Activity 3-9: Mountain Building
... mountain ages, weathering and _______________ wear it down to a lower, more _______________ shape. The most common type of mountain is a _______________ mountain. Folds occur deep within the crust, where high _______________ and pressure causes rock to behave in a _______________ manner. The folded ...
... mountain ages, weathering and _______________ wear it down to a lower, more _______________ shape. The most common type of mountain is a _______________ mountain. Folds occur deep within the crust, where high _______________ and pressure causes rock to behave in a _______________ manner. The folded ...
File - Ms. D. Science CGPA
... Metamorphic rock= great heat, pressure=change in shape & composition When great heat and pressure are applied to rock, the rock can change both its shape and its composition Any rock that forms from another rock as a result of changes in heat or pressure (or both heat and pressure) is a metamorphic ...
... Metamorphic rock= great heat, pressure=change in shape & composition When great heat and pressure are applied to rock, the rock can change both its shape and its composition Any rock that forms from another rock as a result of changes in heat or pressure (or both heat and pressure) is a metamorphic ...
Layers of the earth and convection currents
... – the putty-like layer of the mantle that the tectonic plates float on. ...
... – the putty-like layer of the mantle that the tectonic plates float on. ...
Constructive & Destructive Forces
... • Force that acts on rock to change its shape and volume • Energy is stored in the rock until it breaks or changes shape ...
... • Force that acts on rock to change its shape and volume • Energy is stored in the rock until it breaks or changes shape ...
CHAPTER 2 - EARTHQUAKES – STUDY GUIDE
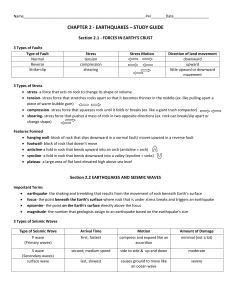
... seismograph- instrument that records and measures seismic waves seismogram- pattern of lines on a seismograph friction- force that opposes the motion of one surface as it moves across another surface ...
... seismograph- instrument that records and measures seismic waves seismogram- pattern of lines on a seismograph friction- force that opposes the motion of one surface as it moves across another surface ...
Ch. 10 Earth Science Study Guide The youngest rocks on the ocean
... An oceanographer (a person who studies the ocean floor) is traveling from the west toward the east on the Atlantic Ocean. She collects rock samples from the seafloor every 5 kilometers. The oceanographer stops when she determines that the rock samples are getting increasingly younger as she moves to ...
... An oceanographer (a person who studies the ocean floor) is traveling from the west toward the east on the Atlantic Ocean. She collects rock samples from the seafloor every 5 kilometers. The oceanographer stops when she determines that the rock samples are getting increasingly younger as she moves to ...
Plate Tectonics U2L4 Cloze Name: ______ 1. The supercontinent
... 1. The supercontinent called ________ formed 300 million years ago and began to break up 200 million years ago. 2. The process by which new oceanic lithosphere sea floor forms when magma rises to Earth’s surface, called ________ _________, occurs at mid-ocean ridges and solidifies, as older existing ...
... 1. The supercontinent called ________ formed 300 million years ago and began to break up 200 million years ago. 2. The process by which new oceanic lithosphere sea floor forms when magma rises to Earth’s surface, called ________ _________, occurs at mid-ocean ridges and solidifies, as older existing ...
Unit C – The Changing Earth(pages 292 – 401)
... organisms. He also proposed the now fundamental law of superposition, which states that younger layers are on top of older layers in a stratigraphic sequence. William Smith realized there is a predictable sequence of rock layers even in very different locations. He invented the idea of using index f ...
... organisms. He also proposed the now fundamental law of superposition, which states that younger layers are on top of older layers in a stratigraphic sequence. William Smith realized there is a predictable sequence of rock layers even in very different locations. He invented the idea of using index f ...
Test Review
... C. the hardness of the rock D. the location where the rock was found B. the layers within the rock ...
... C. the hardness of the rock D. the location where the rock was found B. the layers within the rock ...
Changes to Earths surface powerpoint
... Kinetic energy Potential energy • Kinetic energy of the moving plates can be converted into potential energy when two plates collide and “stick” together. • The potential energy builds up until it is finally converted back into kinetic energy and the plates “slip” ...
... Kinetic energy Potential energy • Kinetic energy of the moving plates can be converted into potential energy when two plates collide and “stick” together. • The potential energy builds up until it is finally converted back into kinetic energy and the plates “slip” ...
Plate tectonics: divergent, convergent, and transform plate boundaries
... Plate tectonics: divergent, convergent, and transform plate boundaries Plate tectonic theory envisions Earth's surface as consisting of plates of rigid lithosphere (the crust and uppermost mantle) moving over, and locally sinking into, a ductile asthenosphere (the rest of the mantle). Those plates m ...
... Plate tectonics: divergent, convergent, and transform plate boundaries Plate tectonic theory envisions Earth's surface as consisting of plates of rigid lithosphere (the crust and uppermost mantle) moving over, and locally sinking into, a ductile asthenosphere (the rest of the mantle). Those plates m ...
