Go For Red - Jump Start Your Heart, Inc.
... will benefit by seeking treatment from clinical centers of excellence focused on this disease, which have the most contemporary medical and surgical treatments available,‖ Maron said. Managing HCM-related heart failure can be complicated, particularly in patients who do not respond to standard drug ...
... will benefit by seeking treatment from clinical centers of excellence focused on this disease, which have the most contemporary medical and surgical treatments available,‖ Maron said. Managing HCM-related heart failure can be complicated, particularly in patients who do not respond to standard drug ...
Clinical Cardiac Electrophysiology - Dartmouth
... about 20% of healthy implantable defibrillator (ICD) Each day the average adults are likely to have heart beats (expands frequent or multiple types and contracts) 100,000 of premature ventricular heartbeats. In the United States moretimes than and pumps about 2,000 gallons of blood. 850,000 people a ...
... about 20% of healthy implantable defibrillator (ICD) Each day the average adults are likely to have heart beats (expands frequent or multiple types and contracts) 100,000 of premature ventricular heartbeats. In the United States moretimes than and pumps about 2,000 gallons of blood. 850,000 people a ...
Cardiac physiology
... Dr. Decker Cardiac cycle 1- Ventricular relaxation (Quiescent period) 2- Ventricular filling (diastole) 3- Ventricular contraction/ejection (systole) Cardiac cycle last about 0.8 seconds 1- Ventricular relaxation (Quiescent period): In the beginning of this phase all four chamber are at rest. As the ...
... Dr. Decker Cardiac cycle 1- Ventricular relaxation (Quiescent period) 2- Ventricular filling (diastole) 3- Ventricular contraction/ejection (systole) Cardiac cycle last about 0.8 seconds 1- Ventricular relaxation (Quiescent period): In the beginning of this phase all four chamber are at rest. As the ...
Anesthesia for non-cardiac surgery in patients with heart failure
... characteristics, treatment patterns, and outcomes appear similar to those of patient with HFpEF. ...
... characteristics, treatment patterns, and outcomes appear similar to those of patient with HFpEF. ...
the Note
... In the walls of the heart, two layers of tissue form a sandwich around a thick layer of muscle called the myocardium. Contractions of the myocardium pump blood through the circulatory system. The right and left sides of the heart are separated by a septum, or wall. The septum prevents the mixing of ...
... In the walls of the heart, two layers of tissue form a sandwich around a thick layer of muscle called the myocardium. Contractions of the myocardium pump blood through the circulatory system. The right and left sides of the heart are separated by a septum, or wall. The septum prevents the mixing of ...
3 Control of heart rate
... the sinoatrial node by the sympathetic nervous system) 2.Inhibitory centre - Decreases heart rate (linked to the sinoatrial node by the parasympathetic nervous system) The centre that is stimulated depends on: •Chemical changes in the blood •Pressure changes in the blood ...
... the sinoatrial node by the sympathetic nervous system) 2.Inhibitory centre - Decreases heart rate (linked to the sinoatrial node by the parasympathetic nervous system) The centre that is stimulated depends on: •Chemical changes in the blood •Pressure changes in the blood ...
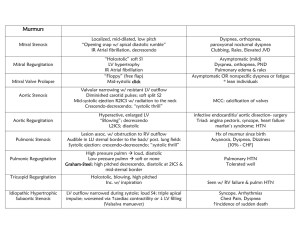
Murmurs - stjpap 2011
... Hypertrophy of chambers, aortic stenosis (LV), tricuspid stenosis (RA), aortic regurgitation ...
... Hypertrophy of chambers, aortic stenosis (LV), tricuspid stenosis (RA), aortic regurgitation ...
Ventricular Septal Defect
... The heart has two ventricles, the left ventricle and the right ventricle. These are the lower pumping chambers of the heart. The right ventricle pumps blood to the lungs to receive oxygen and the left ventricle pumps this oxygenated blood out of heart to the body. A VSD is a “hole” (an opening) in t ...
