directed reading deforming the earth`s crust
... _____ 11. When rock layers break, the resulting surface they break and slide on is a a. wall. c. fault. b. slide. d. fold. _____ 12. When tension pulls rocks apart, it creates a a. normal fault. c. reverse fault. b. fold. d. strike-slip fault. _____ 13. When compression pushes rocks together, it cre ...
... _____ 11. When rock layers break, the resulting surface they break and slide on is a a. wall. c. fault. b. slide. d. fold. _____ 12. When tension pulls rocks apart, it creates a a. normal fault. c. reverse fault. b. fold. d. strike-slip fault. _____ 13. When compression pushes rocks together, it cre ...
Document
... _____ 11. When rock layers break, the resulting surface they break and slide on is a a. wall. c. fault. b. slide. d. fold. _____ 12. When tension pulls rocks apart, it creates a a. normal fault. c. reverse fault. b. fold. d. strike-slip fault. _____ 13. When compression pushes rocks together, it cre ...
... _____ 11. When rock layers break, the resulting surface they break and slide on is a a. wall. c. fault. b. slide. d. fold. _____ 12. When tension pulls rocks apart, it creates a a. normal fault. c. reverse fault. b. fold. d. strike-slip fault. _____ 13. When compression pushes rocks together, it cre ...
01 - Mayfield City Schools
... _____ 11. When rock layers break, the resulting surface they break and slide on is a a. wall. c. fault. b. slide. d. fold. _____ 12. When tension pulls rocks apart, it creates a a. normal fault. c. reverse fault. b. fold. d. strike-slip fault. _____ 13. When compression pushes rocks together, it cre ...
... _____ 11. When rock layers break, the resulting surface they break and slide on is a a. wall. c. fault. b. slide. d. fold. _____ 12. When tension pulls rocks apart, it creates a a. normal fault. c. reverse fault. b. fold. d. strike-slip fault. _____ 13. When compression pushes rocks together, it cre ...
No Slide Title - University of South Alabama
... Plate Tectonic Boundaries Tectonic plates can interact in one of 3 ways 1) Move away from one another: Divergent Plate Boundary 2) Move towards one another: Convergent Plate Boundary 3) Slide past one another: Transform Fault Plate Boundary ...
... Plate Tectonic Boundaries Tectonic plates can interact in one of 3 ways 1) Move away from one another: Divergent Plate Boundary 2) Move towards one another: Convergent Plate Boundary 3) Slide past one another: Transform Fault Plate Boundary ...
Pre-Test: Chapter 7-Plate Tectonics
... 21. What is the order of the layers of the Earth from the surface to the center? a. asthenosphere, lithosphere, mesosphere, outer core, inner core b. lithosphere, asthenosphere, mesosphere, outer core, inner core c. mesosphere, outer core, inner core, lithosphere, asthenosphere d. lithosphere, asthe ...
... 21. What is the order of the layers of the Earth from the surface to the center? a. asthenosphere, lithosphere, mesosphere, outer core, inner core b. lithosphere, asthenosphere, mesosphere, outer core, inner core c. mesosphere, outer core, inner core, lithosphere, asthenosphere d. lithosphere, asthe ...
Planet Earth - Topic 4 (ANSWERS)
... 3. Who is Alfred Wegener? What were some of his ideas? p. 383 A scientist who hypothesized that the continents were once joined together. He called this super continent PANGAEA. The continents were then separated. He called this the ‘Theory of Continental Drift’. 4. Please list the evidence Wegener ...
... 3. Who is Alfred Wegener? What were some of his ideas? p. 383 A scientist who hypothesized that the continents were once joined together. He called this super continent PANGAEA. The continents were then separated. He called this the ‘Theory of Continental Drift’. 4. Please list the evidence Wegener ...
geological time scale - Liberty Union High School District
... slowly. Example: gradual shifting across different continental land forms ...
... slowly. Example: gradual shifting across different continental land forms ...
Earth`s interio
... • P-wave velocity 8 Km/sec & higher • Made of ultramafic rock – Low in silica, high in Fe, Mg – Denser than basalt • Lithosphere – rigid uppermost part of mantle plus crust – tectonic plates – Average thickness of 100 Km. • Asthenosphere ...
... • P-wave velocity 8 Km/sec & higher • Made of ultramafic rock – Low in silica, high in Fe, Mg – Denser than basalt • Lithosphere – rigid uppermost part of mantle plus crust – tectonic plates – Average thickness of 100 Km. • Asthenosphere ...
