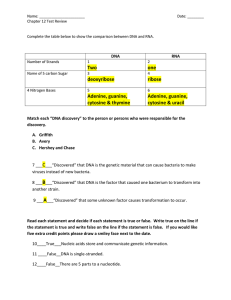
Notes Unit 4 Part 8
... ___________ gene occur most often during ______ replication so affect _____________ cells more often phenotype may or may ______ be altered depending on type of mutation Types of Gene Mutations: 1. point mutation = a gene mutation involving changes in ____ or few nucleotides usually only _____ ...
... ___________ gene occur most often during ______ replication so affect _____________ cells more often phenotype may or may ______ be altered depending on type of mutation Types of Gene Mutations: 1. point mutation = a gene mutation involving changes in ____ or few nucleotides usually only _____ ...
Photosynthesis - Cathedral High School
... Ultraviolet (UV) radiation is easily absorbed by the pyrimidines in DNA. Cause neighboring thymine molecules next to one another to bond together ...
... Ultraviolet (UV) radiation is easily absorbed by the pyrimidines in DNA. Cause neighboring thymine molecules next to one another to bond together ...
Normal pairing
... The UV photoproducts significantly perturb the local structure of the double helix. These lesions interfere with normal base pairing. The C to T transition is the most frequent mutation , but UV light also induces other base substitutions (transversions) and frameshifts, as well as larger duplicatio ...
... The UV photoproducts significantly perturb the local structure of the double helix. These lesions interfere with normal base pairing. The C to T transition is the most frequent mutation , but UV light also induces other base substitutions (transversions) and frameshifts, as well as larger duplicatio ...
chromosomal
... 13.3 Chromosomal Mutations • Types of chromosomal mutations: – Deletion: The loss of all or part of a chromosome – Duplication: A segment is repeated – Inversion: part of the chromosome is reverse from its usual direction. – Translocation: one chromosome breaks off an attaches to another chromosome ...
... 13.3 Chromosomal Mutations • Types of chromosomal mutations: – Deletion: The loss of all or part of a chromosome – Duplication: A segment is repeated – Inversion: part of the chromosome is reverse from its usual direction. – Translocation: one chromosome breaks off an attaches to another chromosome ...
LOYOLA COLLEGE (AUTONOMOUS), CHENNAI – 600 034
... II. State whether the following statements are true or false ...
... II. State whether the following statements are true or false ...
Causes
... sequence. They can result from replication errors, from damage to the DNA, or from errors introduced during repair of damage. Mutations that are changes of a single base pair are called point mutations. • Causes: It may be spontaneous or induced because of different agents • Classifications: are cla ...
... sequence. They can result from replication errors, from damage to the DNA, or from errors introduced during repair of damage. Mutations that are changes of a single base pair are called point mutations. • Causes: It may be spontaneous or induced because of different agents • Classifications: are cla ...
Gene Expression and Mutation GENE EXPRESSION: There are
... undergoes spontaneous mutations. An induced mutation is caused by agents outside the cell called mutagens. Mutagens fall into two general categories: ...
... undergoes spontaneous mutations. An induced mutation is caused by agents outside the cell called mutagens. Mutagens fall into two general categories: ...
DNA-Based Mutations
... 1. Gene Mutations -- error during one of the processes that involves basepairing of nucleic acids (eg. DNA replication, transcription, translation), or, error perpetuated by base-pairing process. *focus of Bio 12 2. Chromosomal Mutations -- where an entire chromosome is affected. eg. Trisomy 21 (3 c ...
... 1. Gene Mutations -- error during one of the processes that involves basepairing of nucleic acids (eg. DNA replication, transcription, translation), or, error perpetuated by base-pairing process. *focus of Bio 12 2. Chromosomal Mutations -- where an entire chromosome is affected. eg. Trisomy 21 (3 c ...
Cell Growth and Reproduction
... • The information in the DNA may be changed. These changes are referred to as mutations. ...
... • The information in the DNA may be changed. These changes are referred to as mutations. ...