Presentation
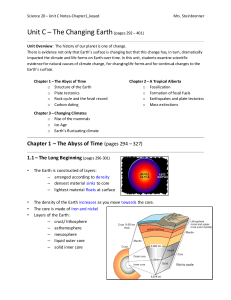
... The Earth is composed of four different layers. The crust is the layer that you live on, and it is the most widely studied and understood. The mantle is much hotter and has the ability to flow. The outer core and inner core are even hotter with pressures so great you would be squeezed into a ball sm ...
... The Earth is composed of four different layers. The crust is the layer that you live on, and it is the most widely studied and understood. The mantle is much hotter and has the ability to flow. The outer core and inner core are even hotter with pressures so great you would be squeezed into a ball sm ...
Name - Schoolwires.net
... magnetometer-measures the strength and direction of the magnetic fields magnetosphere- magnetic field around the earth, caused by an imaginary bar magnet in the center of the earth. ( all the iron ) Ocean plates formed by divergent plate boundaries along mid ocean ridges, where new oceanic crust is ...
... magnetometer-measures the strength and direction of the magnetic fields magnetosphere- magnetic field around the earth, caused by an imaginary bar magnet in the center of the earth. ( all the iron ) Ocean plates formed by divergent plate boundaries along mid ocean ridges, where new oceanic crust is ...
Igneous Rocks
... How quickly the magma cools has an effect on the texture of the igneous rock. ...
... How quickly the magma cools has an effect on the texture of the igneous rock. ...
Chapter 16 Outline (new)
... 5. The plate tectonic theory also helps to explain how certain patterns of biological evolution occurred. C. There are three types of boundaries for lithospheric plates. The boundaries are divergent plate boundaries, where plates move apart in opposite directions, and convergent plate boundaries, wh ...
... 5. The plate tectonic theory also helps to explain how certain patterns of biological evolution occurred. C. There are three types of boundaries for lithospheric plates. The boundaries are divergent plate boundaries, where plates move apart in opposite directions, and convergent plate boundaries, wh ...
Unit 1: Structure of the Earth
... The more rocks there are, the more they weigh. • So the deeper you go, the greater the pressure pushing on you. ...
... The more rocks there are, the more they weigh. • So the deeper you go, the greater the pressure pushing on you. ...
Document
... • Slow creeping motion of the mantle is caused by convection currents, carrying heat from Earth’s interior to the surface ...
... • Slow creeping motion of the mantle is caused by convection currents, carrying heat from Earth’s interior to the surface ...
Geography and Landforms Graffiti
... From the deepest ocean trench to the tallest mountain, plate tectonics explains the features and movement of Earth's surface in the present and the past. Plate tectonics is the theory that Earth's outer shell is divided into several plates that glide over the mantle, the rocky inner layer above the ...
... From the deepest ocean trench to the tallest mountain, plate tectonics explains the features and movement of Earth's surface in the present and the past. Plate tectonics is the theory that Earth's outer shell is divided into several plates that glide over the mantle, the rocky inner layer above the ...
PTYS/ASTR 206 – Section 2 - Lunar and Planetary Laboratory
... C) Chemical differentiation as heavy material sank to core during its formation D) Incoming Solar radiation #2. The process by which heavier materials sank into the centers of terrestrial planets while lighter material rose to the surfaces early in the history of these planets is known as A) seafloo ...
... C) Chemical differentiation as heavy material sank to core during its formation D) Incoming Solar radiation #2. The process by which heavier materials sank into the centers of terrestrial planets while lighter material rose to the surfaces early in the history of these planets is known as A) seafloo ...
STUDY GUIDE
... D. Modified Mercalli scale 3. The theory of plate tectonics best explains which of the following? A. how and why individual plates on Earth’s crust remain in motion B. what keeps individual plates on Earth’s crust from moving C. causes of destructive geological processes on Earth’s surface D. locati ...
... D. Modified Mercalli scale 3. The theory of plate tectonics best explains which of the following? A. how and why individual plates on Earth’s crust remain in motion B. what keeps individual plates on Earth’s crust from moving C. causes of destructive geological processes on Earth’s surface D. locati ...
Powerpoint
... around the Sun, (b) has sufficient mass for its selfgravity to overcome rigid body forces so that it assumes a hydrostatic equilibrium (nearly round) shape, and (c) has cleared the neighbourhood around its orbit. (2) A “dwarf planet” is a celestial body that (a) is in orbit around the Sun, (b) has s ...
... around the Sun, (b) has sufficient mass for its selfgravity to overcome rigid body forces so that it assumes a hydrostatic equilibrium (nearly round) shape, and (c) has cleared the neighbourhood around its orbit. (2) A “dwarf planet” is a celestial body that (a) is in orbit around the Sun, (b) has s ...
Geology

Geology (from the Greek γῆ, gē, i.e. ""earth"" and -λoγία, -logia, i.e. ""study of, discourse"") is an earth science comprising the study of solid Earth, the rocks of which it is composed, and the processes by which they change. Geology can also refer generally to the study of the solid features of any celestial body (such as the geology of the Moon or Mars).Geology gives insight into the history of the Earth by providing the primary evidence for plate tectonics, the evolutionary history of life, and past climates. Geology is important for mineral and hydrocarbon exploration and exploitation, evaluating water resources, understanding of natural hazards, the remediation of environmental problems, and for providing insights into past climate change. Geology also plays a role in geotechnical engineering and is a major academic discipline.