Mid-ocean ridges
... moving with respect to each other These movements result in many of the structural features we see on Earth, like mountains, trenches and ocean basins Plate movement also shapes continents, for example leading to formation of mountains like the Himalayas ...
... moving with respect to each other These movements result in many of the structural features we see on Earth, like mountains, trenches and ocean basins Plate movement also shapes continents, for example leading to formation of mountains like the Himalayas ...
Convergent Boundaries
... material deep within the Earth rises while cooler material near the surface sinks. ◦ This is what causes tectonic plates to move around. ...
... material deep within the Earth rises while cooler material near the surface sinks. ◦ This is what causes tectonic plates to move around. ...
Chapter 8 - Earth Systems
... • What’s here now has been here all along • Layers: ▫ Core – solid inner, liquid outer ▫ Mantle – made of magma ▫ Crust – solid rock ...
... • What’s here now has been here all along • Layers: ▫ Core – solid inner, liquid outer ▫ Mantle – made of magma ▫ Crust – solid rock ...
Plate Tectonics - isd194 cms .demo. ties .k12. mn .us
... • The plates move on a layer of liquid rock located miles below the surface • The plates move slowly across the earth • 200 million years ago – one giant continent existed called Pangea ...
... • The plates move on a layer of liquid rock located miles below the surface • The plates move slowly across the earth • 200 million years ago – one giant continent existed called Pangea ...
Chapter 6 – Earthquakes Part 3
... thick. 2. The Mantle – rocky layer beneath the crust, with areas of molten rock ~ 2885km thick. 3. The Outer Core – molten layer composed mainly of iron and nickel ~ 2270 km thick. 4. The Inner Core – solid metal, iron and nickel ~ 1216 km thick ...
... thick. 2. The Mantle – rocky layer beneath the crust, with areas of molten rock ~ 2885km thick. 3. The Outer Core – molten layer composed mainly of iron and nickel ~ 2270 km thick. 4. The Inner Core – solid metal, iron and nickel ~ 1216 km thick ...
A 13-Page Resource of Earth and Space Science Worksheets
... interior of the earth, as opposed to surface waves that travel near the earth's surface. P and S waves are body waves. This is a fracture along which the blocks of crust on either side have moved relative to one another parallel to the fracture. This is the outermost major layer of the earth, rangin ...
... interior of the earth, as opposed to surface waves that travel near the earth's surface. P and S waves are body waves. This is a fracture along which the blocks of crust on either side have moved relative to one another parallel to the fracture. This is the outermost major layer of the earth, rangin ...
Earthquake Test Study Guide
... 18) What does the Richter scale measure? 19) What is the difference in wave amplitude of an earthquake that measures 4.0 on the Richter scale, to an earthquake that measures 5.0? 20) What does the Mercalli scale measure? (Intensity) 21) How many seismograph readings (wave travel time data) are requi ...
... 18) What does the Richter scale measure? 19) What is the difference in wave amplitude of an earthquake that measures 4.0 on the Richter scale, to an earthquake that measures 5.0? 20) What does the Mercalli scale measure? (Intensity) 21) How many seismograph readings (wave travel time data) are requi ...
Plate Tectonics Review Questions
... 4. Generally, how fast is the motion of the plates? _______________________________________________ 5. What kind of motion would be expected at a transform fault boundary? ...
... 4. Generally, how fast is the motion of the plates? _______________________________________________ 5. What kind of motion would be expected at a transform fault boundary? ...
Earthquakes, Volcanoes, tsunamis
... measure of the amount of energy released. Modified Mercalli Scale- ranges from 1-12 and is based on observations in the areas affected. ...
... measure of the amount of energy released. Modified Mercalli Scale- ranges from 1-12 and is based on observations in the areas affected. ...
SuperScience TE Template
... 1. Which of Earth’s layers features tectonic plates? _______________________________________________ the shifting of tectonic plates ...
... 1. Which of Earth’s layers features tectonic plates? _______________________________________________ the shifting of tectonic plates ...
Geography 1000 - SmartMap.us Home
... An alarm that is based on sound waves (supersonic speed) traveling through the air. ...
... An alarm that is based on sound waves (supersonic speed) traveling through the air. ...
7-3 Lecture PDF
... Three forces interact to cause tectonic plate motion. Convection currents in the mantle produce a force that cause motion called basal drag. The force of ridge push causes the plates to be pushed away from each other at mid ocean ridges. When a plate sinks below another plate, it pulls on the rest o ...
... Three forces interact to cause tectonic plate motion. Convection currents in the mantle produce a force that cause motion called basal drag. The force of ridge push causes the plates to be pushed away from each other at mid ocean ridges. When a plate sinks below another plate, it pulls on the rest o ...
AUGURY, Reconstructing Earth`s mantle convection
... were already there, but the development of computational power and methods was fundamental. Most models were limited in some way – Professor Paul Tackley created a unique tool to partially resolve these problems. After years of appreciating our limitations, we may have given up on the idea of produc ...
... were already there, but the development of computational power and methods was fundamental. Most models were limited in some way – Professor Paul Tackley created a unique tool to partially resolve these problems. After years of appreciating our limitations, we may have given up on the idea of produc ...