Extra Credit Ch. 6 Cell cycle and Mitosis student
... Name_________________________________________Pd._____Date_________ ...
... Name_________________________________________Pd._____Date_________ ...
chapter 12 test review key
... will carry the incorrect information. If a mutation or change of information occurs in a sex cell that means that as mitosis occurs as the organism grows and develops every cell in that particular organism carries the mutation.________________ ...
... will carry the incorrect information. If a mutation or change of information occurs in a sex cell that means that as mitosis occurs as the organism grows and develops every cell in that particular organism carries the mutation.________________ ...
Key ideas age 321 ivaniaa
... the way DNA is translated, a mutation can have many possible effects. A small change in DNA may affect just one amino acid in the protein that result from a gene. ...
... the way DNA is translated, a mutation can have many possible effects. A small change in DNA may affect just one amino acid in the protein that result from a gene. ...
TwoQuestions Darwin Could Not Answer
... • Means “above or upon” the genes • DNA is wrapped around histones – To be activated, gene must be unwound from histones – Different experiences bring new chemicals into the cell which change chemical environment ...
... • Means “above or upon” the genes • DNA is wrapped around histones – To be activated, gene must be unwound from histones – Different experiences bring new chemicals into the cell which change chemical environment ...
Defined - cloudfront.net
... – Some gene mutations change phenotype (physical characteristics) • Example: Can cause a premature stop codon – Some gene mutations don’t change phenotype. • Example: Could be silent or occur in a non-coding region ...
... – Some gene mutations change phenotype (physical characteristics) • Example: Can cause a premature stop codon – Some gene mutations don’t change phenotype. • Example: Could be silent or occur in a non-coding region ...
Unit 3- Section 2
... Deletion-A portion of the chromosome is lost and the information is lost with it. Duplication-A portion from the homologous chromosome is added Inversion- A portion is added but it attaches in the ...
... Deletion-A portion of the chromosome is lost and the information is lost with it. Duplication-A portion from the homologous chromosome is added Inversion- A portion is added but it attaches in the ...
dna-student - WordPress.com
... DNA can be exposed to harmful chemicals that get into the nucleus of a cell. Any of these can cause the order of the nitrogen bases to change which results in a change in the genetic code called a _______________. Sometimes mutations can be beneficial but they are usually neutral. Cancer is one exam ...
... DNA can be exposed to harmful chemicals that get into the nucleus of a cell. Any of these can cause the order of the nitrogen bases to change which results in a change in the genetic code called a _______________. Sometimes mutations can be beneficial but they are usually neutral. Cancer is one exam ...
Lecture 19 Spring 2011
... Induced mutations occur upon exposure to physical or chemical mutagens. Hermann J. Muller and Edgar Alternburg measured the frequency of X-linked recessive lethal mutations in Drosophila. Muller demonstrated that exposing Drosophila sperm to X-rays increased the mutation frequency. ...
... Induced mutations occur upon exposure to physical or chemical mutagens. Hermann J. Muller and Edgar Alternburg measured the frequency of X-linked recessive lethal mutations in Drosophila. Muller demonstrated that exposing Drosophila sperm to X-rays increased the mutation frequency. ...
VII. DNA/ GENES/ AND GENETICS • Describe the relationship
... Give examples of emerging biotechnologies. What modern technologies are currently being implemented to determine evolutionary relationships among species? How are viruses used to treat disease? How can over exposure to sunlight cause skin cancer? Describe the structure and function of the DNA molecu ...
... Give examples of emerging biotechnologies. What modern technologies are currently being implemented to determine evolutionary relationships among species? How are viruses used to treat disease? How can over exposure to sunlight cause skin cancer? Describe the structure and function of the DNA molecu ...
Mutagen
In genetics, a mutagen is a physical or chemical agent that changes the genetic material, usually DNA, of an organism and thus increases the frequency of mutations above the natural background level. As many mutations can cause cancer, mutagens are therefore also likely to be carcinogens. Not all mutations are caused by mutagens: so-called ""spontaneous mutations"" occur due to spontaneous hydrolysis, errors in DNA replication, repair and recombination.