Lesson
... Where on earth are earthquakes likely to occur? What can the patterns in earthquake locations tell us about the structure of the earth? ...
... Where on earth are earthquakes likely to occur? What can the patterns in earthquake locations tell us about the structure of the earth? ...
Fracking MEL - Temple University Sites
... piece—it is made up of many pieces like a puzzle covering the surface of Earth. These puzzle pieces keep slowly moving around, sliding past one another and bumping into each other. These pieces are tectonic plates, and the edges of the plates are called the plate boundaries. The plate boundaries are ...
... piece—it is made up of many pieces like a puzzle covering the surface of Earth. These puzzle pieces keep slowly moving around, sliding past one another and bumping into each other. These pieces are tectonic plates, and the edges of the plates are called the plate boundaries. The plate boundaries are ...
jeopardyplatetech Answer Key
... What was the name of the supercontinent landmass that Wegener named? Why was Wegeners theory rejected? Name three pieces of evidence that Wegener used to support continental drift ...
... What was the name of the supercontinent landmass that Wegener named? Why was Wegeners theory rejected? Name three pieces of evidence that Wegener used to support continental drift ...
hotspots and magnetic reversals
... Volcanoes are formed by: - Subduction - Rift valleys - Hotspots ...
... Volcanoes are formed by: - Subduction - Rift valleys - Hotspots ...
Divergent Boundary
... • 2. Continue with Ch. 7 Section 3 Discussion • 3. Begin work on Plate Tectonics WS ...
... • 2. Continue with Ch. 7 Section 3 Discussion • 3. Begin work on Plate Tectonics WS ...
Slide 1
... A. cooling of magma cells that rises to the Earth’s surface B. magnetic attraction between Earth’s iron core and its poles C. temperature differences between Earth’s oceanic and continental plates D. the Earth’s internal heat producing convection currents in the mantle. ...
... A. cooling of magma cells that rises to the Earth’s surface B. magnetic attraction between Earth’s iron core and its poles C. temperature differences between Earth’s oceanic and continental plates D. the Earth’s internal heat producing convection currents in the mantle. ...
Study Guide for Plate Tectonics Final
... 4. What is a divergent plate boundary? How do the plates move? What happens to the crust at this boundary? What features are formed at a divergent plate boundary? Know the difference between ocean and land divergent boundaries. ...
... 4. What is a divergent plate boundary? How do the plates move? What happens to the crust at this boundary? What features are formed at a divergent plate boundary? Know the difference between ocean and land divergent boundaries. ...
to view the Slideshow
... molten rock will rise and if it breaks through the lithosphere it will create a volcano. It is important to note that since part of the lithosphere is being lost at this point, there must be some other point on the earth where new land is being created, remember ...
... molten rock will rise and if it breaks through the lithosphere it will create a volcano. It is important to note that since part of the lithosphere is being lost at this point, there must be some other point on the earth where new land is being created, remember ...
PLATE TECTONICS
... allowing various kinds of organisms to move across and flourish on continents now separated by oceans. According to Suess and others, the land bridges sank into the ocean long ago and no longer exist. ...
... allowing various kinds of organisms to move across and flourish on continents now separated by oceans. According to Suess and others, the land bridges sank into the ocean long ago and no longer exist. ...
5. Explain the 3 different types of faults.
... Most take place near the edges of tectonic plates Earthquakes can occur at: ◦ Convergent Boundaries (Reverse Fault) ◦ Divergent Boundaries (Normal Fault) ◦ Transform Boundaries (Strike-Slip Fault) ...
... Most take place near the edges of tectonic plates Earthquakes can occur at: ◦ Convergent Boundaries (Reverse Fault) ◦ Divergent Boundaries (Normal Fault) ◦ Transform Boundaries (Strike-Slip Fault) ...
Plate Tectonics PPT
... toward the surface, cools, get denser, and then sinks again with the pull of gravity • Creates convection currents in asthenosphere beneath the plates that cause the plates to move. ...
... toward the surface, cools, get denser, and then sinks again with the pull of gravity • Creates convection currents in asthenosphere beneath the plates that cause the plates to move. ...
Powerpoint Presentation Physical Geology, 10/e
... – Measurements accurate to within 1 cm – Motion rates closely match those predicted using seafloor magnetic anomalies ...
... – Measurements accurate to within 1 cm – Motion rates closely match those predicted using seafloor magnetic anomalies ...
Inside Earth: Chapter 1
... – How is the water in the swimming pool similar to Earth’s interior? How is it different? • The deeper the water in the pool, the greater the pressure, just as pressure is greater the deeper you go beneath the surface of Earth • The water in the pool does not have layers ...
... – How is the water in the swimming pool similar to Earth’s interior? How is it different? • The deeper the water in the pool, the greater the pressure, just as pressure is greater the deeper you go beneath the surface of Earth • The water in the pool does not have layers ...
Figure 01-04 Origin Solar System
... Convection Currents: The movement of a fluid, caused by differences in temperature, that transfers heat from one part of the fluid to another ...
... Convection Currents: The movement of a fluid, caused by differences in temperature, that transfers heat from one part of the fluid to another ...