Lecture 11 Structural Geology
... • Folds in Rock A fold is a bent structure that originally was planar, such as a sedimentary bed. Folds may be produced by either horizontal compression or vertical forces in the crust, just as pushing in on opposite sides of a paper or up from below. ...
... • Folds in Rock A fold is a bent structure that originally was planar, such as a sedimentary bed. Folds may be produced by either horizontal compression or vertical forces in the crust, just as pushing in on opposite sides of a paper or up from below. ...
Weathering, Erosion, and Plate Tectonics
... different features of the earth? ► What are tectonic plates? ► What are the three major Types of Plate ...
... different features of the earth? ► What are tectonic plates? ► What are the three major Types of Plate ...
WHAT IS A PLATE? The surface of the Earth is broken up into large
... warm. Pitch, used for roads, can be brittle when struck with a hammer, but still flow very slowly, just as ice does when a glacier moves downhill. The temperature gradient of the Earth means that, at a certain depth in the upper mantle, peridotite will behave like this too. This occurs when peri ...
... warm. Pitch, used for roads, can be brittle when struck with a hammer, but still flow very slowly, just as ice does when a glacier moves downhill. The temperature gradient of the Earth means that, at a certain depth in the upper mantle, peridotite will behave like this too. This occurs when peri ...
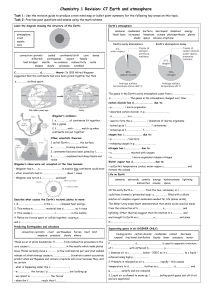
C7 Revision Earth and atmosphere[1].
... core causes c……….……………………. c……………………. in the mantle which make plates move. Plates normally move s………..….. (a few centimetres per year) but sudden release of strain energy causes e…………………………. Scientists cannot accurately predict when earthquakes and volcanic eruptions will occur because they can’t ...
... core causes c……….……………………. c……………………. in the mantle which make plates move. Plates normally move s………..….. (a few centimetres per year) but sudden release of strain energy causes e…………………………. Scientists cannot accurately predict when earthquakes and volcanic eruptions will occur because they can’t ...
C7 Revision Earth and Atmosphere
... core causes c……….……………………. c……………………. in the mantle which make plates move. Plates normally move s………..….. (a few centimetres per year) but sudden release of strain energy causes e…………………………. Scientists cannot accurately predict when earthquakes and volcanic eruptions will occur because they can’t ...
... core causes c……….……………………. c……………………. in the mantle which make plates move. Plates normally move s………..….. (a few centimetres per year) but sudden release of strain energy causes e…………………………. Scientists cannot accurately predict when earthquakes and volcanic eruptions will occur because they can’t ...
Canadian Geography 1202 - Nova Central School District
... - If the plates move apart , magma or liquid rock moves to the surface , cools and forms new igneous rock. - If the plates move toward each other they will scrape or push on top of each other. The lighter plate is usually forced up over the heavier one . This movement often results in the folding o ...
... - If the plates move apart , magma or liquid rock moves to the surface , cools and forms new igneous rock. - If the plates move toward each other they will scrape or push on top of each other. The lighter plate is usually forced up over the heavier one . This movement often results in the folding o ...
Ch 13-Volcanoes
... • Any activity that includes the movement of magma toward or onto Earth’s surface • Magma rises upward through the crust cuz the magma is less dense than surrounding rock • Lava-magma that flows onto Earth’s surface • Vent-opening that lava flows through • Volcano-vent or fissure in Earth’s surface ...
... • Any activity that includes the movement of magma toward or onto Earth’s surface • Magma rises upward through the crust cuz the magma is less dense than surrounding rock • Lava-magma that flows onto Earth’s surface • Vent-opening that lava flows through • Volcano-vent or fissure in Earth’s surface ...
Handout 2-1.b, c, and d Name: Period
... The diagram below shows the interior layers of Earth. The layers in the diagram are representative of arrangement and are not drawn to scale. Use this diagram to match the layers 13-17. 13. mantle 14. lithosphere ...
... The diagram below shows the interior layers of Earth. The layers in the diagram are representative of arrangement and are not drawn to scale. Use this diagram to match the layers 13-17. 13. mantle 14. lithosphere ...
