H.5 - HL transport-system
... Myogenic Rhythm: The heart beat is initiated within the heart muscle itself. • Within the right atrium there are a specialise group of cells called the Sino Atrial Node.(SAN). • These cells can generate an electrochemical potential across the cell membrane and once threshold is reached this can be p ...
... Myogenic Rhythm: The heart beat is initiated within the heart muscle itself. • Within the right atrium there are a specialise group of cells called the Sino Atrial Node.(SAN). • These cells can generate an electrochemical potential across the cell membrane and once threshold is reached this can be p ...
Medicines in Development for Heart Disease and Stroke
... inflammation that occurs in the blood vessels during and immediately following an acute coronary syndrome event. HEART FAILURE A medicine in development to treat ischemic heart failure is a non-viral gene therapy that targets a tissue repair and regeneration pathway in the body. This pathway promote ...
... inflammation that occurs in the blood vessels during and immediately following an acute coronary syndrome event. HEART FAILURE A medicine in development to treat ischemic heart failure is a non-viral gene therapy that targets a tissue repair and regeneration pathway in the body. This pathway promote ...
Cardiac Infections
... May need cardiac monitoring, ECHO, cardiology consult Usually need close Follow-up ...
... May need cardiac monitoring, ECHO, cardiology consult Usually need close Follow-up ...
Slide () - AccessAnesthesiology
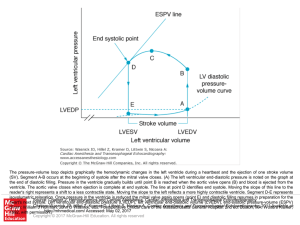
... The pressure-volume loop depicts graphically the hemodynamic changes in the left ventricle during a heartbeat and the ejection of one stroke volume (SV). Segment A-B occurs at the beginning of systole after the mitral valve closes. (A) The left ventricular end-diastolic pressure is noted on the grap ...
... The pressure-volume loop depicts graphically the hemodynamic changes in the left ventricle during a heartbeat and the ejection of one stroke volume (SV). Segment A-B occurs at the beginning of systole after the mitral valve closes. (A) The left ventricular end-diastolic pressure is noted on the grap ...
heart failure - Jantung Sehat
... Givertz MM et al. In: Braunwald E, Zipes DP, Libby P, eds. Heart Disease, A Textbook of Cardiovascular Medicine. 7th edition. ...
... Givertz MM et al. In: Braunwald E, Zipes DP, Libby P, eds. Heart Disease, A Textbook of Cardiovascular Medicine. 7th edition. ...
Heart
... • Hold out your hand and make a fist. If you're a kid, your heart is about the same size as your fist, and if you're an adult, it's about the same size as two fists. • Your heart beats about 100,000 times in one day and about 35 million times in a year. During an average lifetime, the human heart wi ...
... • Hold out your hand and make a fist. If you're a kid, your heart is about the same size as your fist, and if you're an adult, it's about the same size as two fists. • Your heart beats about 100,000 times in one day and about 35 million times in a year. During an average lifetime, the human heart wi ...
Interpretation of Electrocardiogram findings
... An Electrocardiogram (ECG, EKG) is a medical device used to evaluate the heart rhythm and heart muscle damage. A Holter monitor is used to record ECG tracings continuously for 24 hours or longer to monitor the heart rate during daily activities. An echocardiogram is a test that uses sound waves to m ...
... An Electrocardiogram (ECG, EKG) is a medical device used to evaluate the heart rhythm and heart muscle damage. A Holter monitor is used to record ECG tracings continuously for 24 hours or longer to monitor the heart rate during daily activities. An echocardiogram is a test that uses sound waves to m ...
Congestive Heart Failure
... ventricle, then out into body. When left side heart damaged or can’t pump as well, has to work harder. This causes fluid to build up, especially in lungs. That’s why SOB is one of most common symptoms of heart failure. With left-sided HF, may have systolic failure (when heart does not pump out blood ...
... ventricle, then out into body. When left side heart damaged or can’t pump as well, has to work harder. This causes fluid to build up, especially in lungs. That’s why SOB is one of most common symptoms of heart failure. With left-sided HF, may have systolic failure (when heart does not pump out blood ...
Lecture 17
... tPA and other clot-dissolving agents can reduce the amount of damage to the heart muscle and save lives To be effective, they must be given within a few hours after symptoms begin Administered through an intravenous (IV) line in the arm by hospital personnel Patients treated within 90 minutes after ...
... tPA and other clot-dissolving agents can reduce the amount of damage to the heart muscle and save lives To be effective, they must be given within a few hours after symptoms begin Administered through an intravenous (IV) line in the arm by hospital personnel Patients treated within 90 minutes after ...
