FLIPPING AGE INCREASES AWAY FROM OPENING - RIDGE Evidence for Plate Tectonics Ocean Drilling • The data on the ages of seafloor sediment confirmed what the seafloor spreading hypothesis predicted. • The youngest oceanic crust is at the ridge crest, and the oldest oceanic crust is at the continental margins. Which graph best represents the geologic age of the surface bedrock on the ocean bottom? Sea-Floor Spreading is a Divergent Plate Boundary Creates New Crust SPLITS APART CONTINENTS TO CREATE NEW OCEANS Spreading Center New Ocean forming – linear Red Sea When it grows up, it will be like the Atlantic Ocean EAST AFRICAN RIFT VALLEY – CONTINENTAL RIFT In Afar, Ethiopia, a 40-mile magmatic rift that opened up 1 year ago If new crust is created at divergent boundaries, is earth getting larger? CONVERGENT BOUNDARIES – DESTROYS CRUST Oceanic Crust converging with Continental Crust Oceanic crust converging with Oceanic Crust Continental Crust converging with Continental Crust OCEAN CRUST - CONTINENTAL CRUST SUBDUCTION – TRENCH FORMS Oceanic-Continental Convergent Boundary - SUBDUCTION DENSER OCEANIC CRUST GOES DOWN INTO MANTLE OCEAN CRUST –OCEAN CRUST CONVERGENCE - SUBDUCTION Oceanic Crust – Oceanic Crust Older, denser oceanic crust is SUBDUCTED (sinks below) VOLCANIC ISLAND ARC FORMED – ALEUTIAN ISLANDS TRENCH FORMS STARTS OUT AS OCEAN-CONTINENT CONVERGENCE AND THEN AS OCEAN CRUST IS SUBDUCTED TURNS INTO CONTINENT TO CONTINENT Continental Crust – Continental Crust Convergent Boundary NO SUBDUCTION - COLLISION ZONE Collision of India and Asia TRANSFORM PLATE BOUNDARIES Transform Fault Boundaries At a transform fault boundary, plates grind past each other without creating or destroying the lithosphere. SHALLOW EARTHQUAKES Transform faults • Most join two segments of a mid-ocean ridge. • At the time of formation, they roughly parallel the direction of plate movement. Boundaries: Transform SAN ANDREAS TRANSFORM FAULT Transform Fault Boundary AT MID-OCEAN RIDGES More Evidence for Plate Tectonics Earthquake Patterns • Scientists found a close link between deep-focus earthquakes and ocean trenches. • The absence of deep-focus earthquakes along the oceanic ridge system was shown to be consistent with the new theory. Convergent plate (subduction) boundaries have deeper earthquakes Divergent plate boundaries and Convergent Continent-Continent collision zones have shallow earthquakes Convergent IndianAustralian Plate and the Pacific Plate (oceanic crust to oceanic crust) are converging forming the Tonga Trench. Deep EQ’s f07_58_pg196 The greatest number of earthquakes in the cross section occurred at: 1. Sea level 2. Between sea level and a depth of l00 kms. 3. at a depth between 100 – 300 kms. 4. At a depth between 300 – 600 kms. Which cross section has arrows that best represent the relative motion of the crustal plates along the Wadati-Benioff zone beneath the Tonga Trench? SUMMARY 3 PLATE BOUNDARIES DIVERGING CONVERGING (SUBDUCTION ZONE) Oceanic Crust – Continental Crust Oceanic Crust - Oceanic Crust CONVERGING (COLLISION ZONE) Continental Crust – Continental Crust TRANSFORM So, what causes plates to move? • Convection currents: drag and move the lithospheric plates above the asthenosphere (three sources of heat produce the convection currents): (1)Leftover heat from earth’s formation (2)Decay of Radioactive elements (3)Plate friction Convection Cells Convection Currents in the mantle drag and pull the lithospheric plates above them 3 types of plate boundaries caused by convection currents CASCADES MIDATLANTIC RIDGE TRENCH ARROWS IN THE ASTHENOSPHERE SHOW PLATE MOVEMENT DUE TO CONVECTION The arrows shown in the asthenosphere represent the inferred slow circulation of the plastic mantle by a process called (1) insolation (3) conduction (2) convection (4) radiation Mid-ocean ridges (rifts) normally form where tectonic plates are (1) converging (3) stationary (2) diverging (4) sliding past each other The motion of the convection currents in the mantle beneath the Atlantic Ocean appears to be mainly making this ocean basin (1) deeper (3) wider (2) shallower (4) narrower More Evidence for Plate Tectonics Hot Spots • A hot spot is a concentration of heat in the mantle capable of producing magma, which rises to Earth’s surface; The Pacific plate moves over a hot spot, producing the Hawaiian Islands. • Hot spot evidence supports that the plates move over the Earth’s surface. HOT SPOTS • Major regions of volcanic activity in the interior of plates away from plate boundaries. • The cause of these hot spots is thought to be plumes of magma rising up from mantle producing sites of active volcanism. • As the plate moves over a hot spot, a chain of volcanic mountains forms, like Hawaiian Islands Hot Spot This diagram provides evidence that the Pacific Tectonic Plate is moving toward the (1) south (3) southwest (2) east (4) northwest