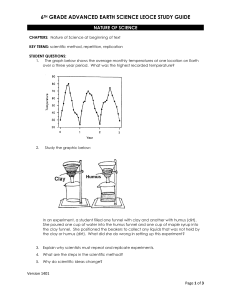
What are Earth`s physical layers?
... mantle made of solid rock that moves very slowly. • The asthenosphere is located below the lithosphere and is often described as “plastic like” • Tectonic plates move on top of the asthenosphere. ...
... mantle made of solid rock that moves very slowly. • The asthenosphere is located below the lithosphere and is often described as “plastic like” • Tectonic plates move on top of the asthenosphere. ...
Grand Challenges for Seismology
... mechanically strong outer shell that makes up the tectonic plates, underlain by the weak asthenosphere, which flows and deforms to accommodate plate motions. The lithosphere often is thought of as the thermal boundary layer between the cold surface of Earth and the planet’s hot interior, but recent ...
... mechanically strong outer shell that makes up the tectonic plates, underlain by the weak asthenosphere, which flows and deforms to accommodate plate motions. The lithosphere often is thought of as the thermal boundary layer between the cold surface of Earth and the planet’s hot interior, but recent ...
I-5 Notes
... • Earthquakes range from shallow to as deep as hundreds of kilometers • Earthquakes also occur at continentcontinent collision zones ...
... • Earthquakes range from shallow to as deep as hundreds of kilometers • Earthquakes also occur at continentcontinent collision zones ...
Plate Tectonics [ TCD IE ]
... • Subduction. The old, cold, thick oceanic plate dives down into the mantle beneath either a continental or another oceanic plate. Bending of the plate results in a deep trench. • Water. Sea water subducted down into the mantle along with the oceanic plate decreases the melting temperature of the ma ...
... • Subduction. The old, cold, thick oceanic plate dives down into the mantle beneath either a continental or another oceanic plate. Bending of the plate results in a deep trench. • Water. Sea water subducted down into the mantle along with the oceanic plate decreases the melting temperature of the ma ...
6TH GRADE ADVANCED EARTH SCIENCE LEOCE STUDY GUIDE
... 18. Describe how weathering/erosion/deposition create deltas, sinkholes, canyons, and dunes 19. Identify the three main types of rocks, how they are formed, how they move through the rock cycle, and which contain fossils. 20. How does deforestation affect Earth’s surface? 21. How are sediments depos ...
... 18. Describe how weathering/erosion/deposition create deltas, sinkholes, canyons, and dunes 19. Identify the three main types of rocks, how they are formed, how they move through the rock cycle, and which contain fossils. 20. How does deforestation affect Earth’s surface? 21. How are sediments depos ...
Chapter 3
... Energy in the Atmosphere • Energy from the sun is transferred in Earth’s atmosphere – Radiation - transfer of energy across space and in the atmosphere – Conduction - flow if heat from a warmer object to a colder object when they are in contact with each other. – Convection - transfer of heat by ai ...
... Energy in the Atmosphere • Energy from the sun is transferred in Earth’s atmosphere – Radiation - transfer of energy across space and in the atmosphere – Conduction - flow if heat from a warmer object to a colder object when they are in contact with each other. – Convection - transfer of heat by ai ...
3 Explanation - Earth`s Layers
... • Seismic waves are used to determine which layers of the Earth are ...
... • Seismic waves are used to determine which layers of the Earth are ...
The Dynamic Planet Revealed - Frankfurt Institute for Advanced
... surface heat flow. However, it is observed that behind oceanic trenches there is a great deal of volcanism, and the measured values of the surf ace heat fl ux are high (Vacquier et al 1966, Sclater & Menard 1967) . This volcanism and the high surface heat flux are attributed to frictional heating on ...
... surface heat flow. However, it is observed that behind oceanic trenches there is a great deal of volcanism, and the measured values of the surf ace heat fl ux are high (Vacquier et al 1966, Sclater & Menard 1967) . This volcanism and the high surface heat flux are attributed to frictional heating on ...
Key Concept Builder
... statement is false, change the underlined word(s) to make it true. Write your changes on the lines provided. ...
... statement is false, change the underlined word(s) to make it true. Write your changes on the lines provided. ...
Earthquakes
... SUBDUCTION ZONE - An elongated region of the Earth's crust where one tectonic plate moves below another resulting in volcanoes and earthquakes. REVERSE FAULT - A type of fault along which the plane of movement slants toward the uplifted side. TRANSFORM FAULT BOUNDARY - A boundary between tectonic pl ...
... SUBDUCTION ZONE - An elongated region of the Earth's crust where one tectonic plate moves below another resulting in volcanoes and earthquakes. REVERSE FAULT - A type of fault along which the plane of movement slants toward the uplifted side. TRANSFORM FAULT BOUNDARY - A boundary between tectonic pl ...
PROGRAM - Tectonic Impacts
... Hardcopy worksheet, Lithospheric plates and their motion with supporting document ...
... Hardcopy worksheet, Lithospheric plates and their motion with supporting document ...
Farallon And Kula Plates David Reed
... Oregon to Yellowstone National Park in northwestern Wyoming. Compared to other geological features in North America, the SRP is very young. It began forming only 16 million years ago (Ma), and is still tectonically active today. The SRP is a result of the movement of the North American Plate over th ...
... Oregon to Yellowstone National Park in northwestern Wyoming. Compared to other geological features in North America, the SRP is very young. It began forming only 16 million years ago (Ma), and is still tectonically active today. The SRP is a result of the movement of the North American Plate over th ...