Chapter 19: The Heart
... found in the mediastinum – medial cavity of thorax 2/3 of mass is left of midsternal Rests on superior surface of the diaphragm Anterior to the vertebral column Posterior to the sternum Flanked by the lungs ...
... found in the mediastinum – medial cavity of thorax 2/3 of mass is left of midsternal Rests on superior surface of the diaphragm Anterior to the vertebral column Posterior to the sternum Flanked by the lungs ...
Real-time and patient-specific simulation of the heart. Application to
... electrophysiological and mechanical behaviour of the heart at scales ranging from cell to tissue and organ levels. Principles of continuum mechanics are key in creating a realistic multi-scale model of the heart. They allow to describe the directly observable behaviour of the heart by incorporating ...
... electrophysiological and mechanical behaviour of the heart at scales ranging from cell to tissue and organ levels. Principles of continuum mechanics are key in creating a realistic multi-scale model of the heart. They allow to describe the directly observable behaviour of the heart by incorporating ...
Chapt05 Lecture 13ed Pt 2
... How do the structure of the vessels and heart match their functions? • The left ventricle is much more __________ than the right ventricle because it must pump blood to the entire body. • The ________ are more muscular than _____ to withstand the higher pressure exerted on them. • The veins have a t ...
... How do the structure of the vessels and heart match their functions? • The left ventricle is much more __________ than the right ventricle because it must pump blood to the entire body. • The ________ are more muscular than _____ to withstand the higher pressure exerted on them. • The veins have a t ...
the effects of exercise
... Changes or adaptations will also occur in each body system if we exercise regularly or train over a period of time e.g. weeks/months. These are called the long term effects of exercise. ...
... Changes or adaptations will also occur in each body system if we exercise regularly or train over a period of time e.g. weeks/months. These are called the long term effects of exercise. ...
Heart Failure Related Deaths - 5
... • Heart failure is subclassed as Asymptomatic (ALVD) OR Symptomatic, and treatment is based upon whether a patient is having symptoms or NOT. HF with preserved EF (usually EF > 45%) • Caused from diastolic dysfunction (impaired relaxation) AND HF symptoms are present Right Ventricle HF • Ejection fr ...
... • Heart failure is subclassed as Asymptomatic (ALVD) OR Symptomatic, and treatment is based upon whether a patient is having symptoms or NOT. HF with preserved EF (usually EF > 45%) • Caused from diastolic dysfunction (impaired relaxation) AND HF symptoms are present Right Ventricle HF • Ejection fr ...
ECG Analysis Electrocardiography (ECG) is an
... Arrhythmic cardiac events, which may be extrasystoles (i.e. cardiac premature heart beats) are early warning signs for serious potential cardiac issues. The relation between supraventricular or ventricular extrasystoles and health risk is important because they can precede myocardial infarction. The ...
... Arrhythmic cardiac events, which may be extrasystoles (i.e. cardiac premature heart beats) are early warning signs for serious potential cardiac issues. The relation between supraventricular or ventricular extrasystoles and health risk is important because they can precede myocardial infarction. The ...
Cardiac System
... The amount of blood pumped by the left ventricle/ heart per beat / contraction During exercise increases are progressive until they gradually level off at a higher level until exercise has ended Due to the sharp increase in blood flow when exercising, a greater oxygen supply is available to the skel ...
... The amount of blood pumped by the left ventricle/ heart per beat / contraction During exercise increases are progressive until they gradually level off at a higher level until exercise has ended Due to the sharp increase in blood flow when exercising, a greater oxygen supply is available to the skel ...
Etiology of congestive heart failure at a tertiary care hospital
... were above the age of 40 years. Males outnumbered females. This may be because of higher prevalence risk factors in males. Moreover, preference is given to male for hospitalization and treatment as compared to females in our society. IHD was recorded as the most common cause of HF in our study. Kh ...
... were above the age of 40 years. Males outnumbered females. This may be because of higher prevalence risk factors in males. Moreover, preference is given to male for hospitalization and treatment as compared to females in our society. IHD was recorded as the most common cause of HF in our study. Kh ...
Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy in Cats
... • Sodium restriction in cats with congestive heart failure; congestive heart failure is a condition in which the heart cannot pump an adequate volume of blood to meet the body's needs ...
... • Sodium restriction in cats with congestive heart failure; congestive heart failure is a condition in which the heart cannot pump an adequate volume of blood to meet the body's needs ...
Heart
... 0.3 second, and represents the approximate length of time required for the ventricles to contract and begin to relax. ...
... 0.3 second, and represents the approximate length of time required for the ventricles to contract and begin to relax. ...
Phases of the Cardiac Cycle Atrial systole begins: Atrial
... during the rapid filling of the ventricle. o Is produced by rapid filling of a dilated ventricle (i.e. systolic heart failure, valvular regurgitation, etc) o Common in children, but usually pathologic in adults S4 o Low frequency sound in late diastole and is coincident with atrial contraction dur ...
