DNA Review Cards
... Describe the process of transcription. What is a mutagen? What is the primary enzyme in transcription. Give examples of mutagens. What type of cell must a mutation occur in to be passed on to offspring? ...
... Describe the process of transcription. What is a mutagen? What is the primary enzyme in transcription. Give examples of mutagens. What type of cell must a mutation occur in to be passed on to offspring? ...
Study Guide for LS
... A change in the order of bases in DNA is called a mutation. A mutation could be caused by x-rays, radioactivity, ultraviolet rays. A mutation in DNA could result in no change, death or a genetic disorder. Your phenotype (physical appearance) can be affected by heredity and the environment. ...
... A change in the order of bases in DNA is called a mutation. A mutation could be caused by x-rays, radioactivity, ultraviolet rays. A mutation in DNA could result in no change, death or a genetic disorder. Your phenotype (physical appearance) can be affected by heredity and the environment. ...
Chapter 20: Cancer
... Several physical and biological agents are also responsible for producing cancer. Some carcinogens exert their effect outside of the DNA. Cancers develop many years after the initial exposure to a carcinogen. 20-3 Cancer Treatments Tumors can be removed surgically or treated with chemotherapy and ra ...
... Several physical and biological agents are also responsible for producing cancer. Some carcinogens exert their effect outside of the DNA. Cancers develop many years after the initial exposure to a carcinogen. 20-3 Cancer Treatments Tumors can be removed surgically or treated with chemotherapy and ra ...
Mutations
... They cause disease because changes in the genome's instructions alter the functions of important proteins that are needed for health. For example, diabetes, cancer, heart disease, and hemophilia all result from mutations that cause harmful effects. ...
... They cause disease because changes in the genome's instructions alter the functions of important proteins that are needed for health. For example, diabetes, cancer, heart disease, and hemophilia all result from mutations that cause harmful effects. ...
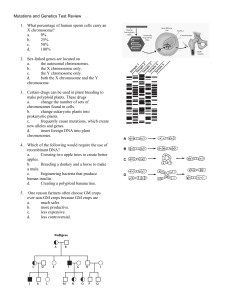
Mutations and Genetics Test Review 1. What percentage of human
... change the number of sets of chromosomes found in cells. b. change eukaryotic plants into prokaryotic plants. c. frequently cause mutations, which create new alleles and genes. d. insert foreign DNA into plant chromosomes. 4. Which of the following would require the use of recombinant DNA? a. Crossi ...
... change the number of sets of chromosomes found in cells. b. change eukaryotic plants into prokaryotic plants. c. frequently cause mutations, which create new alleles and genes. d. insert foreign DNA into plant chromosomes. 4. Which of the following would require the use of recombinant DNA? a. Crossi ...
Cell Theory Quiz Study Guide Name
... 17. The order of the nitrogen bases on the DNA molecule is known as the genetic _______. 18. In 1952, Rosalind ____________ discovered DNA is 2 chains of molecules. 19. In 1953, using the above scientist’s research, _____________ and ____________ made a model of DNA. 20. A _____________________ is a ...
... 17. The order of the nitrogen bases on the DNA molecule is known as the genetic _______. 18. In 1952, Rosalind ____________ discovered DNA is 2 chains of molecules. 19. In 1953, using the above scientist’s research, _____________ and ____________ made a model of DNA. 20. A _____________________ is a ...
Key- PRE-LAB: Before the lab, please answer the following questions:
... substance and reflects background response induced by the diluent or other ingredients (sometimes these are not necessarily inert or known to be without effect) for which the test substance is not responsible. It commonly would give the spontaneous rate of effect (without any trigger). It is importa ...
... substance and reflects background response induced by the diluent or other ingredients (sometimes these are not necessarily inert or known to be without effect) for which the test substance is not responsible. It commonly would give the spontaneous rate of effect (without any trigger). It is importa ...
Wzór streszczenia/Abstract form:
... Oxidative stress influences DNA and other biomolecules damage via oxidative changes to their chemical structure. These changes are believed to increase the risk of cancer, heart disease and aging processes. It has been demonstrated that antioxidants such as ascorbic acid, tocopherols and flavonoids ...
... Oxidative stress influences DNA and other biomolecules damage via oxidative changes to their chemical structure. These changes are believed to increase the risk of cancer, heart disease and aging processes. It has been demonstrated that antioxidants such as ascorbic acid, tocopherols and flavonoids ...
unit in review genetics - Hutchison
... -Mendel’s Law of Independent Assortment -Traits that show continuous variation vs. discontinuous variation ...
