Plate Tectonics Rock Powerpoint
... lithosphere) is broken into a number of more or less rigid, but constantly moving, segments or plates. • Plate boundary – The place where two or more plates in the Earth's crust meet. • Lithosphere – the rigid, brittle layer made up of the crust and the uppermost part of the mantle. It is broken up ...
... lithosphere) is broken into a number of more or less rigid, but constantly moving, segments or plates. • Plate boundary – The place where two or more plates in the Earth's crust meet. • Lithosphere – the rigid, brittle layer made up of the crust and the uppermost part of the mantle. It is broken up ...
Chapter 26: Earth`s Interior
... Secondary (shear) seismic waves will not propagate through the outer core. This is convincing evidence that the outer core is a) b) c) d) e) ...
... Secondary (shear) seismic waves will not propagate through the outer core. This is convincing evidence that the outer core is a) b) c) d) e) ...
Earth`s Interior Reading Packet 1
... enough to melt the silicates and other substances that make it up. Yet most of the earth's interior is not liquid' Why? The enormous pressures inside the earth offset the high temperatures. In much of the earth's interior, high pressures will not allow the matter to melt' The balance between tempera ...
... enough to melt the silicates and other substances that make it up. Yet most of the earth's interior is not liquid' Why? The enormous pressures inside the earth offset the high temperatures. In much of the earth's interior, high pressures will not allow the matter to melt' The balance between tempera ...
Journey to the Center of the Earth Project - Science
... Part 2 - Write a short story to go along with your model. The story is about a scientist (maybe you???) traveling to the center of the Earth. Begin at the crust and describe what you observe traveling through each layer. Although we don’t really have means to travel through the Earth, the descriptio ...
... Part 2 - Write a short story to go along with your model. The story is about a scientist (maybe you???) traveling to the center of the Earth. Begin at the crust and describe what you observe traveling through each layer. Although we don’t really have means to travel through the Earth, the descriptio ...
File - Mr. Medler, Science
... different densities of the hotter and cooler parts. Hot liquids will rise because they are less dense than cold liquids. In the earth’s deep mantle and outer core, the magma is extremely hot and rises because it’s less dense. This hot magma then pushes the cooler magma that is further from the inten ...
... different densities of the hotter and cooler parts. Hot liquids will rise because they are less dense than cold liquids. In the earth’s deep mantle and outer core, the magma is extremely hot and rises because it’s less dense. This hot magma then pushes the cooler magma that is further from the inten ...
Wednesday Sept 8th
... YES!! The density of the plates determines which will be on top after a collision. More dense sinks Less dense goes on top ...
... YES!! The density of the plates determines which will be on top after a collision. More dense sinks Less dense goes on top ...
5. Where would you find the least number of earthquakes?
... How does heat and density change inside the earth as you go deeper into the earth? ...
... How does heat and density change inside the earth as you go deeper into the earth? ...
plate tectonics - Math/Science Nucleus
... 1. Define “plate” to the class. Explain that plates are large areas of the Earth's outer portion (crust and upper mantle) that move together. 2. Explain the concept of stress in rocks to the class. Define the three basic types of stress to the students. You can demonstrate these with the wooden blo ...
... 1. Define “plate” to the class. Explain that plates are large areas of the Earth's outer portion (crust and upper mantle) that move together. 2. Explain the concept of stress in rocks to the class. Define the three basic types of stress to the students. You can demonstrate these with the wooden blo ...
New Research Opportunities in the Earth Sciences
... and ocean, and the formation of the moon. A better understanding of this “early Earth” is essential for establishing the events and processes that allowed Earth to transition from its formative state to the hospitable planet of today. Research directions to expand knowledge of the early Earth inclu ...
... and ocean, and the formation of the moon. A better understanding of this “early Earth” is essential for establishing the events and processes that allowed Earth to transition from its formative state to the hospitable planet of today. Research directions to expand knowledge of the early Earth inclu ...
Unit 1 Landforms and Water Forms
... Reverse – If simple rock layers around a fault push against each other, one block can be pushed up over the other creating a reverse fault. Overthrust – If a plate that has undergone folding has its folded layers pushed up and thrust over layers on the faults other side, overthrust faults occurs. ...
... Reverse – If simple rock layers around a fault push against each other, one block can be pushed up over the other creating a reverse fault. Overthrust – If a plate that has undergone folding has its folded layers pushed up and thrust over layers on the faults other side, overthrust faults occurs. ...
Study Guide: Plate Tectonics Test
... 6. The process which occurs during the convergence of two oceanic plates, or an oceanic-continental plate resulting in old oceanic plate (old sea floor) being recycled back down into the mantle is called: a. sea floor spreading b. convection c. subduction d. elimination 7. The result of two oceanic- ...
... 6. The process which occurs during the convergence of two oceanic plates, or an oceanic-continental plate resulting in old oceanic plate (old sea floor) being recycled back down into the mantle is called: a. sea floor spreading b. convection c. subduction d. elimination 7. The result of two oceanic- ...