Deforming the Earths Crust
... _____ 11. When rock layers break, the resulting surface they break and slide on is a a. wall. c. fault. b. slide. d. fold. _____ 12. When tension pulls rocks apart, it creates a a. normal fault. c. reverse fault. b. fold. d. strike-slip fault. _____ 13. When compression pushes rocks together, it cre ...
... _____ 11. When rock layers break, the resulting surface they break and slide on is a a. wall. c. fault. b. slide. d. fold. _____ 12. When tension pulls rocks apart, it creates a a. normal fault. c. reverse fault. b. fold. d. strike-slip fault. _____ 13. When compression pushes rocks together, it cre ...
evidence that our plates move - HULK SCIENCE
... Focus: The exact location in the Earth’s crust where rock slips. Epicenter: The location on earth’s surface directly above the focus. P – wave or Primary wave -Fastest and first seismic wave to arrive -Travels through solid, liquid, gas S – wave or Secondary Wave -This wave causes the most damage! - ...
... Focus: The exact location in the Earth’s crust where rock slips. Epicenter: The location on earth’s surface directly above the focus. P – wave or Primary wave -Fastest and first seismic wave to arrive -Travels through solid, liquid, gas S – wave or Secondary Wave -This wave causes the most damage! - ...
The Earth`s Interior & Plate Tectonics
... The mantle extends about half way to the center. It's made of solid rock and behaves like an viscous liquid. The convection of heat from the center of the Earth is what ultimately drives the movement of the tectonic plates and cause mountains to rise. ...
... The mantle extends about half way to the center. It's made of solid rock and behaves like an viscous liquid. The convection of heat from the center of the Earth is what ultimately drives the movement of the tectonic plates and cause mountains to rise. ...
Changing Earth
... divided into eras, eras divided into periods, and periods divided into epochs. Each transition corresponds to a transition in the geological strata and associated fossils. ...
... divided into eras, eras divided into periods, and periods divided into epochs. Each transition corresponds to a transition in the geological strata and associated fossils. ...
Topic/Objective: ______ _____ Full Name: __________ Class: __
... and the damage expected at each intensity level. In addition to detecting and locating earthquakes _____________ waves also provide an insight to the Earth’s internal structure. ________________ can travel through any type of material. ________________ can travel through ______________ but not _ ...
... and the damage expected at each intensity level. In addition to detecting and locating earthquakes _____________ waves also provide an insight to the Earth’s internal structure. ________________ can travel through any type of material. ________________ can travel through ______________ but not _ ...
Inside Earth-Chapter 1 - Kenston Local Schools
... the repeating cycle of the rising and falling of the hot material in the mantle (asthenosphere); contributes to the movement of the crustal plates; the movement of fluid, caused by differences in temperature, that transfers heat from one part of the fluid to ...
... the repeating cycle of the rising and falling of the hot material in the mantle (asthenosphere); contributes to the movement of the crustal plates; the movement of fluid, caused by differences in temperature, that transfers heat from one part of the fluid to ...
Plate Tectonics
... • Earth’s crust and upper mantle are broken into sections called plates, they move on a plastic-like layer of the mantle. • Plates and upper mantle form the lithosphere. • Plastic-like layer below is called asthenosphere. ...
... • Earth’s crust and upper mantle are broken into sections called plates, they move on a plastic-like layer of the mantle. • Plates and upper mantle form the lithosphere. • Plastic-like layer below is called asthenosphere. ...
Lithospheric plates - The Old Courthouse Museum Batemans Bay
... • The Geology of Australia – David Johnson, Cambridge University Press, 2004. ...
... • The Geology of Australia – David Johnson, Cambridge University Press, 2004. ...
Geology

Geology (from the Greek γῆ, gē, i.e. ""earth"" and -λoγία, -logia, i.e. ""study of, discourse"") is an earth science comprising the study of solid Earth, the rocks of which it is composed, and the processes by which they change. Geology can also refer generally to the study of the solid features of any celestial body (such as the geology of the Moon or Mars).Geology gives insight into the history of the Earth by providing the primary evidence for plate tectonics, the evolutionary history of life, and past climates. Geology is important for mineral and hydrocarbon exploration and exploitation, evaluating water resources, understanding of natural hazards, the remediation of environmental problems, and for providing insights into past climate change. Geology also plays a role in geotechnical engineering and is a major academic discipline.











![C7 Revision Earth and atmosphere[1].](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/001217671_1-b9cc347117db8dff9935614904a55b09-300x300.png)