... The heart has two ventricles, the left ventricle and the right ventricle. These are the lower pumping chambers of the heart. The right ventricle pumps blood to the lungs to receive oxygen and the left ventricle pumps this oxygenated blood out of heart to the body. A VSD is a “hole” (an opening) in t ...
The Chest Xray and Electrocardiogram
... The Electrocardiogram Many brilliant minds have contributed to the development of electrocardiography as a clinical science. The early history (1900-1945) was dominated by Professor Willem Einthoven in the Netherlands, Sir Thomas Lewis in England and Dr. Frank N. Wilson in the United States. These ...
... The Electrocardiogram Many brilliant minds have contributed to the development of electrocardiography as a clinical science. The early history (1900-1945) was dominated by Professor Willem Einthoven in the Netherlands, Sir Thomas Lewis in England and Dr. Frank N. Wilson in the United States. These ...
myocard*al and per*card*al d*seases
... β-adrenergic blocking agents (propranolol, atenolol) or calcium channel blocking agents (verapamil) may be useful in diminishing ventricular outflow tract obstruction, modifying ventricular hypertrophy, and improving ventricular filling. Although signifi cant symptomatic improvement occurs in some ...
... β-adrenergic blocking agents (propranolol, atenolol) or calcium channel blocking agents (verapamil) may be useful in diminishing ventricular outflow tract obstruction, modifying ventricular hypertrophy, and improving ventricular filling. Although signifi cant symptomatic improvement occurs in some ...
Cardiac Biomarkers - Clinician`s Brief
... response to volume expansion or pressure overload. It is a functional cardiac biomarker that is increased with stress, stretch, or strain on cardiomyocytes due to occult or overt heart disease. Pathophysiology Cardiac TnI Troponin is a protein that regulates interactions between actin and myosin wit ...
... response to volume expansion or pressure overload. It is a functional cardiac biomarker that is increased with stress, stretch, or strain on cardiomyocytes due to occult or overt heart disease. Pathophysiology Cardiac TnI Troponin is a protein that regulates interactions between actin and myosin wit ...
Anatomy of the Heart
... called the left and right atria and the lower chambers are called the left and right ventricles. A wall of muscle called the septum separates the left and right atria and the left and right ventricles. These are referred to as the artial and ventricular septums. You may have heard your doctor refer ...
... called the left and right atria and the lower chambers are called the left and right ventricles. A wall of muscle called the septum separates the left and right atria and the left and right ventricles. These are referred to as the artial and ventricular septums. You may have heard your doctor refer ...
second-degree_heart_block_(mobitz_ii)
... II) often progresses to complete (third-degree) heart block • Prolonged slow heart rate (bradycardia) may cause secondary congestive heart failure or inadequate blood flow to the kidneys; “congestive heart failure” is a condition in which the heart cannot pump an adequate volume of blood to meet th ...
... II) often progresses to complete (third-degree) heart block • Prolonged slow heart rate (bradycardia) may cause secondary congestive heart failure or inadequate blood flow to the kidneys; “congestive heart failure” is a condition in which the heart cannot pump an adequate volume of blood to meet th ...
Second-Degree Heart Block
... • If the pet has deterioration of the electrical impulse conduction system, second-degree heart block (Mobitz type II) often progresses to complete (third-degree) heart block • Prolonged slow heart rate (bradycardia) may cause secondary congestive heart failure or inadequate blood flow to the kidney ...
... • If the pet has deterioration of the electrical impulse conduction system, second-degree heart block (Mobitz type II) often progresses to complete (third-degree) heart block • Prolonged slow heart rate (bradycardia) may cause secondary congestive heart failure or inadequate blood flow to the kidney ...
Second-Degree Heart Block (Second-Degree Atrioventricular Block
... II) often progresses to complete (third-degree) heart block • Prolonged slow heart rate (bradycardia) may cause secondary congestive heart failure or inadequate blood flow to the kidneys; “congestive heart failure” is a condition in which the heart cannot pump an adequate volume of blood to meet th ...