... during the rapid filling of the ventricle. o Is produced by rapid filling of a dilated ventricle (i.e. systolic heart failure, valvular regurgitation, etc) o Common in children, but usually pathologic in adults S4 o Low frequency sound in late diastole and is coincident with atrial contraction dur ...
Ventricular Assist Device Implantation: Considerations for
... The centrifugal LVAD is FDA approved for destination therapy (for patients who are not eligible for heart transplantation) and bridge-totransplantation. The axial LVAD is housed in the ventricle and only has an outflow graft, not requiring the abdominal pocket. It is FDA approved for bridge-totransp ...
... The centrifugal LVAD is FDA approved for destination therapy (for patients who are not eligible for heart transplantation) and bridge-totransplantation. The axial LVAD is housed in the ventricle and only has an outflow graft, not requiring the abdominal pocket. It is FDA approved for bridge-totransp ...
Coronary Artery Disease - Nursing PowerPoint Presentations
... Include:Left ventricular hypertrophy Coronary heart disease (Congestive) heart failure Hypertensive cardiomyopathy Cardiac arrhythmias ...
... Include:Left ventricular hypertrophy Coronary heart disease (Congestive) heart failure Hypertensive cardiomyopathy Cardiac arrhythmias ...
The Heart - TeachLine
... narrowed due to calcification (or other factors). The narrowing causes larger resistance to flow, and required larger pressures to be produced by the LV, and thus larger effort • This results in growth of LV heart tissue (hypertrophy), and eventually in it’s stiffening, and malfunction • Mitral regu ...
... narrowed due to calcification (or other factors). The narrowing causes larger resistance to flow, and required larger pressures to be produced by the LV, and thus larger effort • This results in growth of LV heart tissue (hypertrophy), and eventually in it’s stiffening, and malfunction • Mitral regu ...
usefulness of acoustic cardiography to resolve ambiguos values of b
... Outpatient Clinic for Cardiology and Internal Medicine, Frauenfeld, Switzerland, ...
... Outpatient Clinic for Cardiology and Internal Medicine, Frauenfeld, Switzerland, ...
Heart failure

Heart failure (HF), often referred to as congestive heart failure (CHF), occurs when the heart is unable to pump sufficiently to maintain blood flow to meet the body's needs. The terms chronic heart failure (CHF) or congestive cardiac failure (CCF) are often used interchangeably with congestive heart failure. Signs and symptoms commonly include shortness of breath, excessive tiredness, and leg swelling. The shortness of breath is usually worse with exercise, while lying down, and may wake the person at night. A limited ability to exercise is also a common feature.Common causes of heart failure include coronary artery disease including a previous myocardial infarction (heart attack), high blood pressure, atrial fibrillation, valvular heart disease, excess alcohol use, infection, and cardiomyopathy of an unknown cause. These cause heart failure by changing either the structure or the functioning of the heart. There are two main types of heart failure: heart failure due to left ventricular dysfunction and heart failure with normal ejection fraction depending on if the ability of the left ventricle to contract is affected, or the heart's ability to relax. The severity of disease is usually graded by the degree of problems with exercise. Heart failure is not the same as myocardial infarction (in which part of the heart muscle dies) or cardiac arrest (in which blood flow stops altogether). Other diseases that may have symptoms similar to heart failure include obesity, kidney failure, liver problems, anemia and thyroid disease.The condition is diagnosed based on the history of the symptoms and a physical examination with confirmation by echocardiography. Blood tests, electrocardiography, and chest radiography may be useful to determine the underlying cause. Treatment depends on the severity and cause of the disease. In people with chronic stable mild heart failure, treatment commonly consists of lifestyle modifications such as stopping smoking, physical exercise, and dietary changes, as well as medications. In those with heart failure due to left ventricular dysfunction, angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors or angiotensin receptor blockers along with beta blockers are recommended. For those with severe disease, aldosterone antagonists, or hydralazine plus a nitrate may be used. Diuretics are useful for preventing fluid retention. Sometimes, depending on the cause, an implanted device such as a pacemaker or an implantable cardiac defibrillator may be recommended. In some moderate or severe cases cardiac resynchronization therapy (CRT) may be suggested or cardiac contractility modulation may be of benefit. A ventricular assist device or occasionally a heart transplant may be recommended in those with severe disease despite all other measures.Heart failure is a common, costly, and potentially fatal condition. In developed countries, around 2% of adults have heart failure and in those over the age of 65, this increases to 6–10%. In the year after diagnosis the risk of death is about 35% after which it decreases to below 10% each year. This is similar to the risks with a number of types of cancer. In the United Kingdom the disease is the reason for 5% of emergency hospital admissions. Heart failure has been known since ancient times with the Ebers papyrus commenting on it around 1550 BCE.