* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Automated quantitative assessment of left ventricular mass
Cardiac contractility modulation wikipedia , lookup
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Ventricular fibrillation wikipedia , lookup
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia wikipedia , lookup
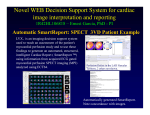
POSTER TECNICOS 1 AUTOMATED QUANTITATIVE ASSESSMENT OF LEFT VENTRICULAR MASS USING TRANSAXIAL TC-99M SESTAMIBI SPECT IMAGING. Rojas G.1, 3, Raff U. 2, Gonzalez P.3,Jaimovich R. 3, 4, Quintana J.C. 4 1 Department of Radiology, Santa Maria Clinic, University of Santiago de Chile, Facultad de Ciencia, Dept. of Physics3 University of Chile, Clinical Hospital, Dep. of Nuclear Medicine, 4 Nuclear Medicine Section, Catholic University Hospital, Santiago, Chile Introduction: The “left ventricular mass” (LVM) using Tc-99m Sestamibi SPECT imaging is a useful parameter to quantitatively stage heart disease affecting the left ventricular and hence its function. Purpose: The LVM is determined without reorienting the images along the long axis of the left ventricle. A comparison with reoriented SPECT images along the long axis of the left ventricle was performed. Material and Methods: Tomographic axial slices were obtained using a standard direct Fourier transform technique with no additional pre or post processing. Validation of the LVM was performed using a heart phantom. Patients were selected according to their pathology: ischemia, myocardial infarction with and without ischemia. Nine normal subjects were included. The axial slices were automatically segmented and the LVM was computed according to the results of cluster segmentation and compared to the results obtained from slices reoriented along the long axis of the LV. Results: the LVM showed the expected variations among different pathological heart conditions and the normal subjects. It can be computed to reliably characterize myocardial perfusion at rest vs. stress in normal subjects and patients with myocardial pathologies. Conclusion: The left ventricular mass obtained from non reoriented tomographic views of the myocardium can be a useful index to quantitatively assess various heart conditions where the myocardium lacks perfusion either between rest and stress studies or longitudinal studies. It can be used as a reliable quantitative parameter in the prognosis of myocardial diseases Correspondence G. Rojas, Address: Department of Radiology, Santa Maria ClinicAvda. Santa Maria 0500, Santiago Chile e-mail: [email protected] Tel: 56-2461 2000