Name_________________________ Earth`s
... The outer layer of the earth is called the __________________. It is made up of tectonic ________________. Just underneath the crust is the _____________________ and right in the middle of the earth is the _____________. Colliding plates produce _______________________ and _____________________ at t ...
... The outer layer of the earth is called the __________________. It is made up of tectonic ________________. Just underneath the crust is the _____________________ and right in the middle of the earth is the _____________. Colliding plates produce _______________________ and _____________________ at t ...
Igneous Rocks - sir
... (geothermal gradient) average between 20 oC to 30 oC per kilometer rocks in the lower crust and upper mantle are near their melting points additional heat may induce melting ...
... (geothermal gradient) average between 20 oC to 30 oC per kilometer rocks in the lower crust and upper mantle are near their melting points additional heat may induce melting ...
Factors Affecting Deformation
... Compressional forces generally produce folds as well as faults. These compressional forces result in a thickening and shortening of the rocks. Q :How do you determine which side of a fault has moved? A: For the fault shown in Figure 5, did the left side move down, or did the right side move up? Sinc ...
... Compressional forces generally produce folds as well as faults. These compressional forces result in a thickening and shortening of the rocks. Q :How do you determine which side of a fault has moved? A: For the fault shown in Figure 5, did the left side move down, or did the right side move up? Sinc ...
Mountain Building at Divergent Boundaries
... Compressional forces generally produce folds as well as faults. These compressional forces result in a thickening and shortening of the rocks. Q :How do you determine which side of a fault has moved? A: For the fault shown in Figure 5, did the left side move down, or did the right side move up? Sinc ...
... Compressional forces generally produce folds as well as faults. These compressional forces result in a thickening and shortening of the rocks. Q :How do you determine which side of a fault has moved? A: For the fault shown in Figure 5, did the left side move down, or did the right side move up? Sinc ...
Earthquakes
... Forces In Earth’s Crust • How does stress in earth’s crust change earth’s surface? ...
... Forces In Earth’s Crust • How does stress in earth’s crust change earth’s surface? ...
Astro 1010 Planetary Astronomy Sample Questions for Exam 4
... c) Observing seismic waves at multiple locations around the planet and how they travel through layers of different characteristics. d) Traveling through the interior in deep caves that go down to the core 11. The theory of plate tectonics holds that a) the crust is broken into plates which slide ove ...
... c) Observing seismic waves at multiple locations around the planet and how they travel through layers of different characteristics. d) Traveling through the interior in deep caves that go down to the core 11. The theory of plate tectonics holds that a) the crust is broken into plates which slide ove ...
plate tectonics - Math/Science Nucleus
... earthquakes help define the boundaries between the plates. Volcanoes form mostly at converging and diverging plate boundaries, where much magma is generated. Earthquakes occur at all three types of boundaries. Because the plates are rigid, they tend to stick together, even though they are constantly ...
... earthquakes help define the boundaries between the plates. Volcanoes form mostly at converging and diverging plate boundaries, where much magma is generated. Earthquakes occur at all three types of boundaries. Because the plates are rigid, they tend to stick together, even though they are constantly ...
AIM: What evidence do we have for the Theory of
... An Idea Before Its Time Wegener’s continental drift hypothesis stated that the continents had once been joined to form a single supercontinent. • Wegener proposed that the supercontinent, Pangaea, began to break apart 200 million years ago and form the present landmasses. ...
... An Idea Before Its Time Wegener’s continental drift hypothesis stated that the continents had once been joined to form a single supercontinent. • Wegener proposed that the supercontinent, Pangaea, began to break apart 200 million years ago and form the present landmasses. ...
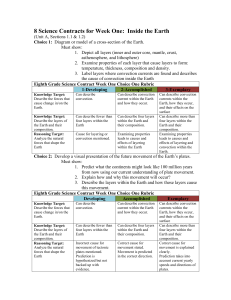
Science Contracts for Week 1
... 8 Science Contracts for Week One: Inside the Earth (Unit A, Sections 1.1 & 1.2) Choice 1: Diagram or model of a cross-section of the Earth. Must show: 1. Depict all layers (inner and outer core, mantle, crust, asthenosphere, and lithosphere) 2. Examine properties of each layer that cause layers to f ...
... 8 Science Contracts for Week One: Inside the Earth (Unit A, Sections 1.1 & 1.2) Choice 1: Diagram or model of a cross-section of the Earth. Must show: 1. Depict all layers (inner and outer core, mantle, crust, asthenosphere, and lithosphere) 2. Examine properties of each layer that cause layers to f ...
Geology

Geology (from the Greek γῆ, gē, i.e. ""earth"" and -λoγία, -logia, i.e. ""study of, discourse"") is an earth science comprising the study of solid Earth, the rocks of which it is composed, and the processes by which they change. Geology can also refer generally to the study of the solid features of any celestial body (such as the geology of the Moon or Mars).Geology gives insight into the history of the Earth by providing the primary evidence for plate tectonics, the evolutionary history of life, and past climates. Geology is important for mineral and hydrocarbon exploration and exploitation, evaluating water resources, understanding of natural hazards, the remediation of environmental problems, and for providing insights into past climate change. Geology also plays a role in geotechnical engineering and is a major academic discipline.