... -Mendel’s Law of Independent Assortment -Traits that show continuous variation vs. discontinuous variation ...
SW describe how techniques such as DNA
... Sex-influenced traits are those that are expressed differently in the two sexes. Such traits are autosomal, which means that the genes responsible for their expression are not carried on the sex chromosomes. ...
... Sex-influenced traits are those that are expressed differently in the two sexes. Such traits are autosomal, which means that the genes responsible for their expression are not carried on the sex chromosomes. ...
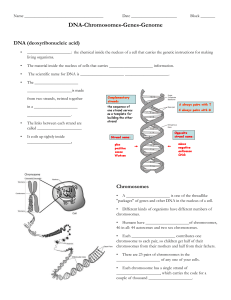
DNA-Chromosomes-Genes-Genome student notesheet
... _____________________ of any one of your cells. • Each chromosome has a single strand of _____________________, which carries the code for a couple of thousand _____________________. ...
... _____________________ of any one of your cells. • Each chromosome has a single strand of _____________________, which carries the code for a couple of thousand _____________________. ...
Unit 4 Resources - Schoolwires.net
... 7. Many chromosome mutations result when chromosomes fail to separate properly during a. mitosis. b. meiosis. c. crossing over. d. linkage. 8. The failure of homologous chromosomes to separate properly is called a. translocation. b. disjunction. c. nondisjunction. 9. Mutations that occur at random a ...
... 7. Many chromosome mutations result when chromosomes fail to separate properly during a. mitosis. b. meiosis. c. crossing over. d. linkage. 8. The failure of homologous chromosomes to separate properly is called a. translocation. b. disjunction. c. nondisjunction. 9. Mutations that occur at random a ...
Gene mutations - mccombsscience
... Occur mostly in plants Gametes that should have a complete set of genes may end up with extra copies of some genes or completely lack others Few chromosome mutations are passed on to the next generation because they zygote usually dies Deletions, insertions, inversions, and ...
... Occur mostly in plants Gametes that should have a complete set of genes may end up with extra copies of some genes or completely lack others Few chromosome mutations are passed on to the next generation because they zygote usually dies Deletions, insertions, inversions, and ...
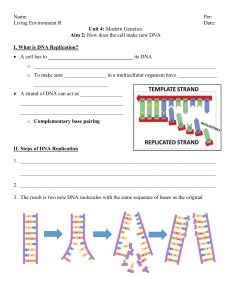
Guided Notes - Boone County Schools
... ● We are a little different from our parents, because we have a mix of ____________ from our parents ○ Half of our DNA comes from mom ○ the other half comes from dad ● Some genes parents pass down are recessive, while some are dominant. ○ anytime a _____________ trait is partnered with rec ...
... ● We are a little different from our parents, because we have a mix of ____________ from our parents ○ Half of our DNA comes from mom ○ the other half comes from dad ● Some genes parents pass down are recessive, while some are dominant. ○ anytime a _____________ trait is partnered with rec ...
Changes in Genetic Material your chromosomes are made up of
... mutations can often result in problems for the organism involved because it results in a change in DNA structure ...
... mutations can often result in problems for the organism involved because it results in a change in DNA structure ...
Mutations Terminology
... and bb are normal kidney shaped eyes Protocol: wide bar females heterozygous for the 3 genes were crossed to normal but x-irradiated males. The wide bar female progeny, ...
... and bb are normal kidney shaped eyes Protocol: wide bar females heterozygous for the 3 genes were crossed to normal but x-irradiated males. The wide bar female progeny, ...
Mutations (power point)
... • Mutagens are chemical or physical agents that interact with DNA to cause mutations. • Physical agents include high-energy radiation like X-rays and ultraviolet light. • Chemical mutagens may operate in several ways. – Some chemicals are base analogues that may be substituted into DNA, but that pa ...
... • Mutagens are chemical or physical agents that interact with DNA to cause mutations. • Physical agents include high-energy radiation like X-rays and ultraviolet light. • Chemical mutagens may operate in several ways. – Some chemicals are base analogues that may be substituted into DNA, but that pa ...
Mutagen
In genetics, a mutagen is a physical or chemical agent that changes the genetic material, usually DNA, of an organism and thus increases the frequency of mutations above the natural background level. As many mutations can cause cancer, mutagens are therefore also likely to be carcinogens. Not all mutations are caused by mutagens: so-called ""spontaneous mutations"" occur due to spontaneous hydrolysis, errors in DNA replication, repair and recombination.