... II) often progresses to complete (third-degree) heart block • Prolonged slow heart rate (bradycardia) may cause secondary congestive heart failure or inadequate blood flow to the kidneys; “congestive heart failure” is a condition in which the heart cannot pump an adequate volume of blood to meet th ...
Heart
... HEART HISTOLOGY 1. Identify the major histological features (listed below) of heart tissue. _____ intercalated discs _____ cardiac muscle fibers _____ Purkinje fibers (These are specialized conductive fibers located within the walls of the ventricles. They are responsible for relaying cardiac impuls ...
... HEART HISTOLOGY 1. Identify the major histological features (listed below) of heart tissue. _____ intercalated discs _____ cardiac muscle fibers _____ Purkinje fibers (These are specialized conductive fibers located within the walls of the ventricles. They are responsible for relaying cardiac impuls ...
The Transport System Study Guide
... Outline the mechanisms that control the heartbeat, including the roles of the SA (sinoatrial) node, AV (atrioventricular) node and conducting fibres in the ventricular walls. Outline atherosclerosis and the causes of coronary thrombosis. Discuss factors that affect the incidence of coronary heart di ...
... Outline the mechanisms that control the heartbeat, including the roles of the SA (sinoatrial) node, AV (atrioventricular) node and conducting fibres in the ventricular walls. Outline atherosclerosis and the causes of coronary thrombosis. Discuss factors that affect the incidence of coronary heart di ...
The HEART - Model High School
... kid, your heart is about the same size as your fist, and if you're an adult, it's about the same size as two fists. Your heart beats about 100,000 times in one day and about 35 million times in a year. During an average lifetime, the human heart will beat more than 2.5 billion times. ...
... kid, your heart is about the same size as your fist, and if you're an adult, it's about the same size as two fists. Your heart beats about 100,000 times in one day and about 35 million times in a year. During an average lifetime, the human heart will beat more than 2.5 billion times. ...
GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY 1. Presence of triad of
... 86. Basic therapy of the 5th step of bronchial asthma treatment includes: 1) daily administration of antiinflammatory preparations 2) high doses of inhalation glucocorticosteroids 3) standard doses of inhalation glucocorticosteroids in combination with prolonged β2-agonists 4) high doses of inhalat ...
... 86. Basic therapy of the 5th step of bronchial asthma treatment includes: 1) daily administration of antiinflammatory preparations 2) high doses of inhalation glucocorticosteroids 3) standard doses of inhalation glucocorticosteroids in combination with prolonged β2-agonists 4) high doses of inhalat ...
17. CV II - EKG-mechanical
... tachycardia (elevated heart rate), bradycardia (depressed heart rate), flutter (rapid rate in a particular chamber), & fibrillation (loss of coordination) • Depressed ST Segment: usually coronary ischemia with angina pectoris Bio 108/508 lec. 17 - p. 2 • Elevated ST Segment (sometimes accompanied by ...
... tachycardia (elevated heart rate), bradycardia (depressed heart rate), flutter (rapid rate in a particular chamber), & fibrillation (loss of coordination) • Depressed ST Segment: usually coronary ischemia with angina pectoris Bio 108/508 lec. 17 - p. 2 • Elevated ST Segment (sometimes accompanied by ...
THE GIANT HEART The Museum`s new Giant Heart is a vibrant
... The projected imagery is all original artwork, created by XVIVO, a medical illustration and animation firm based in Connecticut. XVIVO’s animations are generated at extremely high resolution and displayed on these multiple projectors through a software program called Seventh Sense, which is normally ...
... The projected imagery is all original artwork, created by XVIVO, a medical illustration and animation firm based in Connecticut. XVIVO’s animations are generated at extremely high resolution and displayed on these multiple projectors through a software program called Seventh Sense, which is normally ...
failure of the right ventricle
... blood, wards off the failure of this chamber. The same syndrome of longcontinued right heart failure with persistent ascites is seen occasionally when an enormous enlargement of the right heart has taken place ; I have seen several such cases, but no autopsy was obtainable and the exact anatomical d ...
