Layers of the Earth Study Guide
... 6. It is composed (means made of) minerals and rocks and is mostly made of granite and basalt. 7. The part of the crust where the continents are is known as continental crust. This is the thickest part of the crust. 8. The part of the crust beneath the ocean water is known as the oceanic crust, th ...
... 6. It is composed (means made of) minerals and rocks and is mostly made of granite and basalt. 7. The part of the crust where the continents are is known as continental crust. This is the thickest part of the crust. 8. The part of the crust beneath the ocean water is known as the oceanic crust, th ...
Morphology (-Plate Tectonics)
... 3. Glaciation (technically it is a type of erosion at times and deposition at others) Definition: the establishment and growth of ice sheets due to the build up of excess snow and ice that does not have time to melt or thaw in the summer months. Ice sheets expand during ice ages, which are thought ...
... 3. Glaciation (technically it is a type of erosion at times and deposition at others) Definition: the establishment and growth of ice sheets due to the build up of excess snow and ice that does not have time to melt or thaw in the summer months. Ice sheets expand during ice ages, which are thought ...
Structure of the Earth Crust
... into place for a long periods, allowing pressure to build below the crust. •When the pressure gets too great the plates come unstuck and move. This is an earthquake. ...
... into place for a long periods, allowing pressure to build below the crust. •When the pressure gets too great the plates come unstuck and move. This is an earthquake. ...
Changes to Earth`s Surface
... Sinkholes often appear in areas of _________ rock since it dissolves easily and can cause the land to collapse ...
... Sinkholes often appear in areas of _________ rock since it dissolves easily and can cause the land to collapse ...
8. Mid-Ocean Ridge
... • A tide with the least difference between low and high tide that occurs when the Earth, moon and sun are arranged perpendicular to each other (pull at right angles to the Earth). • Neap tide comes twice a month, in the first and third quarters of the moon. ...
... • A tide with the least difference between low and high tide that occurs when the Earth, moon and sun are arranged perpendicular to each other (pull at right angles to the Earth). • Neap tide comes twice a month, in the first and third quarters of the moon. ...
Ocean waves that wear away an island`s shoreline
... 9. The theory of continental drift states all the continents once were joined as a single supercontinent and have since drifted apart. 10. To support his theory, Alfred Wegener provided evidence from fossils, traces of anciet organisms preserved in rock. 11. The process of sea-floor spreading contin ...
... 9. The theory of continental drift states all the continents once were joined as a single supercontinent and have since drifted apart. 10. To support his theory, Alfred Wegener provided evidence from fossils, traces of anciet organisms preserved in rock. 11. The process of sea-floor spreading contin ...
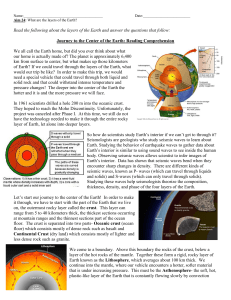
Read the following about the layers of the Earth and answer the
... less dense rock such as granite. We come to a boundary. Above this boundary the rocks of the crust, below a layer of the hot rocks of the mantle. Together these form a rigid, rocky layer of Earth known as the Lithosphere, which averages about 100 km thick. We continue into the mantle, where our vehi ...
... less dense rock such as granite. We come to a boundary. Above this boundary the rocks of the crust, below a layer of the hot rocks of the mantle. Together these form a rigid, rocky layer of Earth known as the Lithosphere, which averages about 100 km thick. We continue into the mantle, where our vehi ...
Evolution of Organisms and Landforms EOG review
... 6. Which best explains how geologic time scales can help scientists study the evolution of life on Earth? A. They describe the existence of rocks before there was life on Earth. B. They show that geological features have evolved at the same rate as organisms. C. They compare the life histories of s ...
... 6. Which best explains how geologic time scales can help scientists study the evolution of life on Earth? A. They describe the existence of rocks before there was life on Earth. B. They show that geological features have evolved at the same rate as organisms. C. They compare the life histories of s ...
Chapter 10
... and Africa. Another fossil that supports Continental Drift, is the plant called Glossopteris, which has been found in Africa, Australia, India, South America, AND Antarctica. Glacial deposits have been found in South America, Africa, India, and Australia. Rock Clues – Similar rocks have been foun ...
... and Africa. Another fossil that supports Continental Drift, is the plant called Glossopteris, which has been found in Africa, Australia, India, South America, AND Antarctica. Glacial deposits have been found in South America, Africa, India, and Australia. Rock Clues – Similar rocks have been foun ...
Geology study guide geology_study_guide
... A. The earth’s crust consists of solid inorganic elements and compounds called minerals and rocks that can sometimes be used as resources. Examples of mineral resources are fossil fuels (coal, oil, and natural gas), metallic minerals (such as aluminum, iron, and copper), and nonmetallic minerals (su ...