Plate Tectonics 1
... Supporting Continental Drift? Alfred Wegner came up with the Continental Drift Hypothesis. His 5 pieces of evidence were: 1) Continents seemed to fit together 2) Similar fossils on each continent 3) Rocks matched (age and composition) 4) Glacial evidence – striations (scratches in rocks matched) + d ...
... Supporting Continental Drift? Alfred Wegner came up with the Continental Drift Hypothesis. His 5 pieces of evidence were: 1) Continents seemed to fit together 2) Similar fossils on each continent 3) Rocks matched (age and composition) 4) Glacial evidence – striations (scratches in rocks matched) + d ...
Layers PangaeaCont drift Convection
... 1. What are the three types of plate boundaries? 2. What are the three specific types of convergent boundaries? ...
... 1. What are the three types of plate boundaries? 2. What are the three specific types of convergent boundaries? ...
which is integral in the stabilization of new continental crust, or by
... Crust formation must therefore occur in at least two stages,first, melting of the mantle to produce basaltic magma,and second,either fractional crystallization or re-melting of the basalt ultimately to produce the more evolved rocks of which continental crust is dominantly composed. The products of ...
... Crust formation must therefore occur in at least two stages,first, melting of the mantle to produce basaltic magma,and second,either fractional crystallization or re-melting of the basalt ultimately to produce the more evolved rocks of which continental crust is dominantly composed. The products of ...
crust - WordPress.com
... How many minerals do you think exist in the crust of the Earth? Geologists have discovered more than 3000 mineral species been in the Earth, but all of them are not of common occurrence. In fact more than 99% of rocks of the crust are made up from only 20 minerals and each rock being composed of two ...
... How many minerals do you think exist in the crust of the Earth? Geologists have discovered more than 3000 mineral species been in the Earth, but all of them are not of common occurrence. In fact more than 99% of rocks of the crust are made up from only 20 minerals and each rock being composed of two ...
Earthquakes
... Tectonic stress (most common), As plates push, pull, or slip past each other, stress increases along faults. Geothermal gradient (variation due to boundary) Deformation is a result of the stress Deformation – the change to the shape of rock in response to stress ...
... Tectonic stress (most common), As plates push, pull, or slip past each other, stress increases along faults. Geothermal gradient (variation due to boundary) Deformation is a result of the stress Deformation – the change to the shape of rock in response to stress ...
Earth,Notes,RevQs,Ch12
... ridges, it is fairly similar in composition and thickness everywhere, and nowhere is it older than 200 million years. Continental crust is highly variable with many different compositions, it is formed in a variety of ways, and it can be as old as 4 billion years. The thinnest crust is found underne ...
... ridges, it is fairly similar in composition and thickness everywhere, and nowhere is it older than 200 million years. Continental crust is highly variable with many different compositions, it is formed in a variety of ways, and it can be as old as 4 billion years. The thinnest crust is found underne ...
Earth and Space Science (Earth`s Interior)
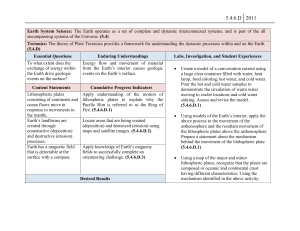
... Topic ESS.1 This topic focuses on the physical features of Earth and how they formed. This includes the interior of Earth, the rock record, plate tectonics and landforms. Content Statement ESS.1.1 The composition and properties of Earth’s interior are identified by the behavior of seismic waves. ESS ...
... Topic ESS.1 This topic focuses on the physical features of Earth and how they formed. This includes the interior of Earth, the rock record, plate tectonics and landforms. Content Statement ESS.1.1 The composition and properties of Earth’s interior are identified by the behavior of seismic waves. ESS ...
Name - OnCourse
... from the center of the ridge, cooling, and building up around the ridge. Another way is through upward-moving ...
... from the center of the ridge, cooling, and building up around the ridge. Another way is through upward-moving ...
Differentiation of the Earth
... cool outer regions of the nebula determined what kinds of condensates were available to form planets. Near Mercury’s orbit, metal started to condense. Moving outwards to Venus and Earth, more rock condensed Only beyond the frost line, which lay between the present-day orbits of Mars and Jupiter, wer ...
... cool outer regions of the nebula determined what kinds of condensates were available to form planets. Near Mercury’s orbit, metal started to condense. Moving outwards to Venus and Earth, more rock condensed Only beyond the frost line, which lay between the present-day orbits of Mars and Jupiter, wer ...
The Theory of Plate Tectonics
... Plate Tectonics • The Earth’s lithosphere is divided into plates that move on top of the asthenosphere. Lithosphere ...
... Plate Tectonics • The Earth’s lithosphere is divided into plates that move on top of the asthenosphere. Lithosphere ...
Geology

Geology (from the Greek γῆ, gē, i.e. ""earth"" and -λoγία, -logia, i.e. ""study of, discourse"") is an earth science comprising the study of solid Earth, the rocks of which it is composed, and the processes by which they change. Geology can also refer generally to the study of the solid features of any celestial body (such as the geology of the Moon or Mars).Geology gives insight into the history of the Earth by providing the primary evidence for plate tectonics, the evolutionary history of life, and past climates. Geology is important for mineral and hydrocarbon exploration and exploitation, evaluating water resources, understanding of natural hazards, the remediation of environmental problems, and for providing insights into past climate change. Geology also plays a role in geotechnical engineering and is a major academic discipline.