... blood, wards off the failure of this chamber. The same syndrome of longcontinued right heart failure with persistent ascites is seen occasionally when an enormous enlargement of the right heart has taken place ; I have seen several such cases, but no autopsy was obtainable and the exact anatomical d ...
ventricles.
... An ear-shaped anterior extension of each atrium is its auricle. The atria and ventricles are separated from each other by a groove called the coronary sulcus The anterior interventricular sulcus and ...
... An ear-shaped anterior extension of each atrium is its auricle. The atria and ventricles are separated from each other by a groove called the coronary sulcus The anterior interventricular sulcus and ...
Automated quantitative assessment of left ventricular mass
... according to the results of cluster segmentation and compared to the results obtained from slices reoriented along the long axis of the LV. Results: the LVM showed the expected variations among different pathological heart conditions and the normal subjects. It can be computed to reliably characteri ...
... according to the results of cluster segmentation and compared to the results obtained from slices reoriented along the long axis of the LV. Results: the LVM showed the expected variations among different pathological heart conditions and the normal subjects. It can be computed to reliably characteri ...
Heart failure

Heart failure (HF), often referred to as congestive heart failure (CHF), occurs when the heart is unable to pump sufficiently to maintain blood flow to meet the body's needs. The terms chronic heart failure (CHF) or congestive cardiac failure (CCF) are often used interchangeably with congestive heart failure. Signs and symptoms commonly include shortness of breath, excessive tiredness, and leg swelling. The shortness of breath is usually worse with exercise, while lying down, and may wake the person at night. A limited ability to exercise is also a common feature.Common causes of heart failure include coronary artery disease including a previous myocardial infarction (heart attack), high blood pressure, atrial fibrillation, valvular heart disease, excess alcohol use, infection, and cardiomyopathy of an unknown cause. These cause heart failure by changing either the structure or the functioning of the heart. There are two main types of heart failure: heart failure due to left ventricular dysfunction and heart failure with normal ejection fraction depending on if the ability of the left ventricle to contract is affected, or the heart's ability to relax. The severity of disease is usually graded by the degree of problems with exercise. Heart failure is not the same as myocardial infarction (in which part of the heart muscle dies) or cardiac arrest (in which blood flow stops altogether). Other diseases that may have symptoms similar to heart failure include obesity, kidney failure, liver problems, anemia and thyroid disease.The condition is diagnosed based on the history of the symptoms and a physical examination with confirmation by echocardiography. Blood tests, electrocardiography, and chest radiography may be useful to determine the underlying cause. Treatment depends on the severity and cause of the disease. In people with chronic stable mild heart failure, treatment commonly consists of lifestyle modifications such as stopping smoking, physical exercise, and dietary changes, as well as medications. In those with heart failure due to left ventricular dysfunction, angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors or angiotensin receptor blockers along with beta blockers are recommended. For those with severe disease, aldosterone antagonists, or hydralazine plus a nitrate may be used. Diuretics are useful for preventing fluid retention. Sometimes, depending on the cause, an implanted device such as a pacemaker or an implantable cardiac defibrillator may be recommended. In some moderate or severe cases cardiac resynchronization therapy (CRT) may be suggested or cardiac contractility modulation may be of benefit. A ventricular assist device or occasionally a heart transplant may be recommended in those with severe disease despite all other measures.Heart failure is a common, costly, and potentially fatal condition. In developed countries, around 2% of adults have heart failure and in those over the age of 65, this increases to 6–10%. In the year after diagnosis the risk of death is about 35% after which it decreases to below 10% each year. This is similar to the risks with a number of types of cancer. In the United Kingdom the disease is the reason for 5% of emergency hospital admissions. Heart failure has been known since ancient times with the Ebers papyrus commenting on it around 1550 BCE.