Biogeochemical cycles – Geological, Chemical
... per year - approximately the rate at which human fingernails grow. • The plates slide about on the layer of hotter, softer mantle. • The mantle is like a supercooled liquid – i.e. a glass. • Where plates encounter each other, stresses and strains build up manifested in extreme cases by violent earth ...
... per year - approximately the rate at which human fingernails grow. • The plates slide about on the layer of hotter, softer mantle. • The mantle is like a supercooled liquid – i.e. a glass. • Where plates encounter each other, stresses and strains build up manifested in extreme cases by violent earth ...
this PDF file
... the bedrock of Southern Mountains basin is formed by metamorphic complex. To determine whether the bedrock was the seismic source, several approaches were carried out as follows. ...
... the bedrock of Southern Mountains basin is formed by metamorphic complex. To determine whether the bedrock was the seismic source, several approaches were carried out as follows. ...
Volcanoes and Plate Tectonics
... A. A volcano is a weak spot in the crust where molten material, or magma, comes to the surface. 1. Magma is a molten mixture of rock-forming substances, gases, and water from the mantle 2. When magma reaches the surface it is called lava 3. After lava cools it forms solid rock 4. The lava released d ...
... A. A volcano is a weak spot in the crust where molten material, or magma, comes to the surface. 1. Magma is a molten mixture of rock-forming substances, gases, and water from the mantle 2. When magma reaches the surface it is called lava 3. After lava cools it forms solid rock 4. The lava released d ...
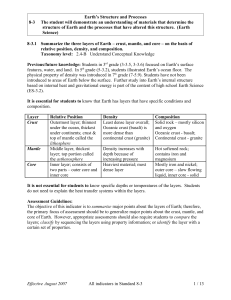
Inside Earth: Layers of the Earth
... From outside to inside, Earth is divided into crust, mantle, and core. Each has a different chemical makeup. Earth can also be divided into layers with different properties. The two most important are lithosphere and asthenosphere. ...
... From outside to inside, Earth is divided into crust, mantle, and core. Each has a different chemical makeup. Earth can also be divided into layers with different properties. The two most important are lithosphere and asthenosphere. ...
Ocean Floor
... Difference between oceanic and continental crust. Understand the processes that are continuously changing Earth’s surface as lithospheric plates move relative to one another. Identify the role of oceanic ridges, transform faults and deep-sea trenches in defining the edges of lithospheric plates. Und ...
... Difference between oceanic and continental crust. Understand the processes that are continuously changing Earth’s surface as lithospheric plates move relative to one another. Identify the role of oceanic ridges, transform faults and deep-sea trenches in defining the edges of lithospheric plates. Und ...
Density of Earth Materials Lab - Mercer Island School District
... its average composition is similar to the rock granite. Granite is a felsic rock (which means it has a high feldspar and silica content), composed of quartz, potassium-rich feldspar, and mica. Mafic rocks contain denser minerals and therefore, oceanic crust is denser than continental crust (the aver ...
... its average composition is similar to the rock granite. Granite is a felsic rock (which means it has a high feldspar and silica content), composed of quartz, potassium-rich feldspar, and mica. Mafic rocks contain denser minerals and therefore, oceanic crust is denser than continental crust (the aver ...
Convection Currents and the Mantle
... • Turn to page 16 in your ISN and answer the following questions… 1.What general statement can you make about the change in temperature through Earth’s interior? 2.What is the overall composition of oceanic crust? ...
... • Turn to page 16 in your ISN and answer the following questions… 1.What general statement can you make about the change in temperature through Earth’s interior? 2.What is the overall composition of oceanic crust? ...
The Earth`s structure
... tectonic theory is recognized as a major milestone in the earth sciences. It is comparable to the revolution caused by Darwin’s theory of evolution or Einstein’s theories about motion and gravity. Plate tectonics provide a framework for interpreting the composition, structure and internal processes ...
... tectonic theory is recognized as a major milestone in the earth sciences. It is comparable to the revolution caused by Darwin’s theory of evolution or Einstein’s theories about motion and gravity. Plate tectonics provide a framework for interpreting the composition, structure and internal processes ...
Science
... evidence, rock, and climate clues. This hypothesis later led to the theory of plate tectonics when evidence was found as to why the plates could move. Plate tectonics explains how many Earth features form. Motion of the Lithospheric Plates • Plates float on the upper part of the mantle. • Convection ...
... evidence, rock, and climate clues. This hypothesis later led to the theory of plate tectonics when evidence was found as to why the plates could move. Plate tectonics explains how many Earth features form. Motion of the Lithospheric Plates • Plates float on the upper part of the mantle. • Convection ...
Geology

Geology (from the Greek γῆ, gē, i.e. ""earth"" and -λoγία, -logia, i.e. ""study of, discourse"") is an earth science comprising the study of solid Earth, the rocks of which it is composed, and the processes by which they change. Geology can also refer generally to the study of the solid features of any celestial body (such as the geology of the Moon or Mars).Geology gives insight into the history of the Earth by providing the primary evidence for plate tectonics, the evolutionary history of life, and past climates. Geology is important for mineral and hydrocarbon exploration and exploitation, evaluating water resources, understanding of natural hazards, the remediation of environmental problems, and for providing insights into past climate change. Geology also plays a role in geotechnical engineering and is a major academic discipline.