... A. The earth’s crust consists of solid inorganic elements and compounds called minerals and rocks that can sometimes be used as resources. Examples of mineral resources are fossil fuels (coal, oil, and natural gas), metallic minerals (such as aluminum, iron, and copper), and nonmetallic minerals (su ...
Emery APES: Chapter 14 Exam Version B 7 April 2015 May the
... 4. Waste soil and rock removed during surface mining is called a. hazardous waste b. gangue c. spoil d. tailings e. smelt 5. A series of large waves generated in the ocean by an earthquake, landslide, or volcanic activity are called a. pipe waves b. quake waves c. seismic waves d. rollers e. tsunami ...
... 4. Waste soil and rock removed during surface mining is called a. hazardous waste b. gangue c. spoil d. tailings e. smelt 5. A series of large waves generated in the ocean by an earthquake, landslide, or volcanic activity are called a. pipe waves b. quake waves c. seismic waves d. rollers e. tsunami ...
Earthquakes and Volcanoes
... break and move, the underground origin of the earthquake. Epicenter – The point directly above the focus, on the earth’s surface where the origin of an earthquake is above ground. ...
... break and move, the underground origin of the earthquake. Epicenter – The point directly above the focus, on the earth’s surface where the origin of an earthquake is above ground. ...
Scott Foresman Science
... speed and direction. Some stop completely when they reach the outer core. By studying the vibrations from earthquakes everywhere, scientists can learn about Earth’s layers. Scientists can also learn about the mantle and core through laboratory experiments. Materials that are likely inside Earth are ...
... speed and direction. Some stop completely when they reach the outer core. By studying the vibrations from earthquakes everywhere, scientists can learn about Earth’s layers. Scientists can also learn about the mantle and core through laboratory experiments. Materials that are likely inside Earth are ...
Chapter 2: Earth as a System STUDY NOTES Chapter 2 Section 1
... part of Earth below the mantle. • core ...
... part of Earth below the mantle. • core ...
Structure of the earth
... • Continental crust- composed primarily of granite, is thicker sedimentary and metamorphic rocks which form the continents • Oceanic crust- composed primarily of basalt, is thinner. ...
... • Continental crust- composed primarily of granite, is thicker sedimentary and metamorphic rocks which form the continents • Oceanic crust- composed primarily of basalt, is thinner. ...
Rock Cycle homework
... Igneous rock is any rock that forms from magma or lava. The name “igneous” comes from the Latin word ignis, meaning “fire.” Igneous rocks are classified according to their origin, texture, and mineral composition. Extrusive rock is igneous rock formed from lava that erupted onto Earth’s surface. Bas ...
... Igneous rock is any rock that forms from magma or lava. The name “igneous” comes from the Latin word ignis, meaning “fire.” Igneous rocks are classified according to their origin, texture, and mineral composition. Extrusive rock is igneous rock formed from lava that erupted onto Earth’s surface. Bas ...
Review of The Precambrian Earth: Tempos and Events
... The early Earth is the topic of the first introductory chapter, and the spirit of this well-deserving editorial initiative is expressed in a declared intention to follow both the principle «the present is the key to the past» and its opposite «the past is the key to the present». Obviously nothing r ...
... The early Earth is the topic of the first introductory chapter, and the spirit of this well-deserving editorial initiative is expressed in a declared intention to follow both the principle «the present is the key to the past» and its opposite «the past is the key to the present». Obviously nothing r ...
Bell Ringer - Hart County Schools
... • Hypothesis 2- the plates are driven by the force of gravity acting on their own massive weight. ...
... • Hypothesis 2- the plates are driven by the force of gravity acting on their own massive weight. ...
1-5 Review and Reinforce
... 4. Describe what happens when a. two plates carrying oceanic crust collide, b. two plates carrying continental crust collide, and c. a plate carrying oceanic crust collides with a plate carrying continental crust. 5. Explain what force caused the movement of the continents from one supercontinent to ...
... 4. Describe what happens when a. two plates carrying oceanic crust collide, b. two plates carrying continental crust collide, and c. a plate carrying oceanic crust collides with a plate carrying continental crust. 5. Explain what force caused the movement of the continents from one supercontinent to ...
Geology

Geology (from the Greek γῆ, gē, i.e. ""earth"" and -λoγία, -logia, i.e. ""study of, discourse"") is an earth science comprising the study of solid Earth, the rocks of which it is composed, and the processes by which they change. Geology can also refer generally to the study of the solid features of any celestial body (such as the geology of the Moon or Mars).Geology gives insight into the history of the Earth by providing the primary evidence for plate tectonics, the evolutionary history of life, and past climates. Geology is important for mineral and hydrocarbon exploration and exploitation, evaluating water resources, understanding of natural hazards, the remediation of environmental problems, and for providing insights into past climate change. Geology also plays a role in geotechnical engineering and is a major academic discipline.