Mid-Ocean Ridge
... Answer the following in complete sentences: In what state of matter does the inner core exist? What ocean has the greatest average depth? What hemisphere contains the greatest percentage of ocean water? What term from yesterday’s earth picture does this ...
... Answer the following in complete sentences: In what state of matter does the inner core exist? What ocean has the greatest average depth? What hemisphere contains the greatest percentage of ocean water? What term from yesterday’s earth picture does this ...
A new Paradigm… Plate Tectonics
... 200 million years ago ► Panthalassa – one large ocean ► Noted puzzle-like fit of modern continents ...
... 200 million years ago ► Panthalassa – one large ocean ► Noted puzzle-like fit of modern continents ...
Passing Plates I - The Theory By Trista L
... rocks and that they rested on heavier crystal material. Wegener also pointed out that the fossils of a 270 million year old Mesosaur were found in eastern South America and western Africa. Even though other scientists used the idea of a land bridge to explain the fossils, Wegener held on to his cont ...
... rocks and that they rested on heavier crystal material. Wegener also pointed out that the fossils of a 270 million year old Mesosaur were found in eastern South America and western Africa. Even though other scientists used the idea of a land bridge to explain the fossils, Wegener held on to his cont ...
Rock Cycle Game-1
... evaporite, etc. near the earth's surface. 1) Stay a nonclastic sedimentary rock. Roll again. 2) Get uplifted, exposed, and eroded. Take the chemical weathering pathway and become ions dissolved in water. Go to hydrosphere/biosphere. 3) Get uplifted, exposed, and eroded. Take the mechanical weatherin ...
... evaporite, etc. near the earth's surface. 1) Stay a nonclastic sedimentary rock. Roll again. 2) Get uplifted, exposed, and eroded. Take the chemical weathering pathway and become ions dissolved in water. Go to hydrosphere/biosphere. 3) Get uplifted, exposed, and eroded. Take the mechanical weatherin ...
Faults
... • Reverse faults form as a result of horizontal and vertical compression that squeezes rock and creates a shortening of the crust. This causes rock on one side of a reverse fault to be pushed up relative to the other side. ...
... • Reverse faults form as a result of horizontal and vertical compression that squeezes rock and creates a shortening of the crust. This causes rock on one side of a reverse fault to be pushed up relative to the other side. ...
File
... collision-zone boundaries between plates. Example - ______________________ have many earthquakes along reverse faults. Strike-Slip Faults Here blocks of rock move ______________________________________ of the fault plane. Stress that pushes blocks of rock _____________________ causes earthquakes a ...
... collision-zone boundaries between plates. Example - ______________________ have many earthquakes along reverse faults. Strike-Slip Faults Here blocks of rock move ______________________________________ of the fault plane. Stress that pushes blocks of rock _____________________ causes earthquakes a ...
Chapter 14 Geology and nonrenewable Minerals
... • There Are Three Major Types of Rocks (3) • Igneous • Forms below or at earth’s surface from magma • Granite • Lava rocks • Metamorphic • Preexisting rock subjected to high pressures, high temperatures, and/or chemically active fluids • Anthracite • Slate • Marble • The Earth’s Rocks Are Recycled V ...
... • There Are Three Major Types of Rocks (3) • Igneous • Forms below or at earth’s surface from magma • Granite • Lava rocks • Metamorphic • Preexisting rock subjected to high pressures, high temperatures, and/or chemically active fluids • Anthracite • Slate • Marble • The Earth’s Rocks Are Recycled V ...
Earth’s Structure
... and iron are liquids in the outer core. • This layer is liquid because the temperature is still very high, but the pressure is not as great as it is in the inner core. ...
... and iron are liquids in the outer core. • This layer is liquid because the temperature is still very high, but the pressure is not as great as it is in the inner core. ...
Eliana
... earthquakes occurring, and are they more likely to occur in certain locations? Are there parts of the world that are more prone to them? Is there a relationship between earthquakes and volcanoes? What is causing the earthquakes? All of these questions are challenging, but reasonable. I, as lead scie ...
... earthquakes occurring, and are they more likely to occur in certain locations? Are there parts of the world that are more prone to them? Is there a relationship between earthquakes and volcanoes? What is causing the earthquakes? All of these questions are challenging, but reasonable. I, as lead scie ...
Plate Tectonics Internet Scavenger Hunt - wikifuller
... 10. What could Alfred Wegener not explain about his theory continental drift? Mini quiz: Circle correct response 1. Which of the following provide evidence for Plate Tectonics? a. fossils and rocks matched up b. ocean currents and sea temperature c. continents fit like a puzzle d. both a and c 2. Wh ...
... 10. What could Alfred Wegener not explain about his theory continental drift? Mini quiz: Circle correct response 1. Which of the following provide evidence for Plate Tectonics? a. fossils and rocks matched up b. ocean currents and sea temperature c. continents fit like a puzzle d. both a and c 2. Wh ...
Geology

Geology (from the Greek γῆ, gē, i.e. ""earth"" and -λoγία, -logia, i.e. ""study of, discourse"") is an earth science comprising the study of solid Earth, the rocks of which it is composed, and the processes by which they change. Geology can also refer generally to the study of the solid features of any celestial body (such as the geology of the Moon or Mars).Geology gives insight into the history of the Earth by providing the primary evidence for plate tectonics, the evolutionary history of life, and past climates. Geology is important for mineral and hydrocarbon exploration and exploitation, evaluating water resources, understanding of natural hazards, the remediation of environmental problems, and for providing insights into past climate change. Geology also plays a role in geotechnical engineering and is a major academic discipline.


![Plate Tectonics [ TCD IE ]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/000728998_1-eea64118f8dd5f3d44e4d2914cefeaa2-300x300.png)